Table of contents
What is SVEEP?
The Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation (SVEEP) program is an initiative by the Election Commission of India aimed at promoting greater electoral participation through comprehensive voter education.
Vision: Universal and enlightened participation of citizens in elections and democracy.
Goal: To enlighten, enable and empower every citizen to register as a voter and cast his/her vote at every election in an informed and ethical manner.
- It was developed to inform, motivate, and facilitate voters, ensuring widespread and informed participation in the electoral processes.
Here’s a quick revision of the program's objectives and aspects:
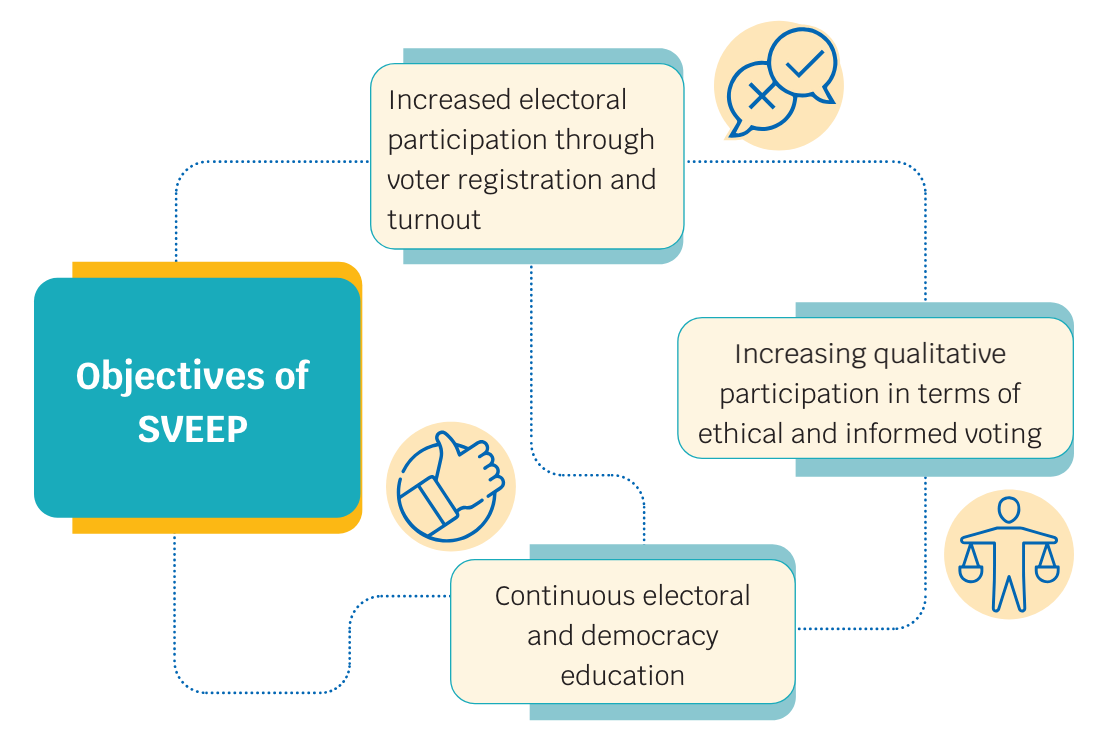
SVEEP Objectives (2022-25)
The objectives envisaged for SVEEP strategy (2022-25) are:
- Increase voter turnout to 75% in Lok Sabha elections 2024 by:
- Purifying the electoral roll of every polling booth
- Bridging the gender gap in enrolment and turnout
- Ensuring inclusion of all non-voters/ marginalised sections through targeted interventions, technological solutions and policy changes
- Addressing urban and youth apathy in electoral participation
- Turning around all low-turnout constituencies and polling stations
- To enhance the quality of electoral participation in terms of informed and ethical voting through continuous electoral and democracy education
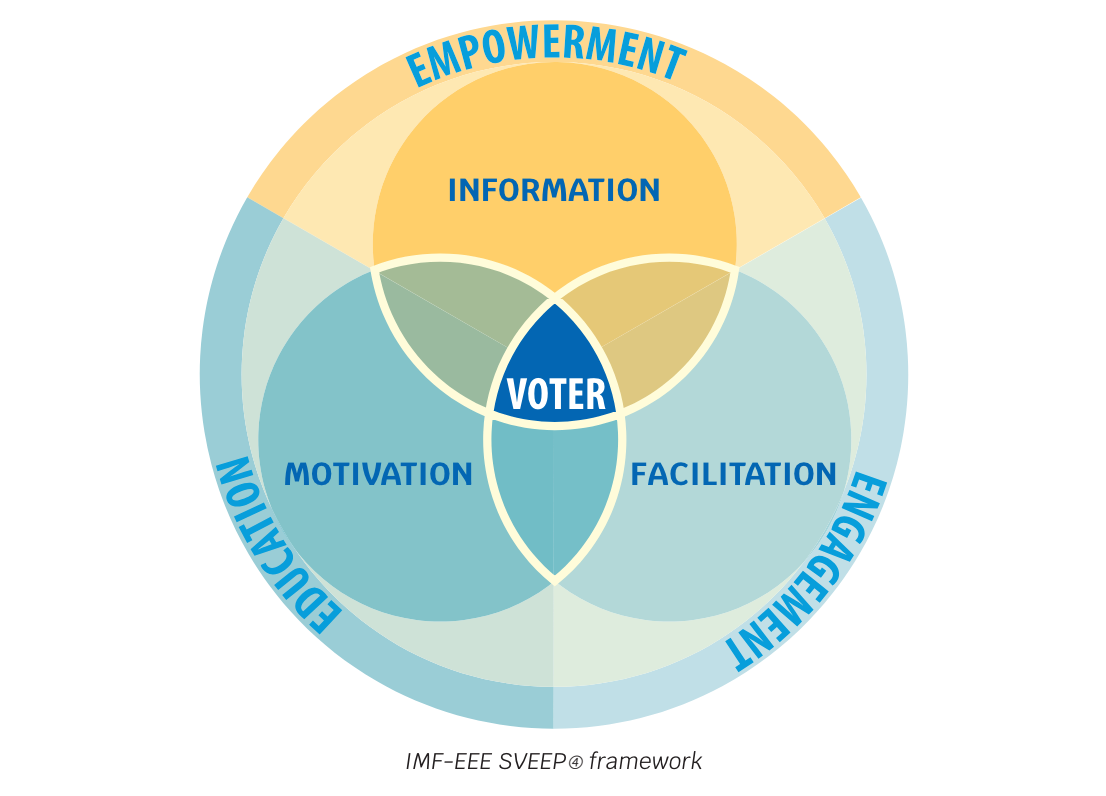
- Transition from the erstwhile IMF (Information, Motivation and Facilitation) paradigm to a more holistic IMF-EEE (Information, Motivation, Facilitation, Engagement, Education and Empowerment) paradigm.
Key Features and Initiatives
- Outreach Campaigns: Extensive use of media, including social media, to reach voters.
- Campaigns are customized linguistically and culturally for different regions to maximize impact.
- Educational Materials: Distribution of brochures, flyers, and posters that detail the voting process and highlight the importance of each individual's vote.
- Interactive Platforms: Organising interactive sessions such as workshops, seminars, and roadshows to engage directly with the electorate and address their questions.
