Table of contents
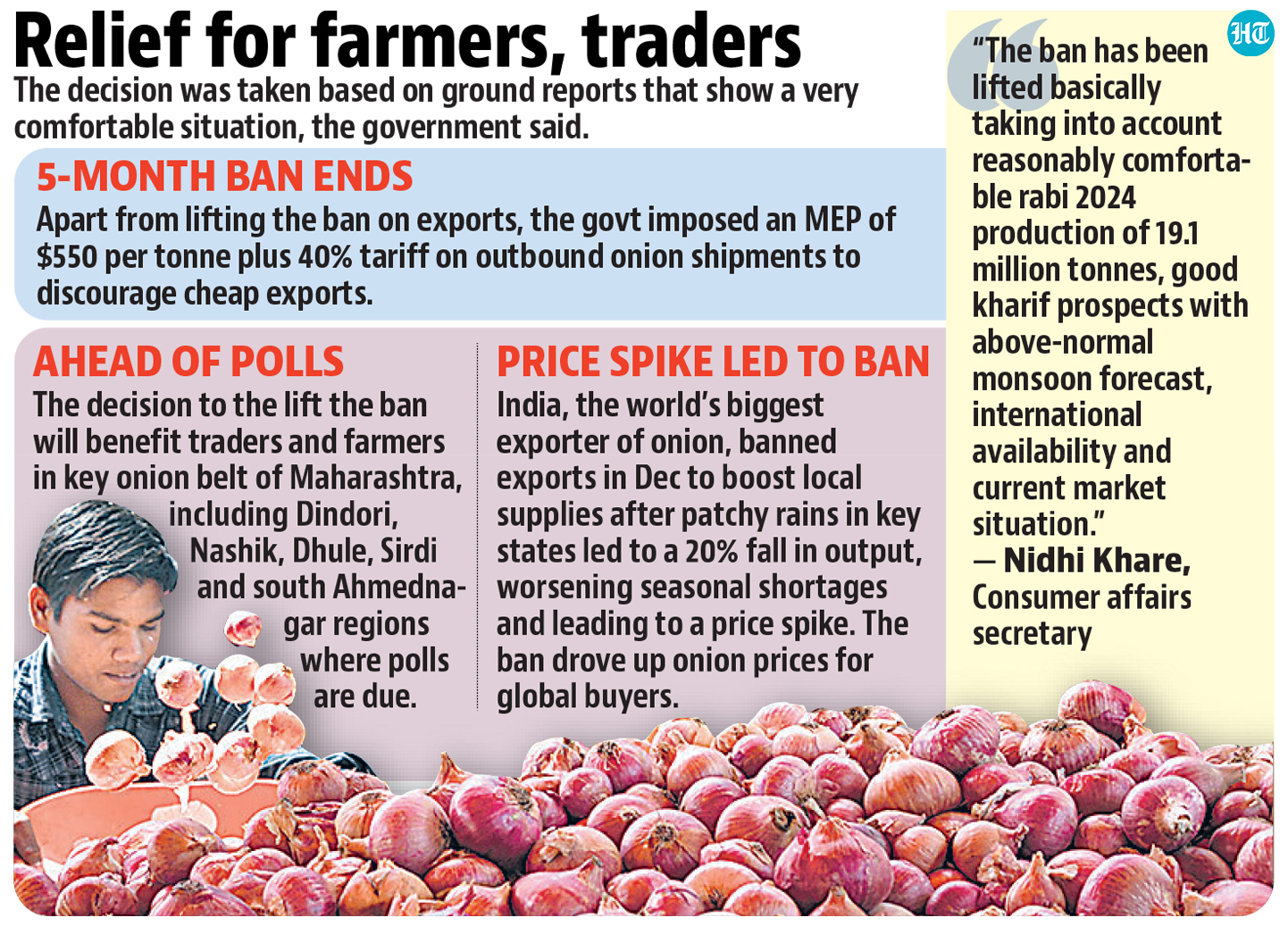
The Indian government's recent decision to lift the ban on onion exports, with new stipulations including a minimum export price and an export duty, plays a significant role in the economics of onion pricing in India, particularly during election seasons.
Background
- The ban on onion exports was initially imposed to manage domestic supply and curb rising prices.
- With elections approaching, such policies are becoming more visible as they impact both consumer prices and farmer incomes.
