Table of contents
Introduction
The United Nations (UN) is an international organization founded on October 24, 1945, after World War II.
- It was established to promote peace, security, and cooperation among countries worldwide.
- The UN replaced the ineffective League of Nations and sought to prevent future conflicts and foster international collaboration.
Founding Members
The UN started with 51 founding member states, including major powers like the United States, the Soviet Union, China, the United Kingdom, and France.
Membership
As of now, the UN has 193 member states, encompassing nearly every sovereign country in the world.
Headquarters
The UN's headquarters is located in New York City, USA.
- It also has major offices in Geneva, Switzerland; Vienna, Austria; and Nairobi, Kenya.
Objectives
The UN aims to:
- Maintain international peace and security.
- Develop friendly relations among nations.
- Achieve international cooperation in solving international problems.
- Promote human rights and fundamental freedoms.
Principal Organs
With the founding of the United Nations in 1945, six principal organs were established as part of the UN Charter to carry out its functions and objectives:
General Assembly

- Function: The main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN.
- It is the only UN body with universal representation because all 193 UN member states are represented.
- Each year in September, all members of the UN meet to discuss and decide on matters of peace and security, admission of new members and budgetary matters
- Decision making on above topics requires a two-thirds majority of the General Assembly and other decisions are taken by simple majority.
- The President of the General Assembly is elected each year by assembly for a one-year term.
Security Council

- Function: Responsible for maintaining international peace and security.
- It is a body of fifteen member states.
- The five permanent members include China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- The ten non-permanent members are elected for two-year terms by the General Assembly.
- It is a powerful body because of the “Veto power” under which any permanent member can veto or reject any resolution of the Security Council and this is deemed as the most undemocratic character of the UN.
- There have been instances when veto power is used for international inaction on war crimes and crimes against humanity.
International Court of Justice
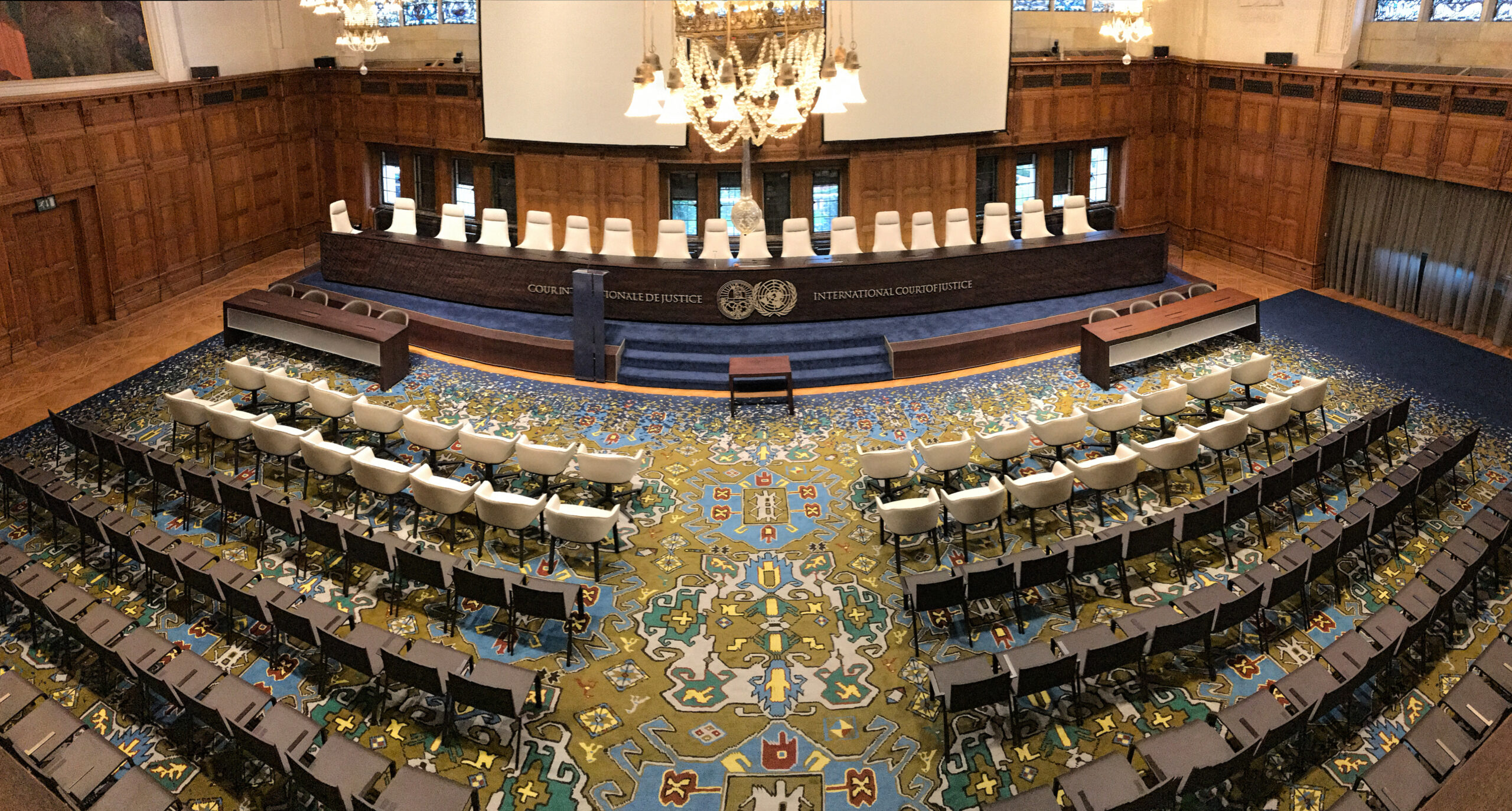

