Table of contents
Why in the news?
- The Okavango Delta is currently in the news due to a severe drought impacting the region.
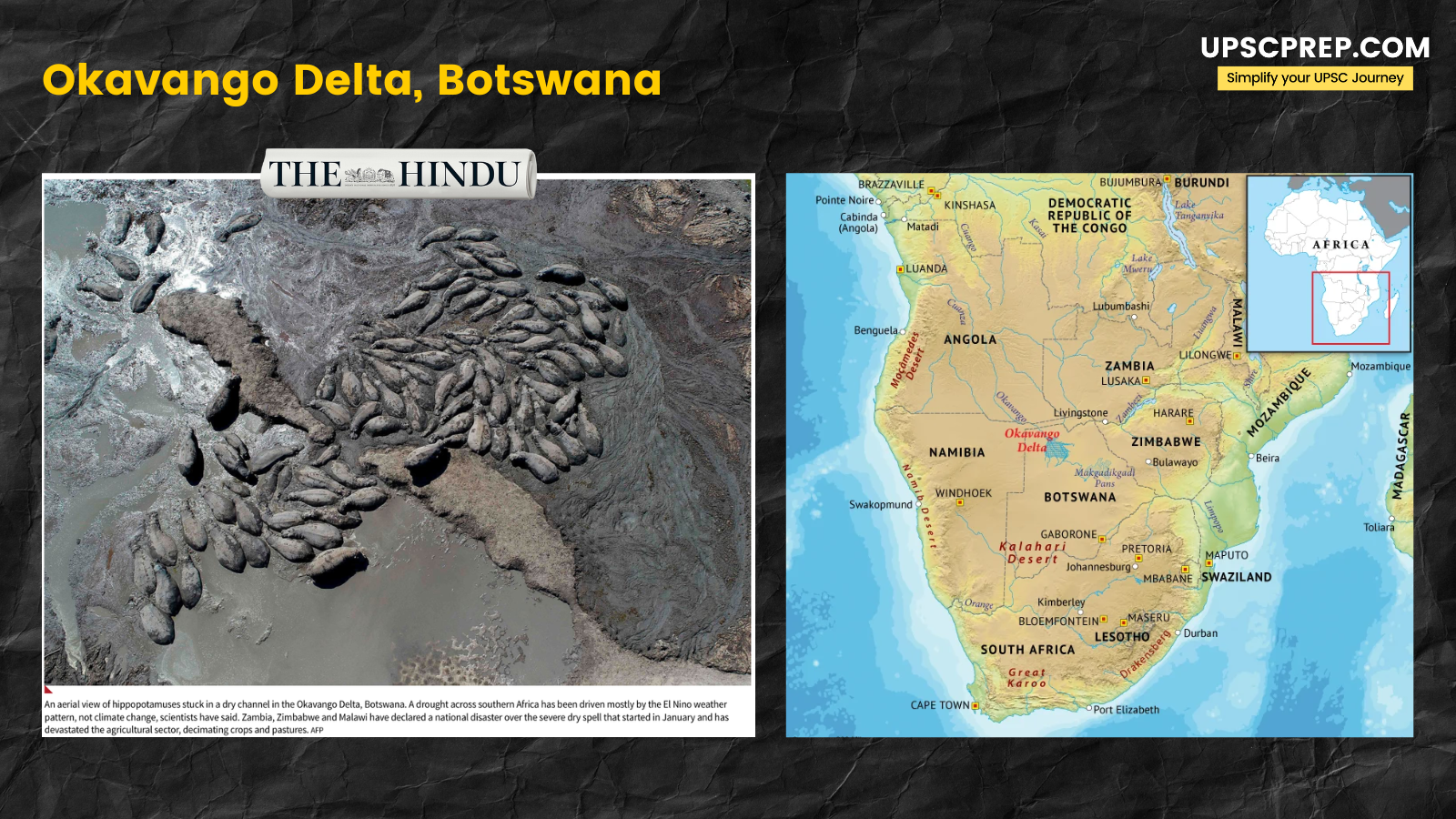
- This drought, predominantly driven by the El Niño weather pattern, has caused significant drying in the delta, affecting wildlife and the local ecosystem.
- Hippos, for example, have been found stuck in dried-up channels.