Recent Changes
- The government has lifted the ban, leading to an effective lower limit of $770 per ton for exports, by setting:
- A Minimum Export Price (MEP) of $550 per ton
- A 40% Export Duty
- This is aimed at maintaining domestic supply and stabilizing prices while allowing exports to benefit farmers.
Factors Affecting Onion Prices in India

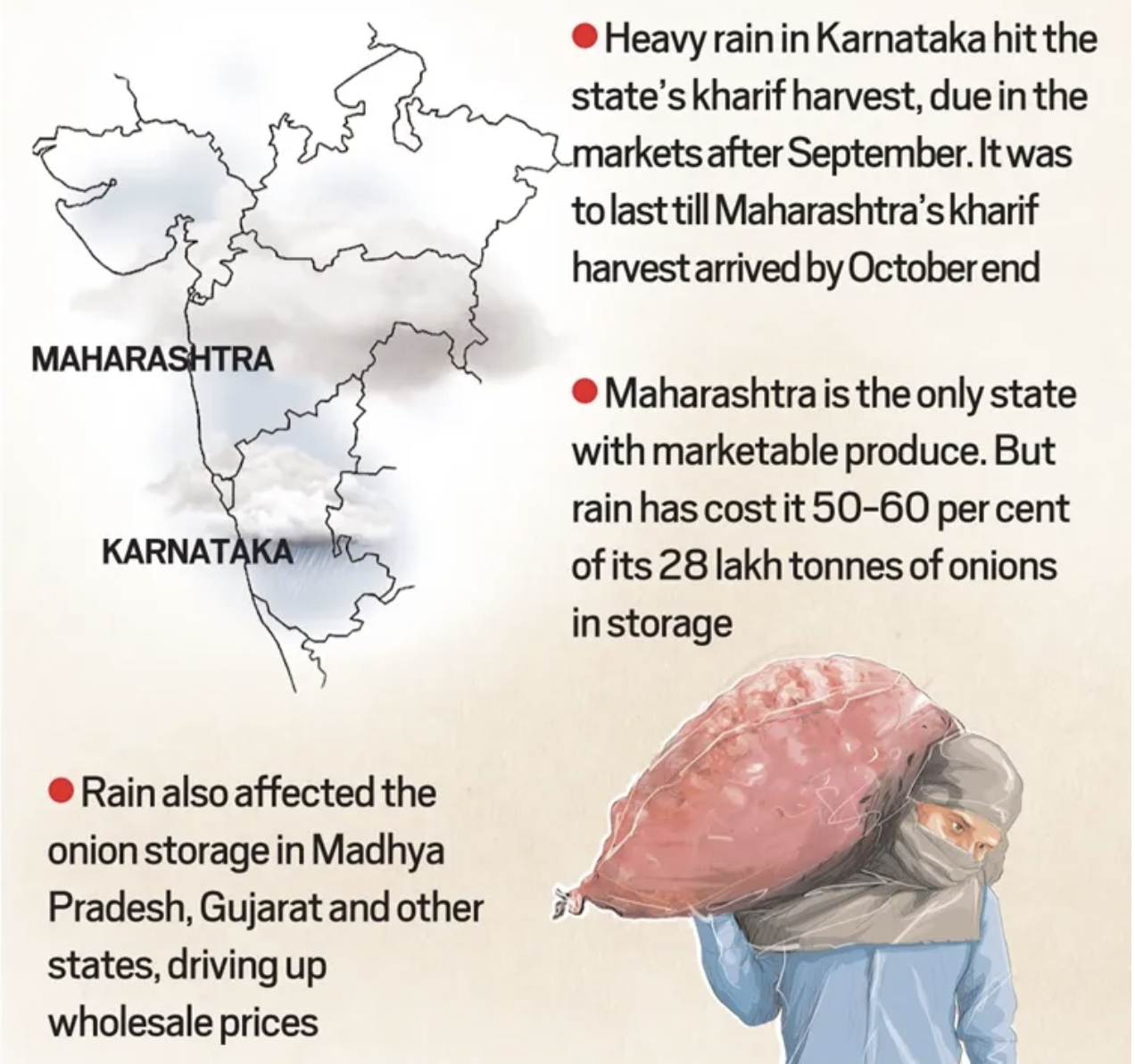
- Weather Conditions: Onion production depends heavily on the weather.