Headquarters: The Hague, Netherlands
Date of Inception: April 1946
- Function: The principal judicial organ of the United Nations.
- The court is the successor of the Permanent Court of International Justice established by the League of Nations in 1920.
- The seat of the ICJ is at the Peace Palace in The Hague and is the only principal organ of the United Nations not located in New York.
- The Court’s function is to settle legal disputes submitted to it by States and to give advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by the United Nations in accordance with international law.
Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)

- Function: The principal body for coordination, policy review, policy dialogue, and recommendations on economic, social, and environmental issues.
- It is the chief body for implementation of internationally agreed sustainable development goals.
- It has 54 Members, elected by the General Assembly for overlapping three-year terms.
- ECOSOC coordinates the work of the 14 UN specialized agencies, ten functional commissions and five regional commissions.
UN Secretariat

- Function: Carries out the day-to-day work of the UN.
- The Secretariat comprises the Secretary-General and tens of thousands of international UN staff members who carry out the day-to-day work of the UN as mandated by the General Assembly and the Organization’s other principal organs.
- Provides studies, information, and facilities needed by the UN.
- It is headed by the Secretary-General.
- The Secretary-General is the organisation's chief administrative officer, appointed by the General Assembly on the recommendation of the Security Council for a five-year, renewable term.
- UN staff members are recruited internationally and locally, and work in duty stations and on peacekeeping missions all around the world.
Trusteeship Council

- Function: Established to oversee trust territories' administration and ensure adequate steps were taken for their self-governance and independence.
- It placed the trust territory (a non-self-governing territory) under an administrative authority.
- It was similar to the League of Nations mandate, which was a legal status for some territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I.
- The council had to provide supervision for 11 Trust Territories placed under the administration of seven member states for self-government and independence in future.
- All Trust Territories had attained self-government or independence by 1994 and the Trusteeship Council suspended operation on 1 November 1994.h

Secretary-General
The Secretary-General is the chief administrative officer of the UN and a symbol of the organization's ideals.
The current Secretary-General is António Guterres, who assumed office on January 1, 2017.

Specialised Agencies
Articles 57 and 63 of the United Nations Charter provide for the creation of specialized agencies.
IFAD

Headquarters: Rome, Italy
Date of Establishment: December 15, 1977
- The International Fund for Agricultural Development was formed as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference.
- This conference was in the aftermath of global food shortages and widespread famine and malnutrition in the Sahel region of Africa.
ITU

Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
Date of Establishment: May 17, 1865
- International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations in areas like information and communication technologies.
- Founded in 1865, it is the oldest among all the specialized agencies of the United Nations.
- Based in Geneva, it works on the principle of international cooperation between member states and the private sector.
- It allocates global radio spectrum and satellite orbits, ensures seamless interconnection of networks and improves its access to underserved communities.
FAO

Headquarters: Rome, Italy
Date of Establishment: October 16, 1945
- The Food and Agriculture Organization was set up in Quebec City during the first session of the United Nations in 1945.
- FAO is a specialized agency dealing in international efforts to defeat hunger.
- FAO helps developing countries to modernize agriculture, forestry and fisheries for good nutrition and food security.
WHO

Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
Date of Establishment: April 7, 1948
- The World Health Organization was established in 1948 with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is an intergovernmental organization working in collaboration with member states through the respective health ministries.
- It is responsible for providing leadership on global health matters, setting norms and standards, providing evidence-based policy options, shaping the health research agenda, providing technical support to countries and monitoring and assessing health trends.
ILO

Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
Date of Establishment: October 1919 (became a UN specialized agency in 1946)
- The International Labour Organization has a mandate to advance social justice and decent work by setting international labor standards.
- It also encourages decent employment opportunities with proper social protection.
- It was created as an agency of the League of Nations in 1919, as part of the Treaty of Versailles.
- The ILO became the first United Nations specialized agency in 1946 by signing of the United Nation agreement.
Funds and Programs
UNDP

