Table of contents
Introduction
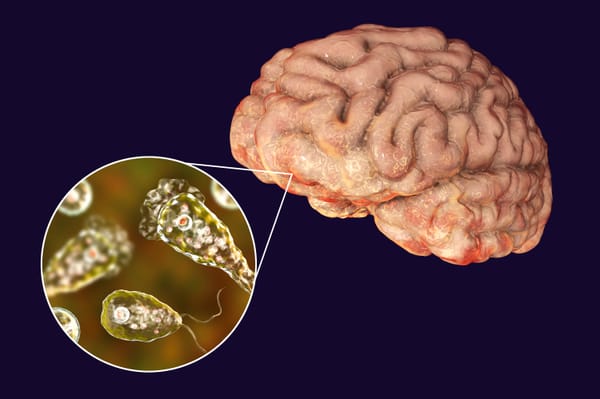
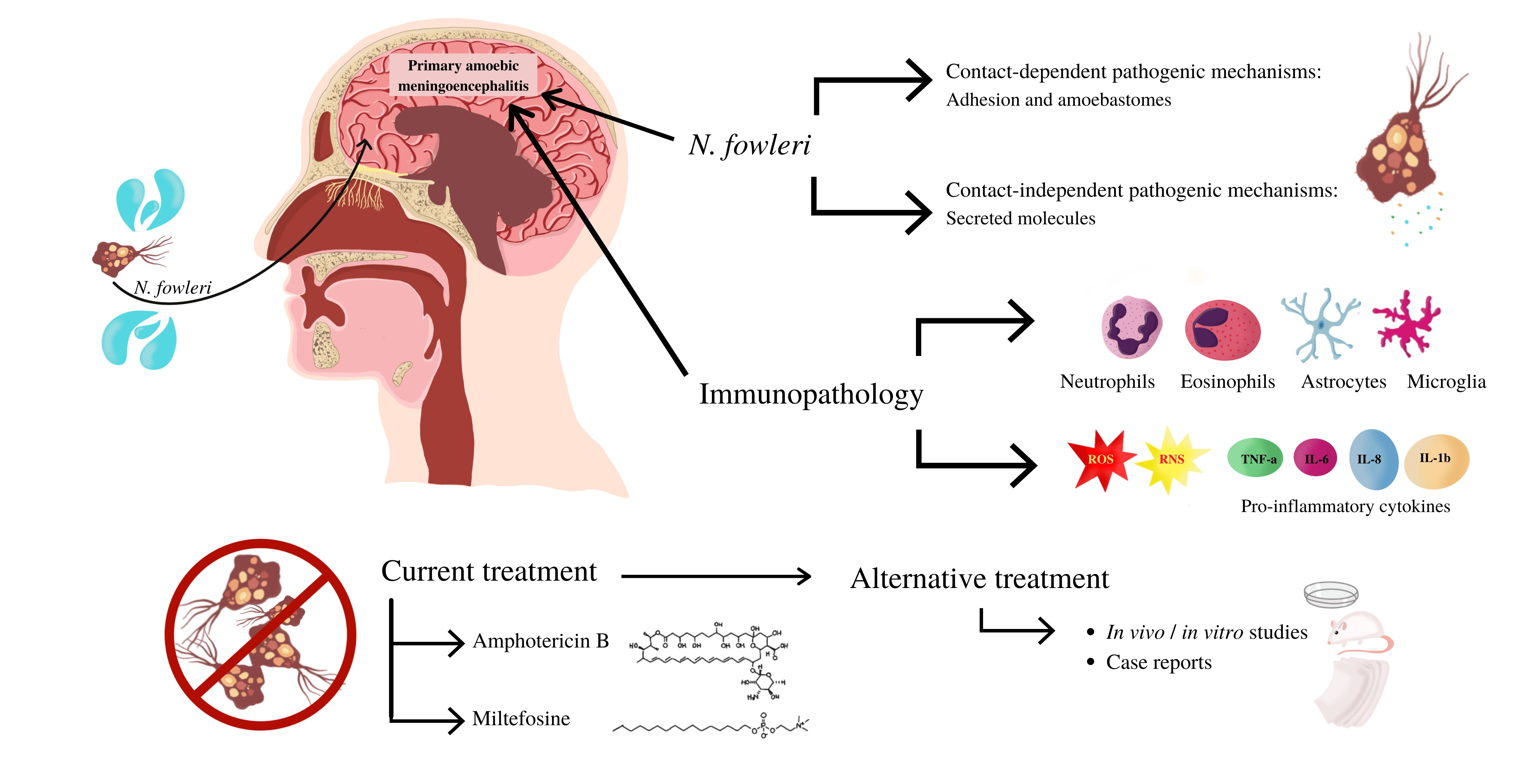
Primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare and deadly brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the "brain-eating amoeba."