- The situation has become dire enough that Botswana has taken emergency actions, such as pumping water into drying channels to aid stranded animals.
This drought has also led neighbouring countries like Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Malawi to declare National Disasters due to the extensive damage to agriculture.
- UNESCO has called on Namibia, Angola and Botswana to extend the boundary of the UNESCO World Heritage site upstream to save it from commercialization.
- Okavango River is the fourth longest river in Southern Africa.
- It flows down channels and rivers and seeps through peatlands along the Angola-Namibia border and into northern Botswana, where it fans out into one of the world's most iconic and distinctive inland deltas.
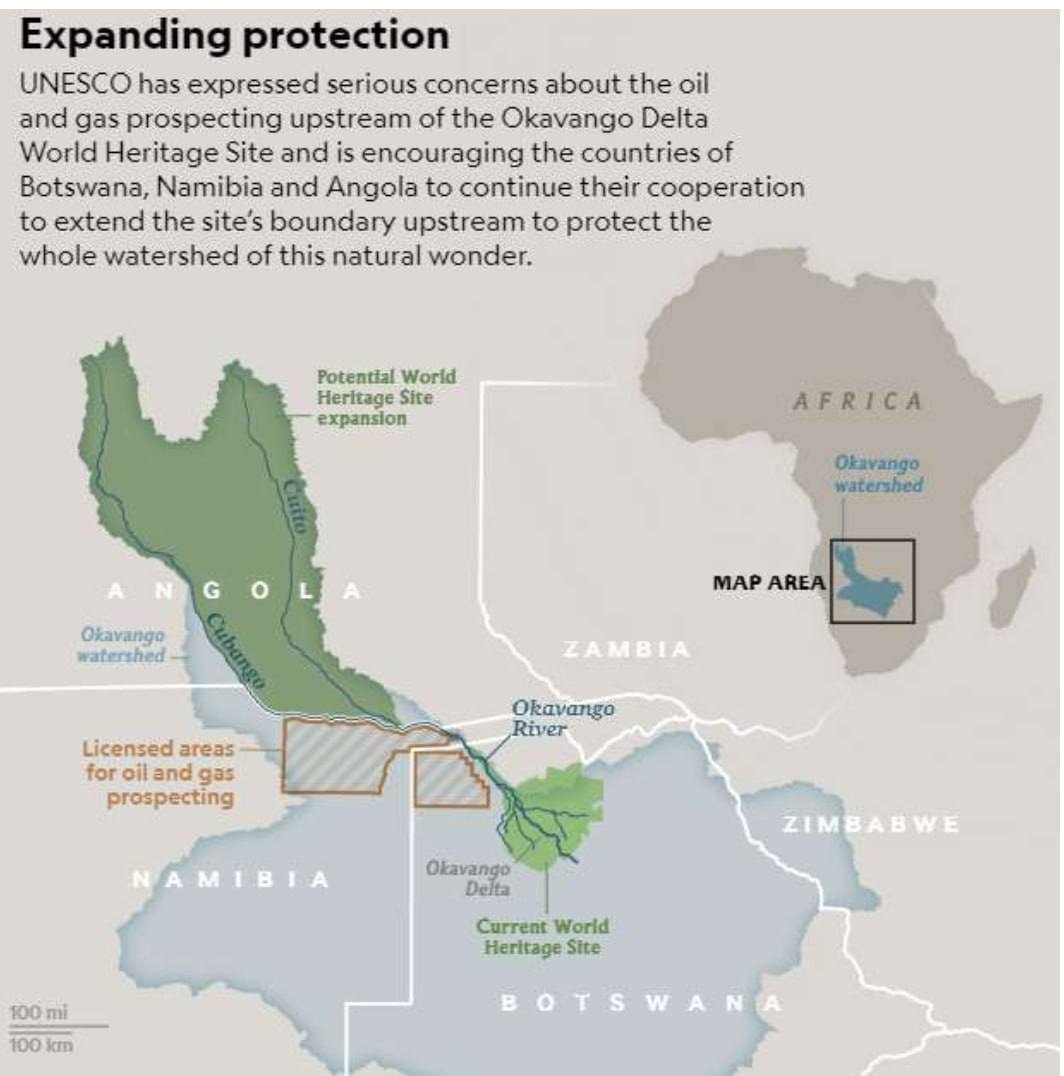
About: Okavango Delta
This delta in north-west Botswana comprises permanent marshlands and seasonally flooded plains.