Headquarters: New York City, USA
Date of Inception: November 22, 1965
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) was established in 1965 for renderIng advice, training and support to developing countries generally and least developed countries specifically.
- It is funded entirely by voluntary contributions from member nations.
- The UNDP Executive Board has representatives from 36 countries serving on a rotation basis.
- Work of UNDP is central to the United Nations Sustainable Development Group spanning 165 countries and uniting the 40 UN funds for the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
UNICEF

Headquarters: New York City, USA
Date of Inception: December 11, 1946
- Originally known as the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund, it provides emergency food and healthcare to children and mothers in countries post World War II.
- Its mandate was extended in 1950 to address the needs of children and women in developing countries.
- It became a permanent part of the United Nations in 1953 when the words “international” and “emergency” were removed from “UNICEF”, though the original acronym is still used.
- United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF)
- A 36-member executive board formulates policies, approves programs and oversees administrative and financial plans with contributions from governments and private donors..
- The members are government representatives elected by the United Nations Economic and Social Council for three-year terms.
UNFPA

Headquarters: New York City, USA
Date of Inception: 1969
- Formerly the United Nations Fund for Population Activities, UNFPA is the United Nations sexual and reproductive health agency.
- It aims for a world where every pregnancy is wanted, every young person’s potential is fulfilled and every childbirth is safe..
- In 2018, UNFPA launched efforts like
- Ending unmet need for family planning
- Ending preventable maternal death
- Ending gender-based violence and harmful practices
UN-HABITAT

Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
Date of Inception: 1978
- The United Nations Human Settlements Programme is for a better urban future by promoting socially and environmentally sustainable human settlements.
- It was formed in 1978 after the First UN Conference on Human Settlements and Sustainable Urban Development in Vancouver.
- 2nd United Nations Conference on Human Settlements (Habitat II) in Istanbul, focussed on adequate shelter for all and development of sustainable human settlements in an urbanizing world.
- The 3rd United Nations Conference on Housing and Sustainable Urban Development (Habitat III) was held in 2016 in Quito with focus on Goal-11 of the Sustainable Development Goals.
UNEP

Headquarters: Nairobi, Kenya
Date of Inception: June 5, 1972
- The United Nations Environment Programme sets the global environmental agenda and ensures implementation of the environmental dimension of sustainable development.
- It was an outcome of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment (Stockholm Conference) in June 1972.
- UNEP and the World Meteorological Organization established the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in 1988 to assess climate change.
- The secretariats for the multilateral environmental agreements hosted by UNEP include:
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS)
- Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer
- Basel Convention on the Control of Trans-boundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes and Their Disposal
- Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants
- Minamata Convention on Mercury
- Rotterdam Convention on the Prior Informed Consent Procedure for Certain Hazardous Chemicals and Pesticides in International Trade
UNESCO

Headquarters: Paris, France
Date of Inception: November 16, 1945
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) promotes peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, culture, and communication.
- It was established on November 16, 1945.
- UNESCO seeks to foster dialogue among civilizations, cultures, and peoples based on respect for commonly shared values.
- UNESCO's primary objectives include:
- Promoting education for all, focusing on lifelong learning and inclusive quality education.
- Advancing scientific cooperation and innovation to address global challenges.
- Protecting cultural heritage and promoting the diversity of cultural expressions.
- Ensuring freedom of expression and access to information.
UN Peacekeeping
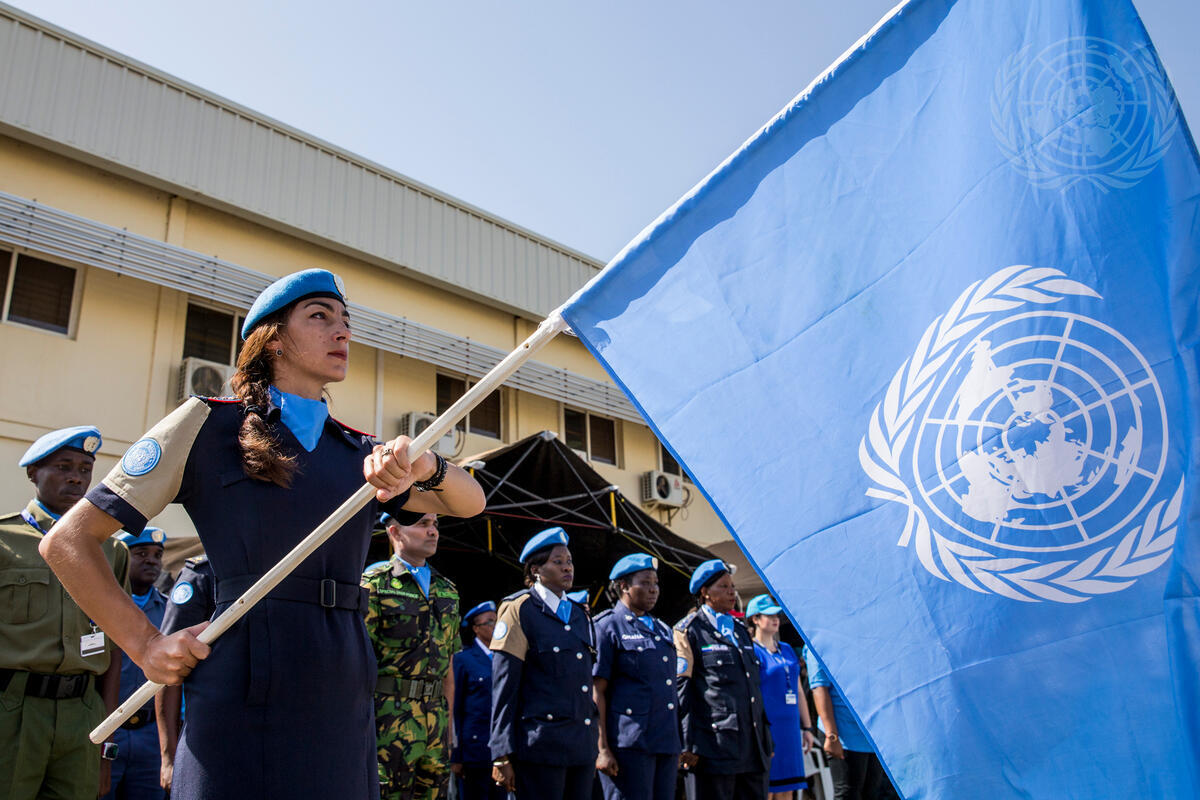


