Table of contents
The World Bank's latest Women, Business, and Law Index paints a complex picture of gender equality in India, offering reasons for both celebration and concern.
India's Ranking
- India ranks 113th out of 190 countries, a slight improvement from 129th previously.
- While this might seem low, it reflects the addition of new indicators like "Safety" impacting the rankings.
How is calculated?
The World Bank's Women, Business and Law (WBL) index uses a combination of legal frameworks and supportive frameworks to measure how laws and regulations impact women's economic opportunities in a particular country.
Legal Frameworks (70% weightage)
- This section analyzes eight core areas through binary (yes/no) questions:
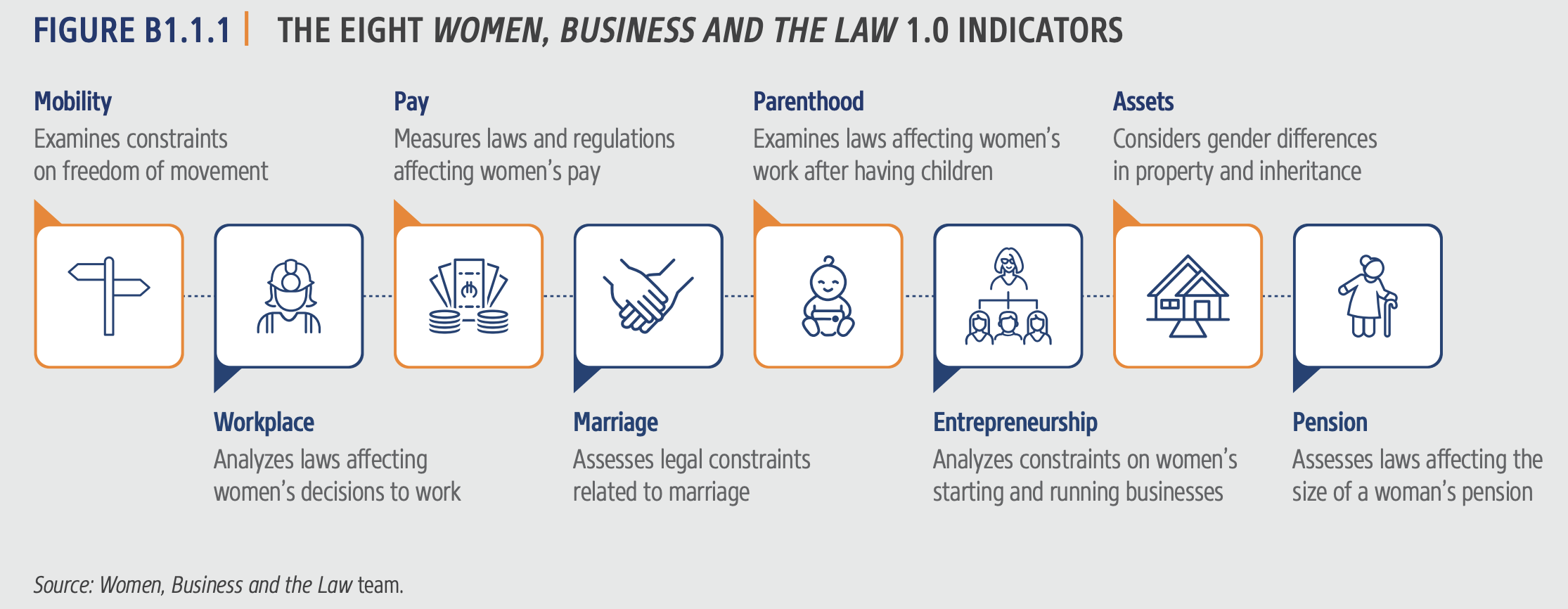
- Scores for each area are obtained by averaging the responses (1 for yes, 0 for no) and scaling them to 100.
- The overall legal framework score is the average of the scores from all eight areas. (This makes up 70% of the total WBL index score.)