- Cultural Events: Incorporation of cultural activities, like concerts and exhibitions, to draw public interest and disseminate voter education in an entertaining way.
- Example: Jashn-e-Jugalbandhi musical show in Srinagar.
- Partnerships: Collaboration with NGOs, educational institutions, and corporate entities to broaden the reach of voter education efforts.
- Special Focus Groups: Special initiatives to engage youth, women, and the marginalized sections of society to ensure comprehensive electoral participation.


Adaptations to Challenges
- Localized and Diverse Communication Strategies
- The ECI has developed region-specific campaigns that cater to local languages, cultures, and norms to ensure the message of electoral participation resonates across diverse voter bases.
- Tools Used: These include traditional media like radio and TV, along with folk performances, street plays, and local art, which are highly effective in rural and remote areas.



- Leveraging Technology and Social Media
- To address the challenge of misinformation and reach the tech-savvy younger population, the ECI utilizes social media platforms, official apps like Voter Helpline, and websites to disseminate accurate and timely information.
- Tools Used: Digital tools such as interactive websites, online tutorials, and social media campaigns help in engaging users and correcting misinformation effectively.
- Targeted Efforts for Marginalized Communities
- Special focus is given to marginalized and underrepresented groups through targeted interventions.
- This includes setting up special camps for voter registration and education in areas with low female voter turnout or in regions inhabited by marginalized communities.
- Training and Capacity Building
- The ECI regularly conducts training sessions for Booth Level Officers (BLOs) and other electoral staff to ensure they are well-equipped to assist and guide voters.
- Facilitation Measures
- This includes better facilities for the elderly, pregnant women, and persons with disabilities.
- Ramps, wheelchairs, braille voting sheets, and transportation facilities in remote areas are some of the facilitation measures implemented.
- Feedback Mechanisms
- Online feedback forms, toll-free numbers, and after-poll surveys are utilized to gather voter feedback.