The United Nations deploys peacekeeping missions to conflict zones to promote stability and peace.
- These missions involve military personnel, police, and member-state civilian workers.
- Multinational Efforts: Peacekeeping missions are typically composed of personnel from a variety of countries, demonstrating an international commitment to resolving conflicts.
- Mandates: Each peacekeeping mission operates under a specific mandate from the UN Security Council, which outlines its objectives and the scope of its authority.
- Civilian Components: Besides military and police units, peacekeeping missions include civilian experts who work on various aspects of governance, human rights, and development.
The military personnel in peacekeeping missions are often referred to as "Blue Helmets" due to their distinctive headgear.
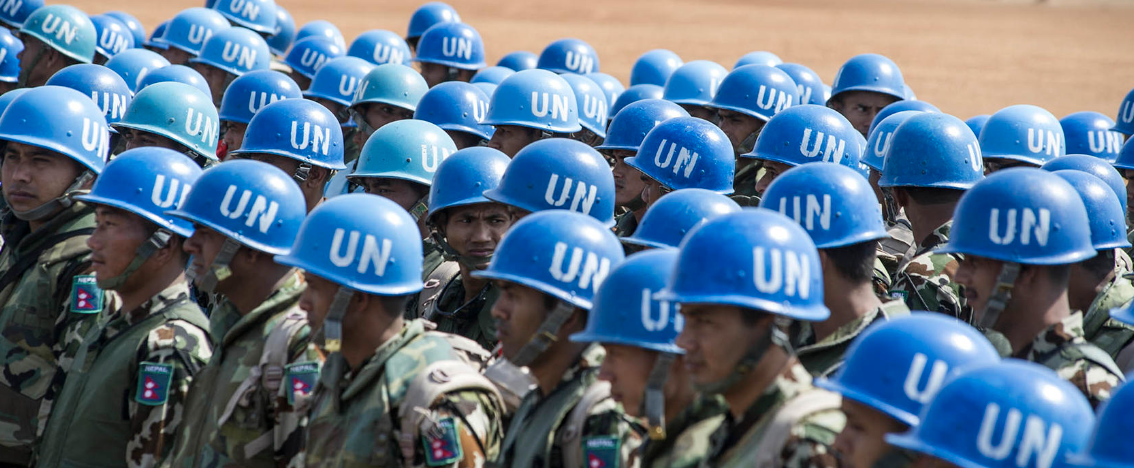