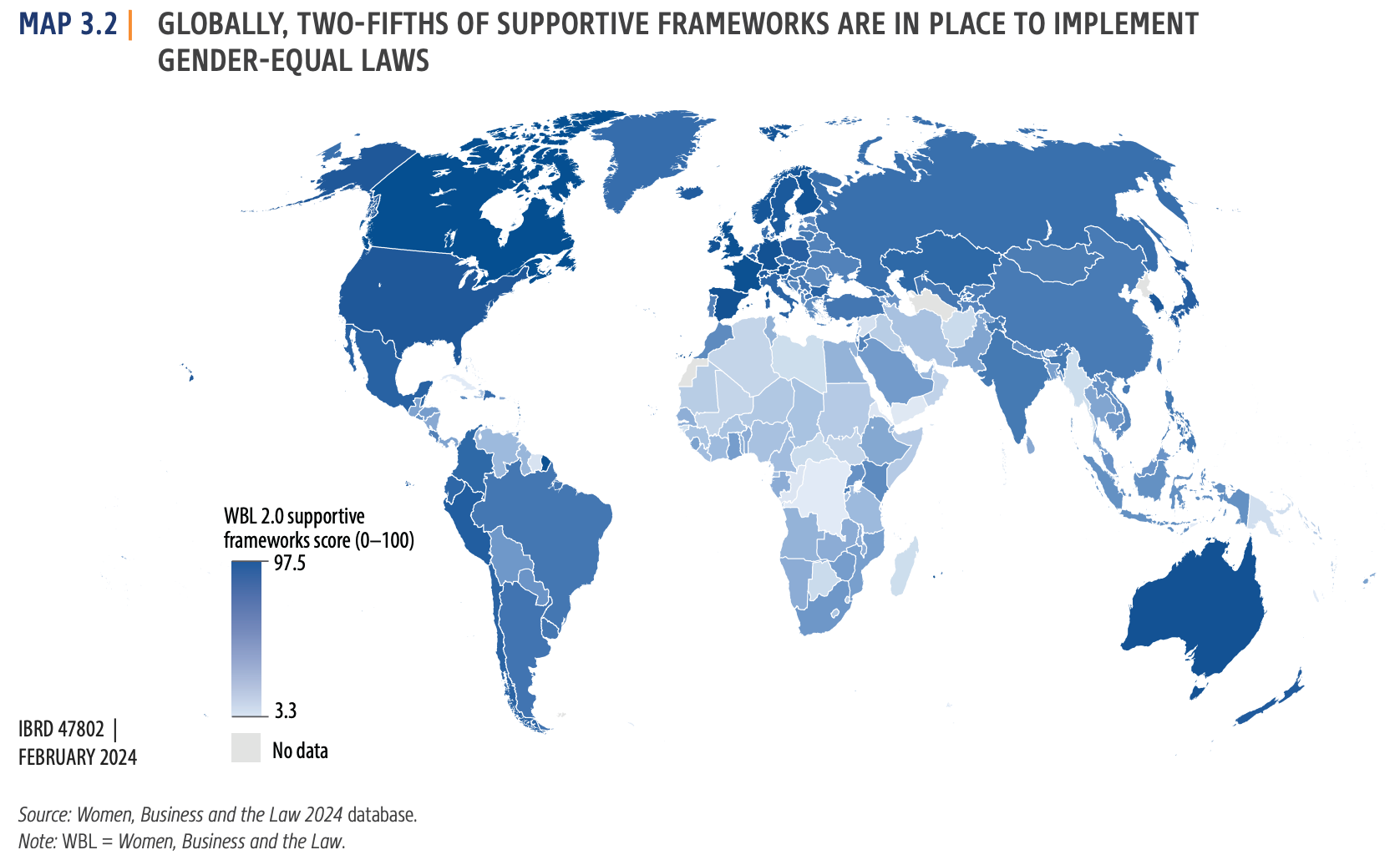
Supportive Frameworks (30% weightage)
- In previous editions, this section assessed whether a country has established frameworks to support the legal rights. This could include:
- Government programs for women entrepreneurs
- Services like childcare facilities
- Budgets allocated for women's development
- Procedures for enforcing gender equality laws
- Inspections to ensure compliance
- Penalties for non-compliance
- The existence and quality of these frameworks were likely evaluated and assigned a score.
- The weightage for supportive frameworks was historically 30% of the total WBL index score.
Overall Score
- The final WBL index score is a weighted average of the legal frameworks score (70%) and the supportive frameworks score (30%).