- Good monsoon rains -> Good harvest -> Lower prices.
- Drought or excessive rain -> Crop damage, reduce supply -> High prices.
- Supply and Demand: The fundamental economic principle affecting prices.
- If supply is low due to poor harvests and demand remains high, prices will rise.
- Pest Attacks and Diseases: These can reduce the yield of onion crops, affecting the overall supply.
- Conversely, a bumper crop can lead to an excess supply and lower prices.
- If supply is low due to poor harvests and demand remains high, prices will rise.

- Government Policies: These include export bans or restrictions, minimum export prices, and import regulations.
- Such measures are used to stabilize domestic markets.
- For instance,
- They might ban exports to make sure there are enough onions available in the domestic market.
- Or, they might set a minimum export price to ensure farmers can still make money from onions they sell overseas.
- Cost of Production: Increases in the cost of inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and labor can lead to higher prices for onions as farmers try to maintain their profit margins.
- Transportation and Storage: The logistics of getting onions from farms to markets can significantly impact prices.
- Poor transportation infrastructure or inadequate storage facilities can lead to increased wastage and higher prices.
- Market Speculation: Traders and middlemen may speculate on future price rises, hoarding stocks to sell at a higher price later.
- This speculation can artificially inflate prices.
- International Market Dynamics: Global demand and supply conditions also affect prices.
- If major onion-exporting countries face a shortfall, it can increase the demand for Indian onions abroad, pushing up prices.
- Political Factors: Election cycles can influence onion prices as governments may implement short-term measures to keep prices low and avoid public dissatisfaction.

- Economic Policies: Decisions on taxation, such as the imposition of export duties, and economic conditions that affect currency exchange rates can also influence the pricing of onions, especially in terms of exports.
- Global Market Influence: Since India exports onions to other countries, what happens in those countries can affect onion prices in India.
- For instance, if a major onion-producing country like Egypt decides to export more or fewer onions, it could affect onion prices worldwide, including in India.

Consequences of Price Fluctuations
- Impact on Consumer Budgets: High onion prices can strain consumer budgets, as onions are a staple in Indian cooking.
- Inflationary Pressure: Significant increases in onion prices can contribute to overall food inflation, affecting economic stability.
- Farmer Distress: While high prices can benefit farmers, sudden price drops due to oversupply can lead to losses, affecting their livelihood.