Peacekeeping operations are designed to help countries navigate the difficult path from conflict to peace.
- They provide crucial support during the implementation of peace agreements:
- Facilitate the political process
- Protect civilians
- Assist in the disarmament, demobilization, and reintegration of former combatants
- Support the organization of elections
- Protect and promote human rights
- Assist in restoring the rule of law
Peacekeeping missions often operate in hostile and complex environments, facing challenges such as limited resources, difficult terrain, and ongoing security threats. UN peacekeeping plays a crucial role in maintaining international peace and security, helping create conditions where peace can flourish.
Major Interventions
Korean War (1950-1953)
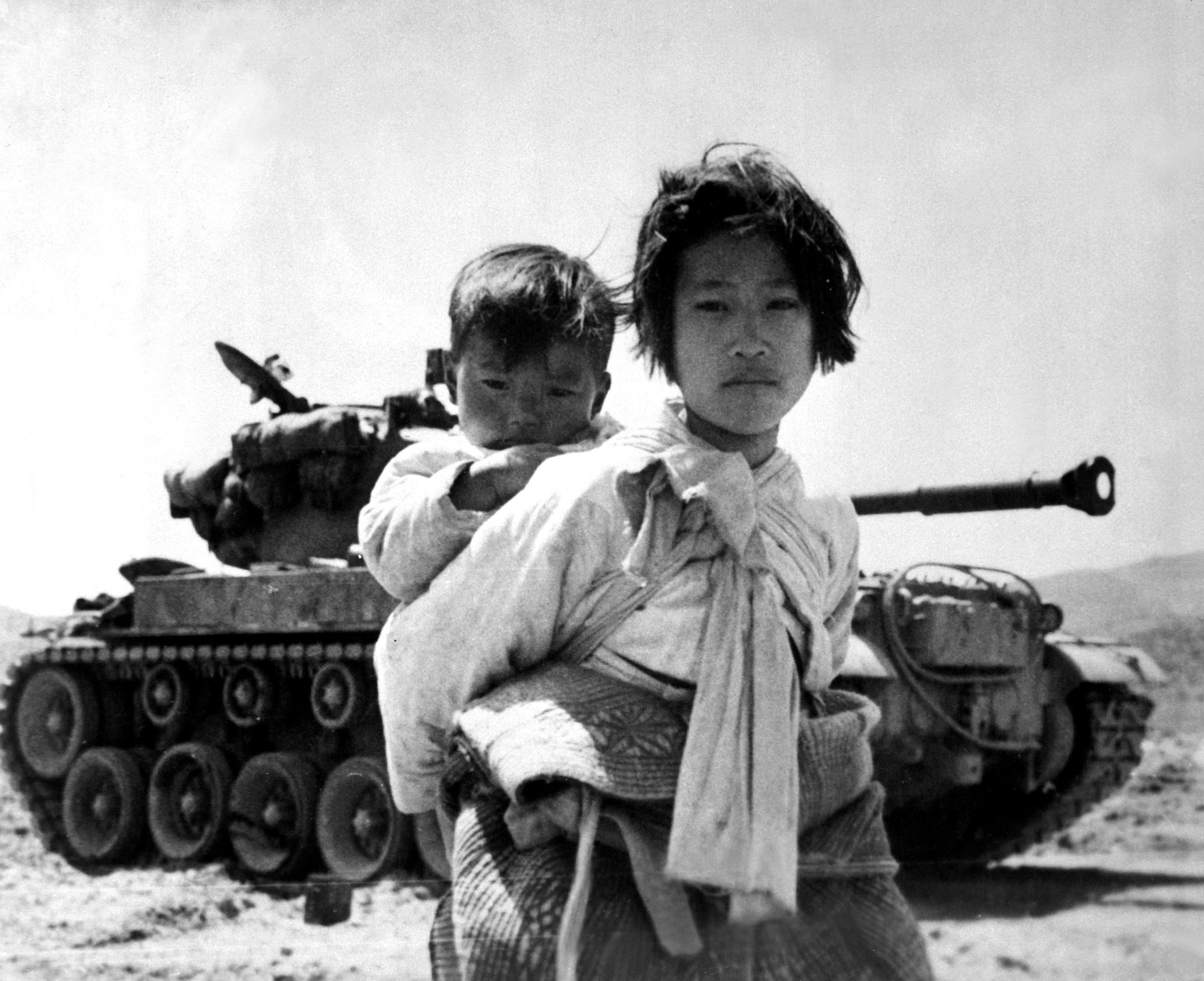