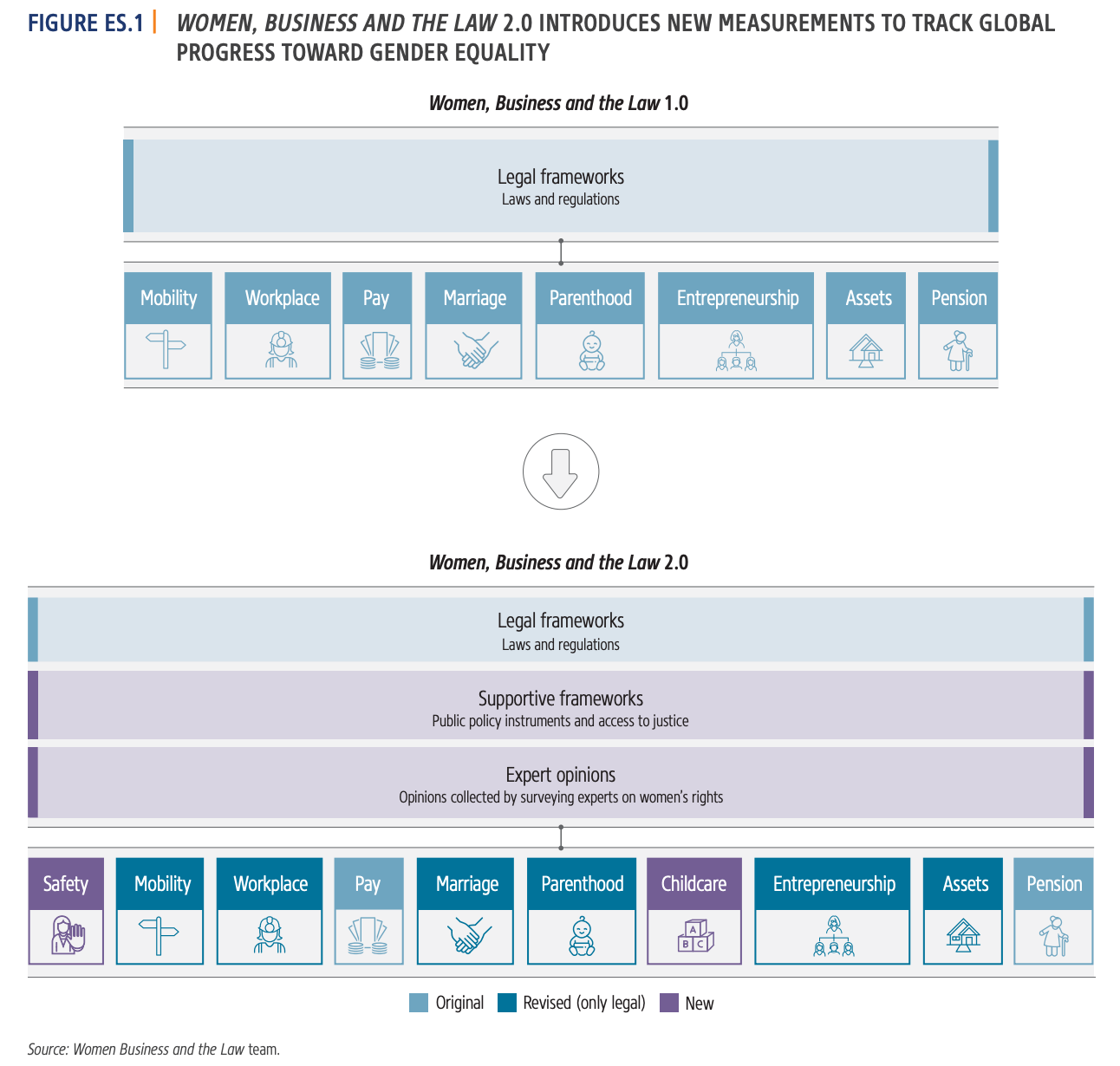
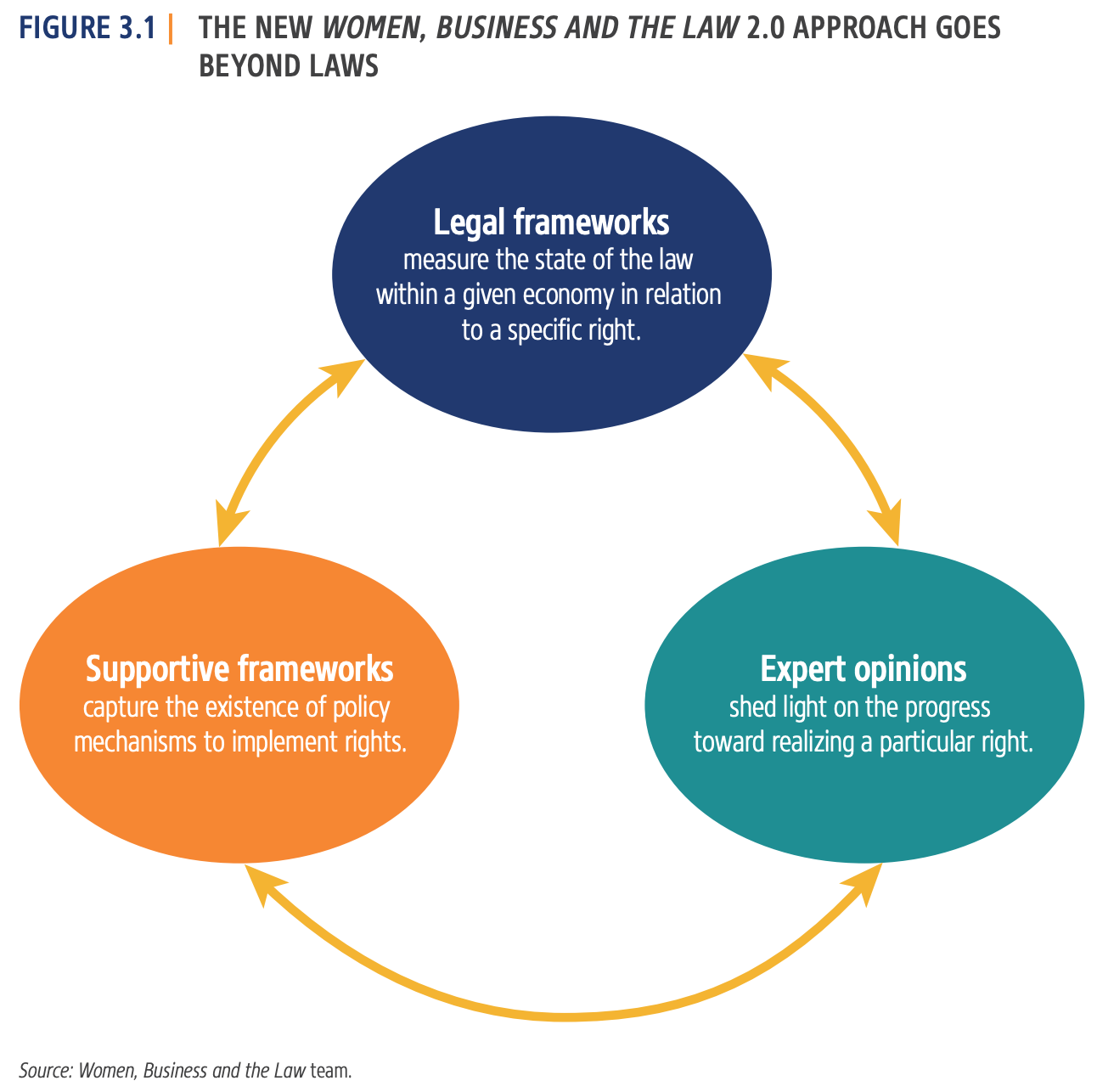
Key Findings
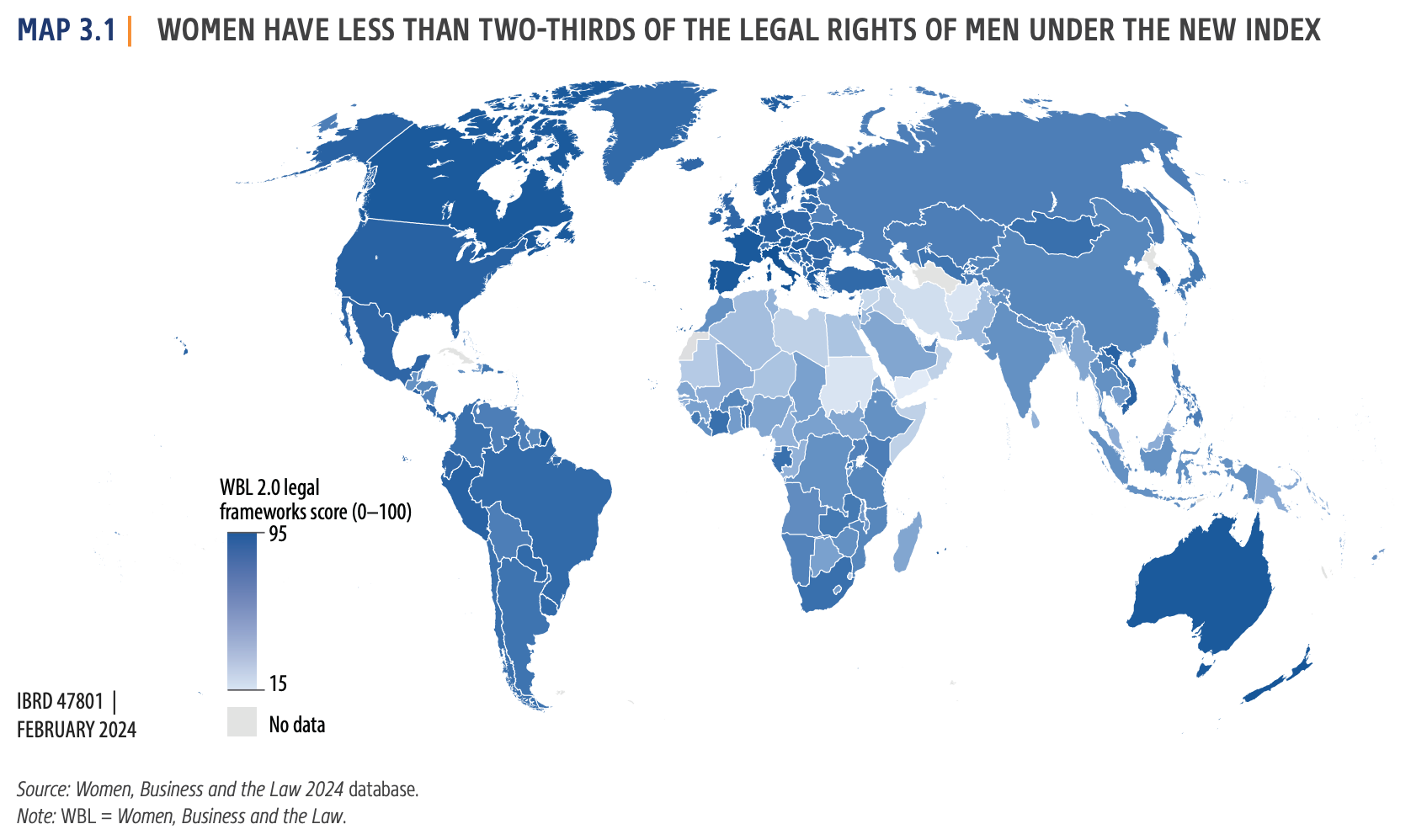
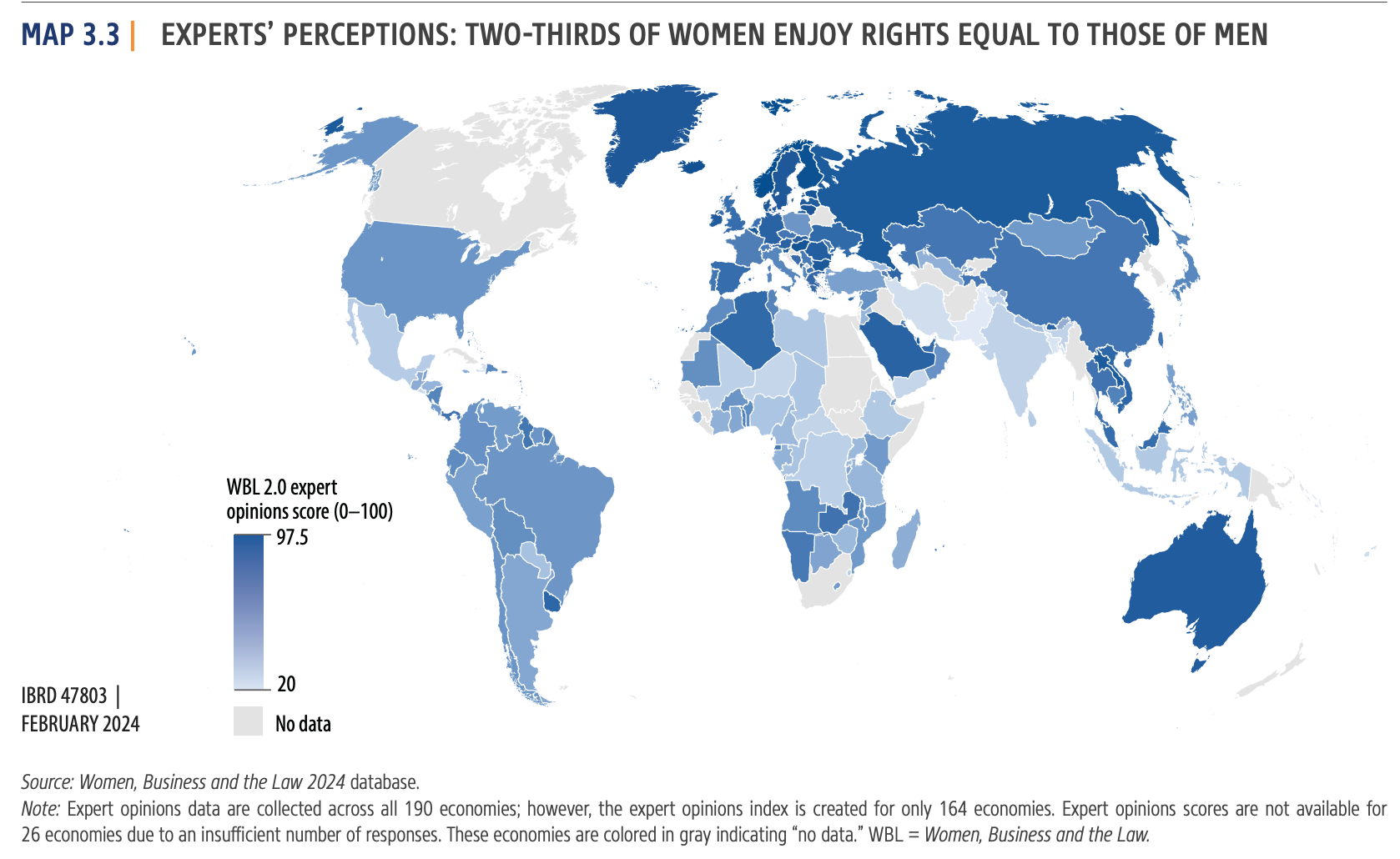
- India scores 60% on legal rights for women compared to men, lower than the global average (64.2%).
- The score of 74.4% has remained stagnant for several years.
- 14 countries, including developed nations like Denmark and Canada, achieve a perfect score.
- Even some developing countries outperform India.
Positives
- Slight Improvement in Ranking: India climbed 16 spots to 113th out of 190 countries.
- Strong Legal Framework: India maintained its score of 74.4%, indicating a solid foundation in legal rights for women.