This single-celled organism led to the tragic death of a five-year-old girl in Kozhikode, Kerala.
What is PAM?
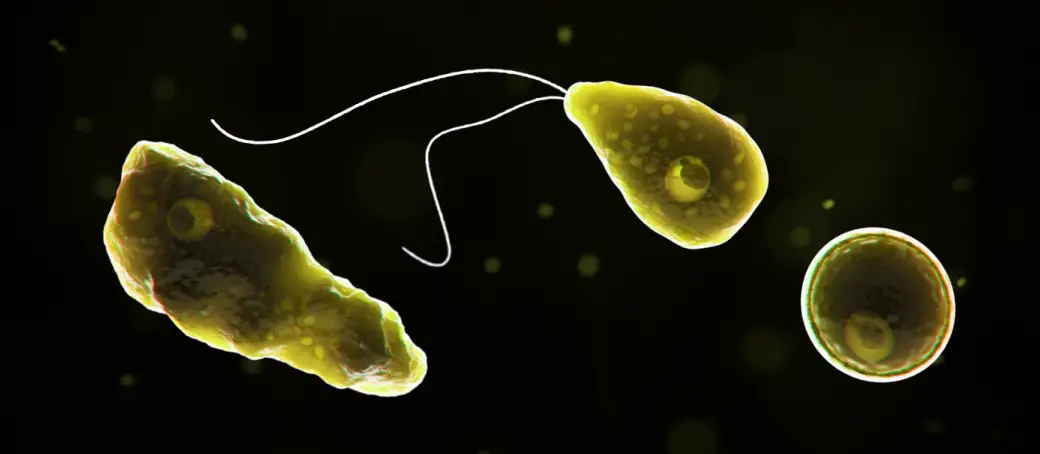
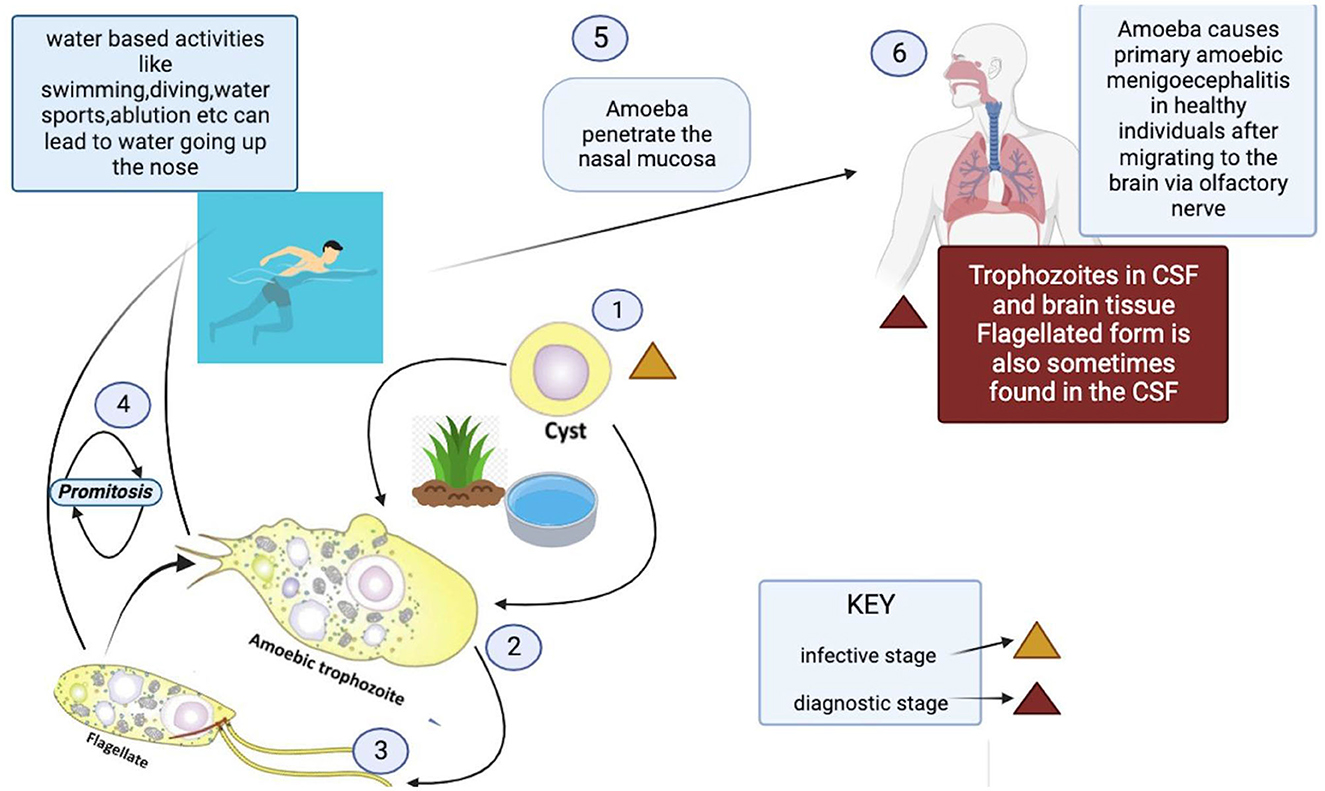
- PAM is an acute brain infection caused by Naegleria fowleri, a free-living amoeba found in warm freshwater and soil.
- It infects individuals when contaminated water enters the nose, travels to the brain, and destroys brain tissue, causing severe swelling.

Where is Naegleria fowleri Found?
- Warm freshwater bodies: lakes, rivers, hot springs.
- Poorly maintained swimming pools, splash pads, surf parks.
- Survives in water temperatures up to 115°F (46°C).

How Does Naegleria fowleri Infect People?
- Enters the body through the nose, typically during swimming.
- Travels to the brain, causing tissue destruction and inflammation.
- Not spread by drinking contaminated water or from person to person.
Symptoms
Initial Symptoms of Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis include:
- Headache
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Advanced Symptoms:
- Stiff neck
- Confusion
- Seizures
- Hallucinations
- Coma


Prognosis
- Rapid progression from initial symptoms to death, usually within 1 to 18 days.
- High fatality rate, often leading to coma and death within five days of symptom onset.
Treatment
Currently, there is no consistently effective treatment for PAM. Doctors use a combination of drugs:
- Amphotericin B
- Azithromycin
- Fluconazole
- Rifampin
- Miltefosine
- Dexamethasone
Past Incidents in India
- 20 reported cases of PAM in India.
- Kozhikode case is the seventh in Kerala.
- Notable cases in Alappuzha (2016, 2023), Malappuram, Thrissur.
- High incidence in Kerala likely due to numerous water bodies.
Conclusion
Naegleria fowleri, though rare, poses a serious risk in warm freshwater environments. Awareness, early detection, and stringent water safety measures are crucial to prevent future infections and fatalities.
Previous Post