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- Data analytics and monitoring tools assess the reach and impact of various initiatives, helping in fine-tuning the strategies based on real-time data.
Impact and Success
- Enhanced Voter Awareness: Significant improvement in the awareness levels among voters about the electoral process and their rights as voters.
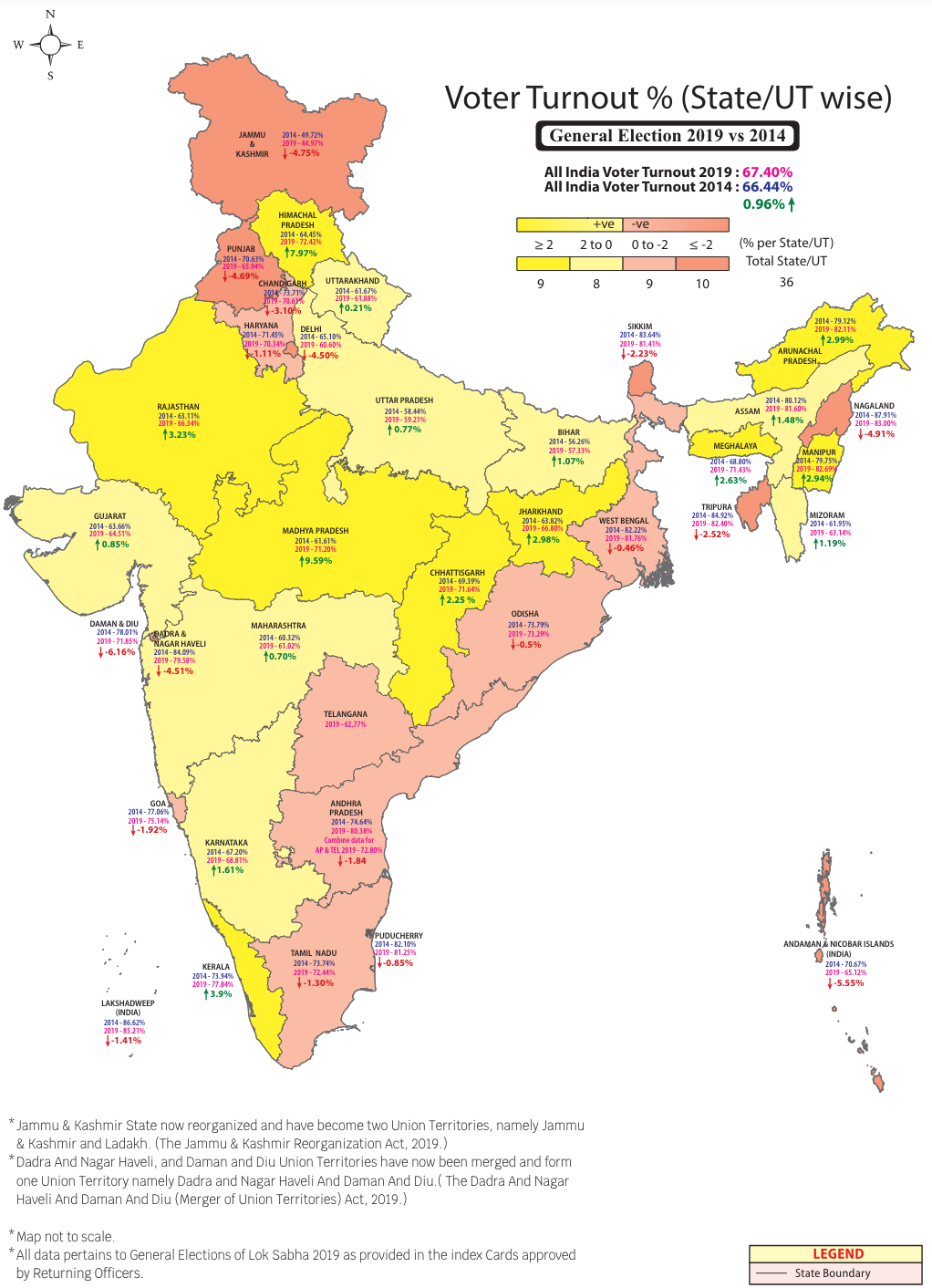
- Increased Voter Turnout: Historical low-turnout areas and demographics have shown improvement in participation rates following SVEEP interventions.
- Positive Behavioral Changes: Reduction in electoral malpractices due to heightened awareness and ethical voting promotions.
Conclusion
The SVEEP program plays a crucial role in strengthening democracy in India by ensuring a more informed, aware, and participative electorate.
By addressing both general and specific barriers to electoral participation, SVEEP aims to enhance the quality and quantity of democratic engagement across the country.
Previous Post