- Focus on Safety and Childcare: The inclusion of these aspects potentially boosted India's ranking.
Negatives
- Below Average Score: India still falls behind the global average of 64.2% legal rights for women.
- Stagnant Progress: The country's legal framework score hasn't improved over recent years.
- Lagging Behind Peers: Several developing nations and even some with lower GDPs outperform India.
- Limited Support Systems: India only has 54.2% of the necessary supportive frameworks established, hindering women's participation.
Unequal Care Burden: Women shoulder significantly more unpaid caregiving responsibilities.
We can't clear UPSC for you.
But with our personalised mentor support, you'll be ready to do it yourself.
Global Challenges
- No country achieves complete legal equality for women.
- Women globally spend more time on unpaid care work compared to men, impacting employment.
- Limited quality childcare services hinder women's participation in the workforce.
- Few economies prioritize gender-sensitive criteria in public procurement, limiting women's entrepreneurial opportunities.
The Importance of Gender Equality
- Increasing women's economic participation is crucial for economic growth and development.
- Empowering women strengthens their voice and influence on decisions that directly affect them.
Looking Ahead
The WBL report highlights the need for India to address legal and practical gaps to ensure equal rights and opportunities for women.
This includes:
- Strengthening Supportive Frameworks: Implementing programs and services that empower women.
- Improving Childcare Infrastructure: Providing quality childcare options to ease women's employment barriers.
- Promoting Women Entrepreneurs: Enacting policies that encourage women-owned businesses. Promoting gender-sensitive public procurement policies.
- Breaking Gender Barriers: Eliminating discriminatory laws and practices. Addressing issues like pay equity, pensions, and property rights.
This International Women's Day, India has an opportunity to reflect on progress made and areas needing improvement. By addressing legal and practical inequalities, India can unlock the full potential of its women and propel economic growth.
Previous Post