- It is one of the very few major interior delta systems that do not flow into a sea or ocean, with a wetland system that is almost intact.
- The river empties onto open land, flooding the savannah and creating a unique and diverse ecosystem.
- One of the unique characteristics of the site is that the annual flooding from the River Okavango occurs during the dry season.
- Hence, the native plants and animals have synchronized their biological cycles with these seasonal rains and floods.
- It is an exceptional example of the interaction between climatic, hydrological and biological processes.
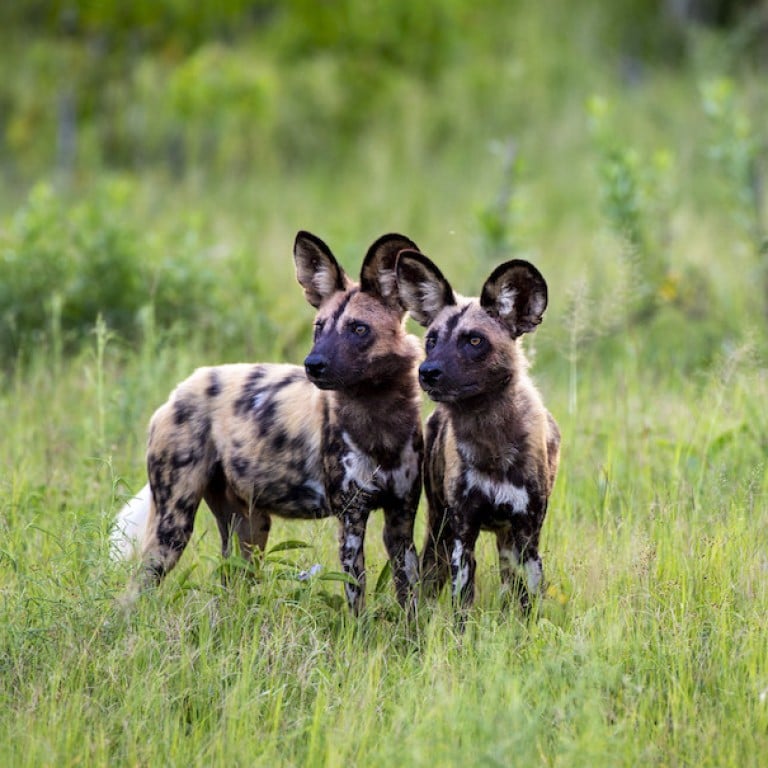
- The Okavango Delta is home to some of the world’s most endangered species of large mammal, such as the cheetah, white rhinoceros, black rhinoceros, African wild dog and lion.
It is also known for its exceptional natural beauty and is a UNESCO World Heritage site, making it a vital location for biodiversity conservation and a popular destination for eco-tourism.




Why does it flood in the dry season?
The Okavango Delta in Botswana experiences flooding during the dry season due to a combination of geographical and climatic factors:
- Source of Water: The delta is fed by the Okavango River, which originates in the highlands of Angola. The river's waters travel approximately 1,600 kilometers, reaching the delta.
- Timing of Rainfall: Angola's primary rainy season is from October to April. The water takes months to travel from Angola, arriving in the Okavango Delta around June, during Botswana’s dry season.
- Flat Terrain: The delta is situated in a very flat area. The gentle gradient slows the water's flow, spreading it widely across the 15,000 square kilometers of the delta.
- Evaporation and Transpiration: High temperatures during Botswana's dry season cause significant evaporation and transpiration. However, the volume of water arriving from Angola is substantial enough to overcome losses, resulting in flooding.
- Natural Basin: The delta acts like a natural basin or endorheic basin with no outlet to the sea, causing the incoming river water to spread out and create the seasonal floods.
These factors combine to make the Okavango Delta a unique hydrological system where peak flooding occurs counterintuitively during the local dry season.
Why is it facing drought now?
The Okavango Delta is facing drought conditions this year due to several factors, primarily influenced by regional climatic patterns:
- El Niño Impact: The El Niño weather phenomenon, characterized by the warming of the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, affects weather patterns worldwide. It typically leads to reduced rainfall in Southern Africa, including the catchment areas of the Okavango River in Angola.