- Political Ramifications: Given the essential nature of onions in Indian cuisine, significant fluctuations in onion prices can lead to public discontent, influencing electoral politics.
Impacts of Price Fluctuations
- Economic Impact: The agriculture sector's performance, particularly in onion-heavy regions, can influence local and national economies.
- Social Impact: Price volatility can lead to social unrest or dissatisfaction among the population, particularly among lower-income groups.
- Policy Adjustments: Frequent fluctuations often lead governments to revise or implement new agricultural and trade policies to stabilize the market.
Major Onion-Producing Regions in India
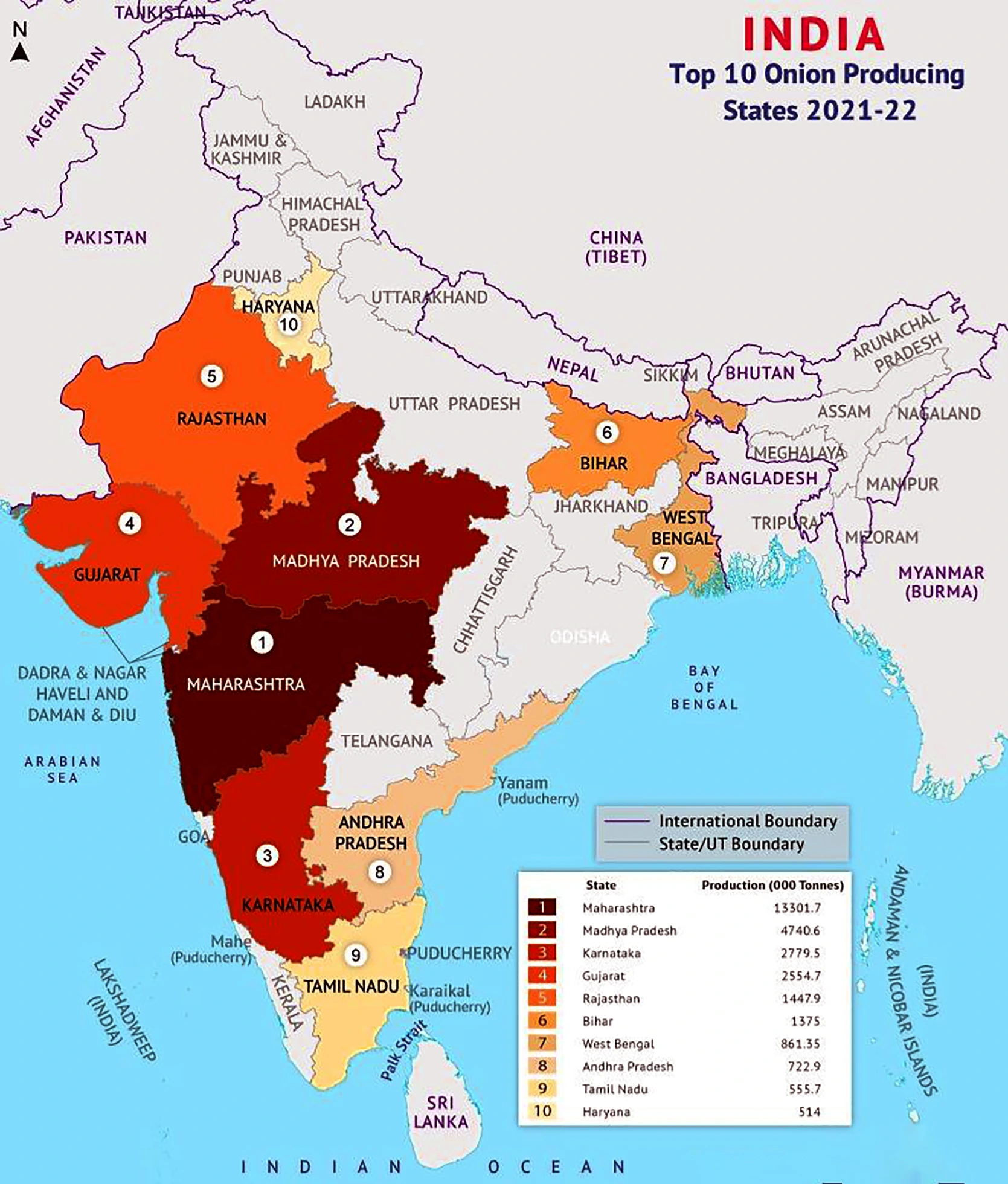
India, being one of the largest producers of onions in the world, has several key regions where onion cultivation is prevalent:
- Maharashtra: This state is the top producer of onions in India, with districts like Nashik, Ahmednagar, and Solapur leading in cultivation.
- Madhya Pradesh: The second largest producer, contributing significantly to the national output.
- Karnataka: Another major contributor to India's onion production, especially in districts like Bangalore Rural and Kolar.
- Gujarat, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Telangana are also notable for their onion production.
These regions benefit from suitable climatic conditions and well-established agricultural practices that support onion cultivation.

Impact of Monsoon
- Positive Impact: Adequate monsoon rains are crucial for good onion yields, especially for the kharif and late kharif crops.
- Negative Impact: Excessive rainfall can lead to crop damage, diseases, and a reduction in yield. It can also affect the sowing and harvesting timings.
Overall, the monsoon's reliability largely determines the volume of onion production, affecting both domestic supply and export capabilities.
Recent Changes in Agricultural Policies in India
Recent changes in India's agricultural policies include:
- Farm Bill Repeal: The government's decision to repeal controversial farm laws after widespread protests was a significant policy shift.
- Export and Import Adjustments: Policies governing the export and import of essential commodities like onions and pulses have been frequently adjusted to manage domestic supply and price stability.
- Subsidy Reforms: There has been a push to reform subsidies for fertilizers and irrigation to promote sustainable agriculture.
- Focus on Organic Farming: There is an increased focus on promoting organic farming and non-traditional agriculture through government incentives.
These fluctuations in onion prices not only affect economic conditions but also have broader socio-political impacts, reflecting the importance of onions in Indian society and economy.
Image Credits - Text: Partha Biswas, Illustration: Suvajit Dey (The Indian Express)
Previous Post