Table of contents
Why in the News?
Event: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has joined Project Nexus.
Initiative: This is a multilateral international initiative aimed at enabling instant cross-border retail payments by interlinking domestic fast payment systems.

- An agreement was signed by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the central banks of India, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand on June 30, 2024, in Basel, Switzerland.
- Indonesia, which has been involved from the early stages, continues to be involved as a special observer.

- Collaboration: The RBI has been collaborating bilaterally with various countries to link India’s fast payments system — Unified Payments Interface (UPI), with their respective domestic fast payments systems for cross-border Person-to-Person (P2P) and Person-to-Merchant (P2M) payments.
Bilateral vs. Multilateral Connectivity: While bilateral connectivity has benefits, a multilateral approach like Nexus could further enhance the international reach of Indian payment systems.
Background
- Development: In 2021, the BIS Innovation Hub (BISIH) Singapore Centre developed a blueprint for connecting instant payment systems across borders.
- Prototype: In 2022, a working prototype of Nexus was built, connecting the test systems of Eurosystem’s TIPS, Malaysia’s RPP, and Singapore’s FAST payment system.
- Usability: Nexus focuses on usability, allowing the use of proxies like mobile phone numbers to address cross-border payments without needing long IBANs or local account details.
- Proxy Services: The prototype connected services like TIPS’s Mobile Proxy Lookup, Malaysia’s DuitNow, and Singapore’s PayNow.
What is Project Nexus?

- Project Nexus is conceptualised by the Innovation Hub of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
- It aims to enable instant cross-border payments by connecting multiple domestic instant payment systems globally.
- The project explores how to build on the success of domestic instant payments to improve the speed, cost, transparency and accessibility of cross-border payments.
- The project has produced a comprehensive blueprint for standardising the way that domestic instant payment systems connect, lowering the obstacles for countries that wish to offer instant cross-border payments.
In over 70 countries today, domestic payments reach their destination in seconds at near-zero cost to the sender or recipient. This is thanks to the growing availability of instant payment systems.

Connecting the instant payment systems to each other can enable cross-border payments from sender to recipient within 60 seconds (in most cases).

Working of NEXUS
Nexus is designed to standardise the way that instant payment systems connect to each other.

- Rather than a payment system operator building custom connections for every new country that it connects to, the operator can make one connection to the Nexus platform.
- This single connection allows a fast payment system to reach all other countries on the network.