- Delayed or Reduced Rainfall: During El Niño events, the rainfall in Angola, where the Okavango River originates, can be significantly delayed or reduced. This results in less water flowing into the Okavango Delta.
- Increased Evaporation: The drought is exacerbated by higher temperatures during El Niño years, leading to increased evaporation rates. This further reduces the water levels in the delta, impacting the available water even more.
- Regional Drought: Southern Africa has been experiencing a regional drought, affecting Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Malawi severely. This broader regional drought affects the entire ecosystem and hydrological cycle, contributing to less water reaching the delta.
- Agricultural Impact: The drought affects not only the water levels in the delta but also the surrounding areas which are dependent on regular water flow for agriculture. The reduced flow impacts agriculture and wildlife, as seen with difficulties faced by species like hippopotamuses that rely on delta waters.
The situation in the Okavango Delta is a direct consequence of these interconnected climatic and environmental factors, leading to significant challenges for the ecosystem and the communities dependent on it.
Read more - What is a Delta?
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts in the Okavango Delta are critical due to its unique biodiversity and status as a UNESCO World Heritage site. These efforts include:
- Wildlife Management: The delta is home to numerous species of animals, including endangered species such as the African wild dog, cheetahs, and black and white rhinoceros.
- Conservation programs focus on protecting these species from poaching and habitat loss.
- Community Involvement: Local communities are actively involved in conservation efforts.
- This includes community-based natural resource management programs, where locals have a say in and benefit from the sustainable management of natural resources.
- COMPACT Programme: The Community Management for Protected Areas for Conservation (COMPACT).
- Botswana Community & Conservation Initiative (BCCI) to support regional conservation by rural communities in developing sustainable land-use practices.
- This includes community-based natural resource management programs, where locals have a say in and benefit from the sustainable management of natural resources.
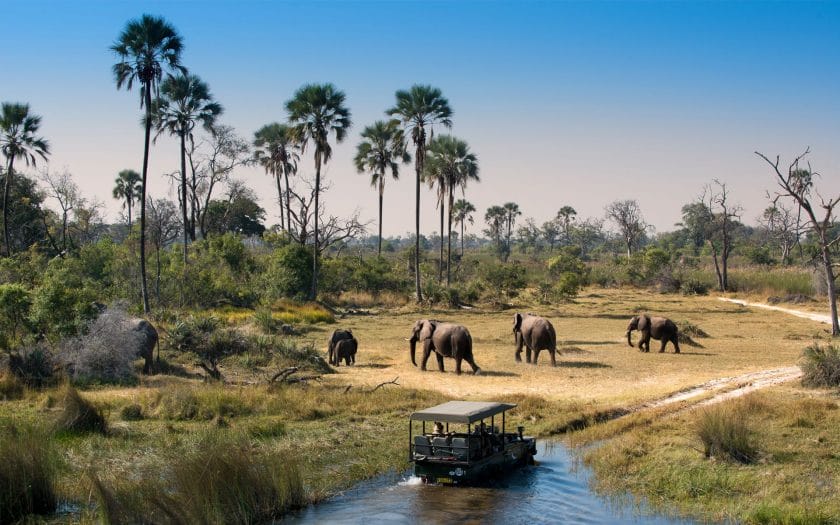
- Eco-Tourism: Eco-tourism is a major part of the delta's economy, providing financial incentives for conservation.
- Tour operators and lodges typically follow strict environmental guidelines to minimize impact on the environment and support conservation initiatives.



- Research and Monitoring: Continuous research and monitoring are conducted to understand ecological dynamics and the impact of human activity on the delta.
- This data helps in making informed decisions about managing the delta.
- Water Management: Since the delta relies on water flowing from Angola, regional cooperation is crucial.
- Efforts are made to ensure sustainable water use upstream to maintain adequate water flow into the delta.
- Anti-Poaching Measures: Increased patrols and the use of technology such as drones help combat poaching within the delta, ensuring the safety of wildlife.
These conservation efforts are essential to preserving the ecological integrity of the Okavango Delta, enabling it to continue supporting a wide range of biodiversity and providing benefits to local communities.
Previous Post