The UN Security Council authorized military intervention to repel North Korean aggression against South Korea, leading to a ceasefire and the establishment of the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ).
Suez Crisis (1956)
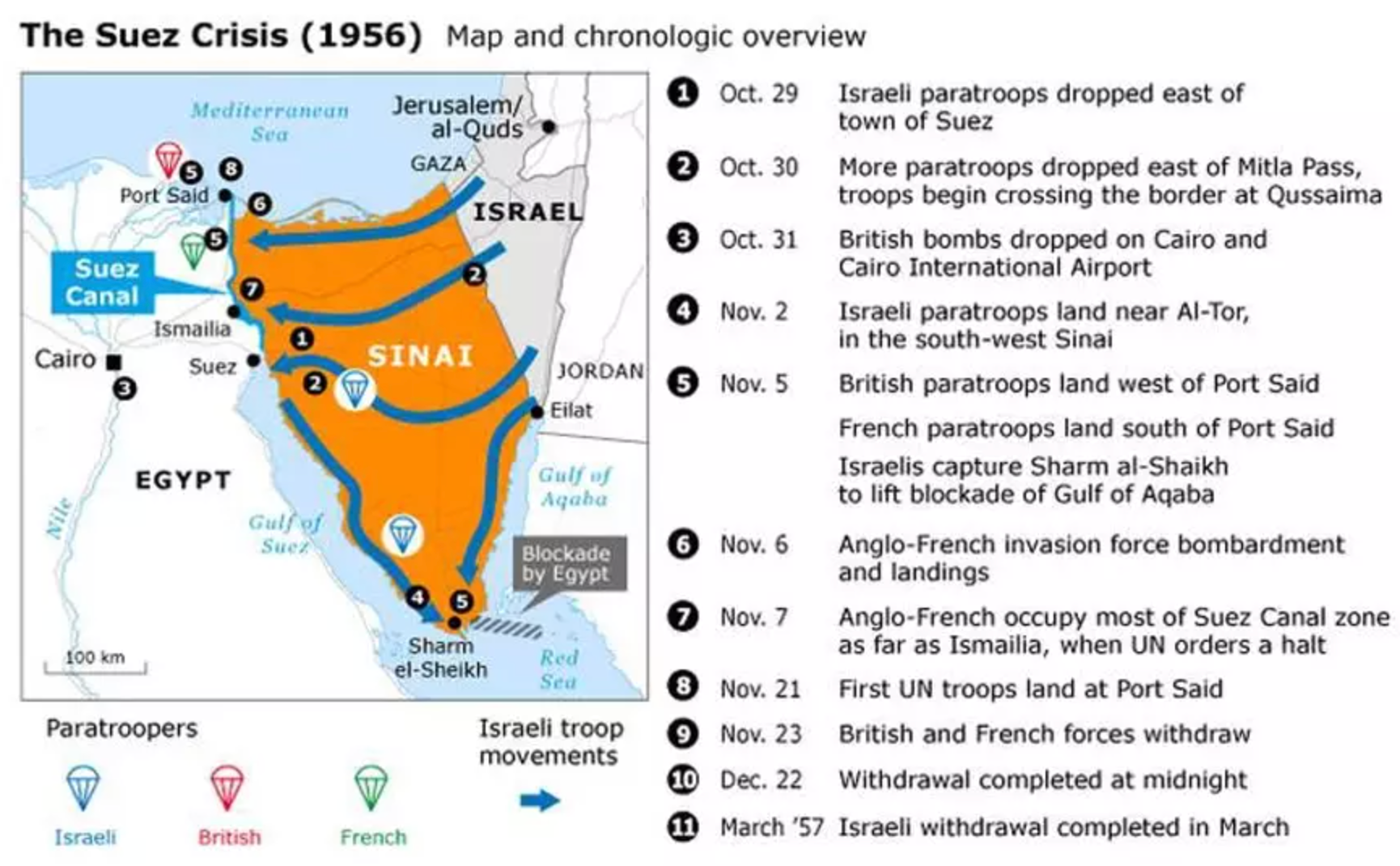

The UN intervened to resolve the Suez Crisis by establishing the United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) to ensure the withdrawal of invading forces from Egypt and the reopening of the Suez Canal.
Congo Crisis (1960-1964)
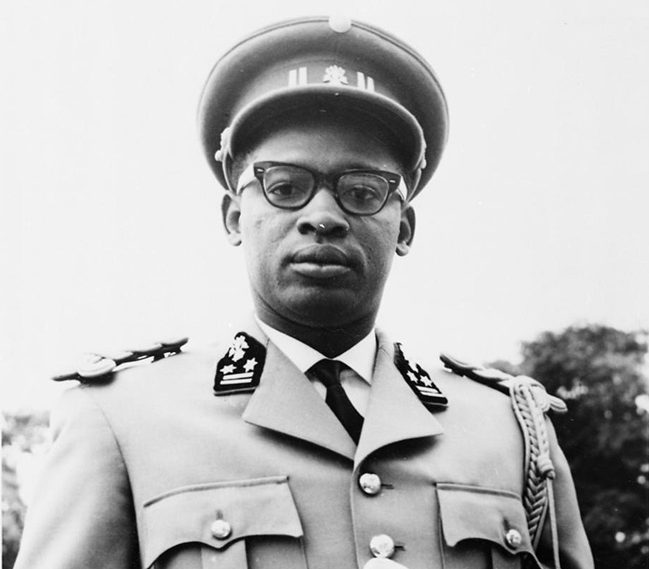