Nexus could significantly accelerate the growth of instant cross-border payments.
- This has been a collaborative effort between the BIS Innovation Hub (BISIH) and interested central banks and instant payment systems that has been developed and refined over three phases of work.
Future Phases
- In the next and final phase of Nexus, the BISIH will support a coalition of countries interested to implement Nexus.
- Phase four will see central banks of Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and domestic instant payment systems who worked together in phase three joined by the Reserve Bank of India, expanding the potential user base to India's Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- Going forward, the platform can be extended to more countries. It is expected to go live by 2026.
The coalition of countries have agreed to work towards establishing a new entity, the Nexus Scheme Organisation (NSO), which will be responsible for managing the Nexus scheme and its rulebook.
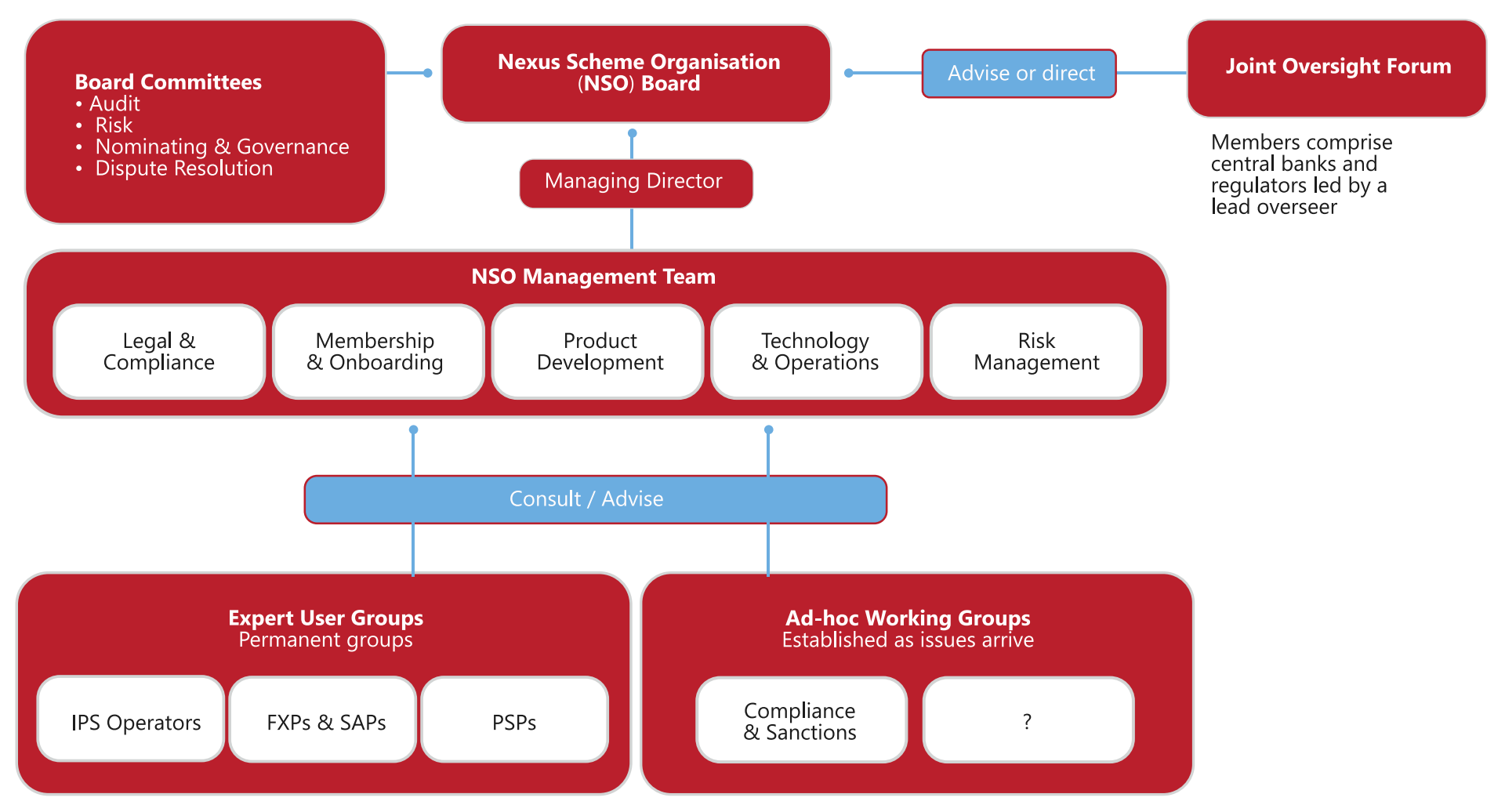
- While the BIS will not own or operate the NSO, it will continue its support by playing an advisory role as participating countries work towards taking Nexus live.
Benefits of Nexus
Speed
- Current Scenario: Traditional cross-border payments are slow due to dependency on multiple banks and central banks' operating hours.
- Nexus Advantage: Cross-border payments can be completed in 60 seconds or less, operating 24/7/365.
- Design Principle: Payments should be completed within 60 seconds.
Cost
- Current Scenario: High costs due to the need for correspondent accounts and routing through larger banks.
- Nexus Advantage: Lower transaction fees and reduced administrative costs by eliminating the need for correspondent accounts.
- Design Principle: Lower barriers to entry and reduce administrative costs.
Access
- Current Scenario: Limited by financial inclusion and correspondent banking relationships.
- Nexus Advantage: Access through non-bank PSPs and simplified processes using proxies like mobile numbers.
- Design Principle: Anyone who can send/receive domestic payments should be able to do so cross-border through Nexus.
Transparency
- Current Scenario: Variable fees and uncertainty about the final amount received.
- Nexus Advantage: Upfront fee calculation and immediate payment status updates.
- Design Principle: Fees and FX rates should be shown upfront, and the sender should know the exact amount credited to the recipient.
Safety, Security, and Resilience
- Current Scenario: Cross-border credit risk due to correspondent banking relationships.
- Nexus Advantage: Builds on existing IPS risk management frameworks, reducing reliance on correspondent banking and mitigating cross-border credit risk.
- Design Principle: Reduce cross-border exposure and rely on domestic IPS settlement arrangements.
Interlinking IPS through Nexus enhances the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, accessibility, transparency, and security of cross-border payments, aligning with the Financial Stability Board’s (FSB) targets.
Source: BIS Innovation Hub
Previous Post