The UN deployed the United Nations Operation in the Congo (ONUC) to restore order, support the government, and prevent the secession of provinces, ultimately aiding in the stabilization of the country.
Rwanda Genocide (1994)
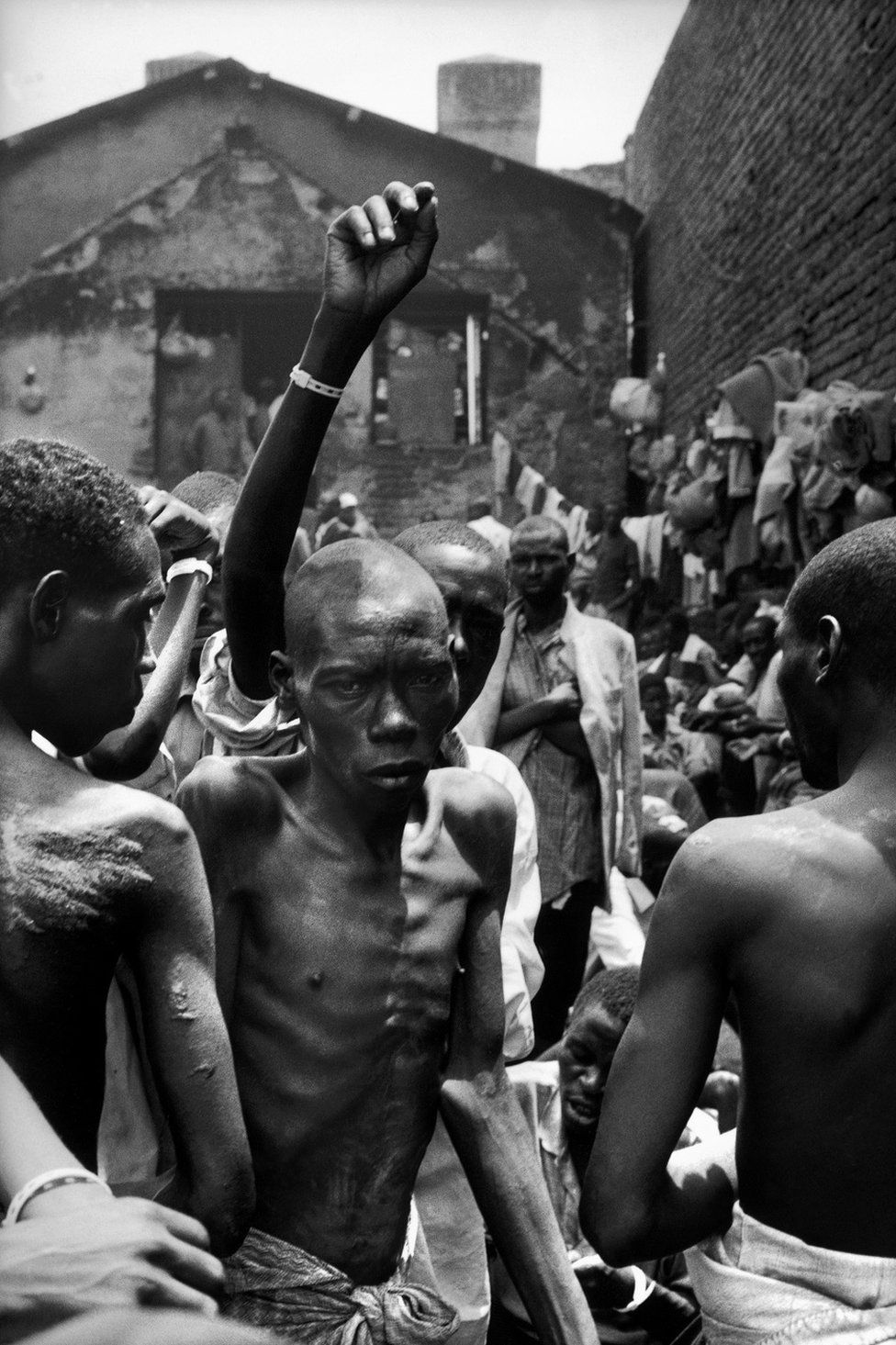



Despite initial failures, the UN has since taken significant steps to address the aftermath of the Rwandan Genocide, promoting justice through the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda and supporting reconciliation efforts.
East Timor Independence (1999-2002)
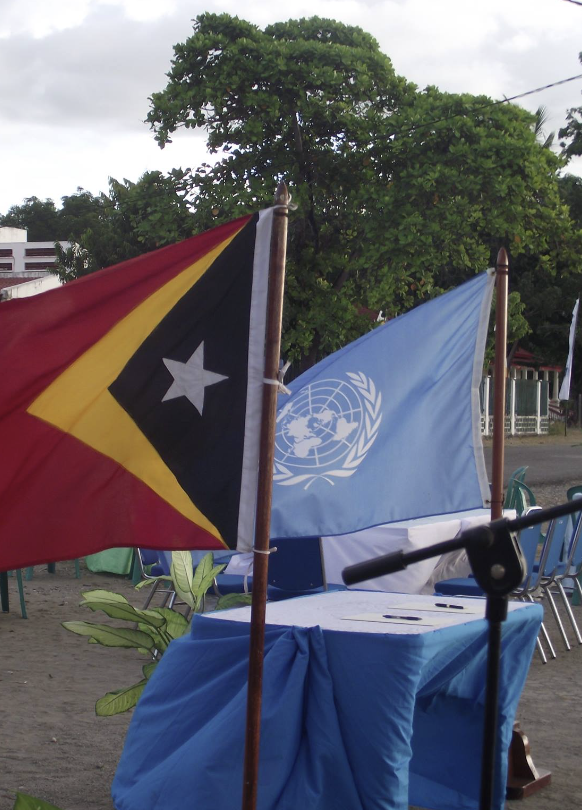



The UN-administered East Timor during its transition to independence from Indonesia, providing peacekeeping forces, organizing elections, and supporting the establishment of government institutions.
Haiti Earthquake (2010)
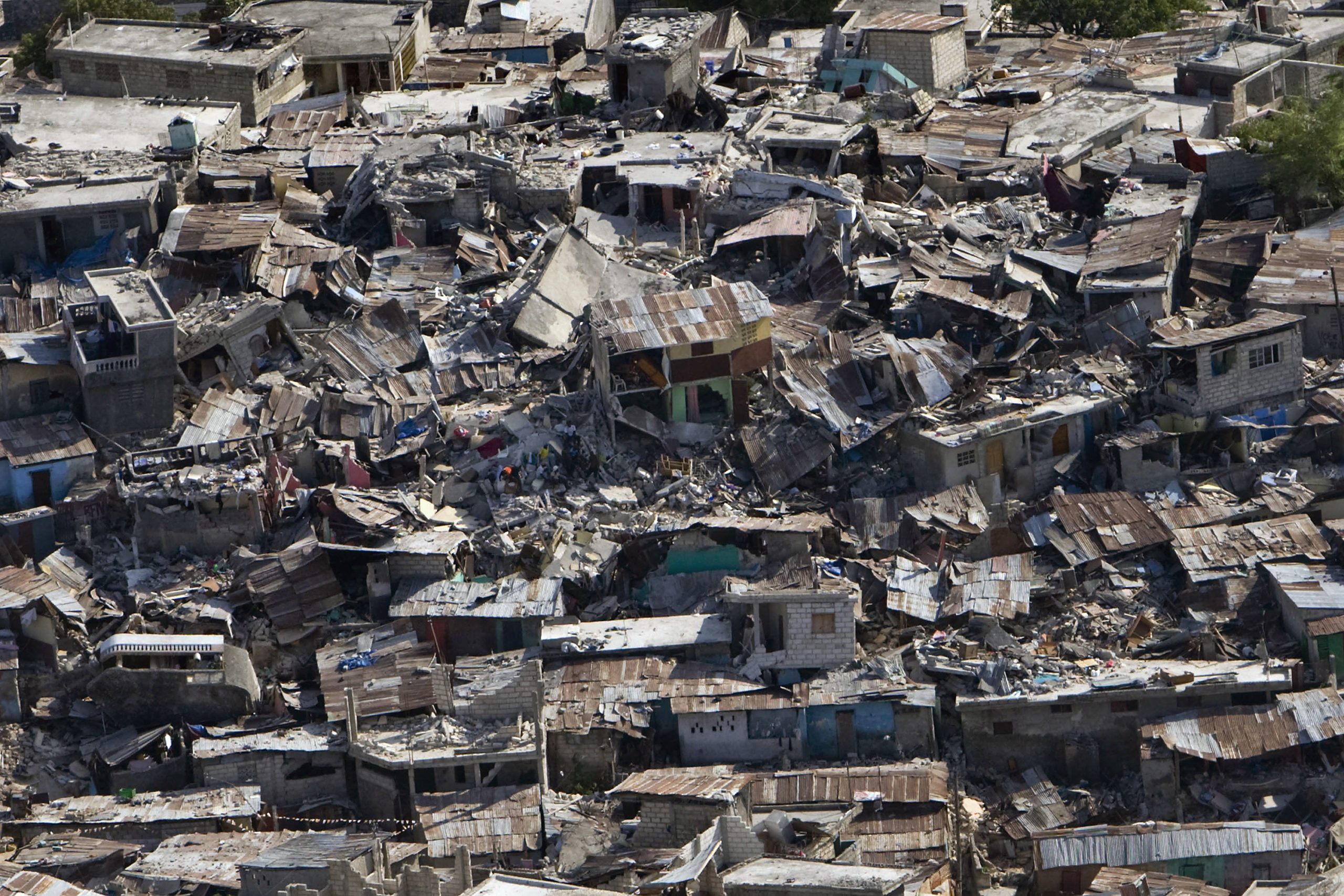



Following the devastating earthquake, the UN coordinated extensive humanitarian relief efforts, providing food, medical care, and rebuilding infrastructure through the United Nations Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH).
Sustainable Development Goals (2015-Present)


The UN's 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all member states, has specific goals and targets to eradicate poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all.
The UN continues to be a vital platform for international cooperation, addressing global challenges, and striving to create a more peaceful and just world.
Previous Post