Questions
- While digital financial services can expand financial inclusion in India, various challenges need to be addressed in this regard. Discuss. (150 words) 10
- India needs to accord more significance to nutritional security than food security. Comment. In this context, suggest a framework that should be adopted by the government to achieve nutritional self-reliance. (250 words) 15
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023
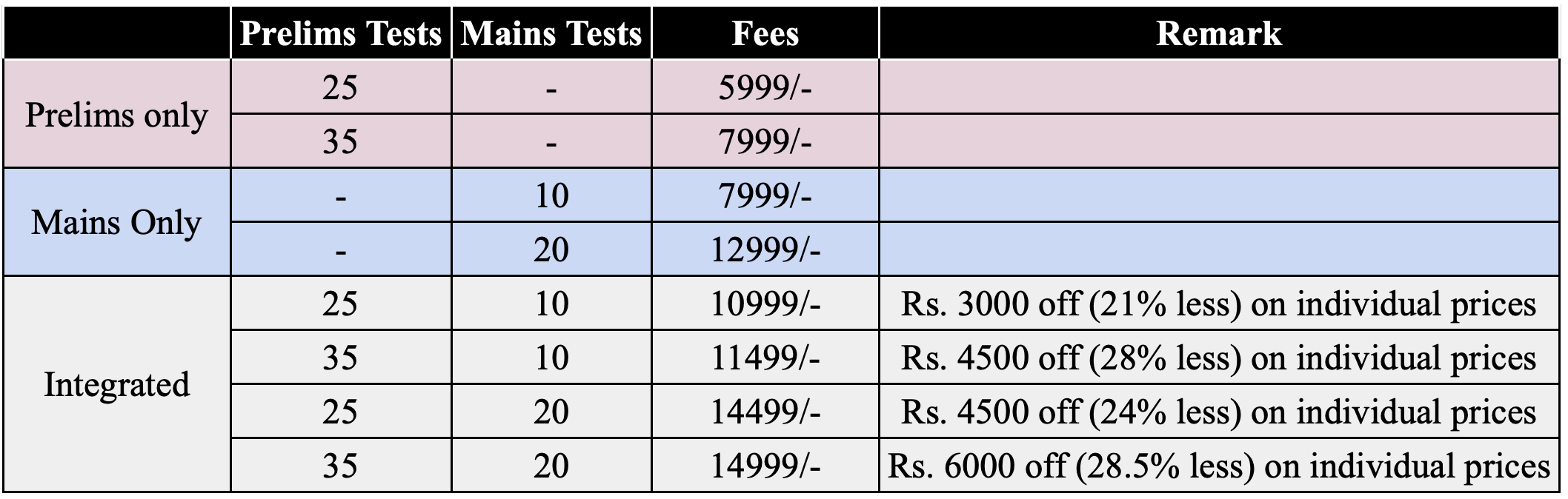
Model Solutions
1. While digital financial services can expand financial inclusion in India, various challenges need to be addressed in this regard. Discuss. (150 words) 10
Model Structure
Introduction:
- India has witnessed a fourfold increase in POS terminals between 2015-19, increase in the number of debit cards to 835 million in 2019, 600% increase in UPI user (2015-2021).
Main Body:
- Digital financial services can expand financial inclusion in India as it:
- Involves the deployment of digital means to reach currently financially excluded and underserved populations.
- Provide affordable, convenient and secure banking service to poor individuals.
- Deemed as a safer alternative as it can reduce the circulation of fake currency and also reduce risks of loss, theft etc. posed by cash-based transactions.
- Digital transactions are fast and quick.
- Check leakage and provide support to the intended beneficiary.
- Challenges associated:
- Digital divide: According to the ‘Indicators of Household Social Consumption on Education in India’ report, approximately 15% of rural households have an internet connection compared to around 42% urban households, increasing their chance of being excluded from digital financial inclusion programmes.
- Digital Illiteracy: Digital finance providers moving into lower income markets will face multiple challenges due to widespread financial and digital illiteracy.
- Lack of digital infrastructure: leads digital service providers withdrawing the provision of specific digital finance services to high-risk rural areas or communities.
- Lack of adequate regulatory framework: The regulation of payments and digital finance in India is a complex web of institutions and rule-setting bodies
- Fear of being brought into the tax net: mostly among small merchants and shopkeepers..
- Increased cyber security threats.
Conclusion:
- Proper regulatory and consumer protection frameworks should be developed to sustain the digital financial industry. Customer protection frameworks should also be strengthened. or
- Digital literacy should be disseminated widely under schemes such as Digital India, Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan etc. or
- More support for local level innovation can encourage entrepreneurs and institutions outside of metro cities to build digital products and services that respond to more regional or localised issues.
2. India needs to accord more significance to nutritional security than food security. Comment. In this context, suggest a framework that should be adopted by the government to achieve nutritional self-reliance. (250 words) 15
Model Structure
Introduction:
- Food security is defined as the availability and the access of food to all people; whereas nutrition security demands the intake of a wide range of foods which provides the essential needed nutrients.
Main body:
- Need to accord more significance to nutritional security than food security:
- Persistence of undernutrition:
- According to the Global Nutrition Report, 2020, 37.9% of children under 5 years of age are stunted and 20.8% are wasted.
- Under-nutrition is also prevalent in adults with 22.5% being underweight and 38% being stunted.
- Micronutrient deficiency:
- As per the National Family Health Survey 4, 58.6% of children, 53.2% of non-pregnant women and 50.4% of pregnant women were anaemic in 2016.
- The National Nutrition Survey revealed that zinc deficiency was found among 19% of preschool children and 32% of adolescents.
- Prevalence of deficiencies of Vitamin B12, Vitamin A and Vitamin D hovered between 14% to 31% for pre-school children to adolescents.
- Rising Obesity and prevalence of non-communicable diseases: According to the ‘Food and National Security Analysis, India, 2019’, the energy and protein intake from cereals has decreased in both rural and urban India, largely because of increased consumption of other food items such as milk and dairy products, oils and fat and relatively unhealthy food such as fast food, processed food and sugary beverages. This has led to rising obesity among adults and children.
- Increase in the burden of non-communicable diseases, around 5.8 million people die per year in India due to such preventable deaths.
Without nutrition security, it is not possible to achieve an active and healthy life for all. Moving from food security to achieving nutritional self-reliance will require a different strategy.
- Increase in the burden of non-communicable diseases, around 5.8 million people die per year in India due to such preventable deaths.
- Persistence of undernutrition:
- Framework to achieve nutritional self-reliance:
- Nutrition dimension should be mainstreamed into national missions like Food Security Act, National Health Mission etc.,
- With defined input and output parameters for monitoring.
- Various schemes that tackle malnutrition can be dovetailed under one authority to achieve better outcomes.
- Draw area production plans for animal husbandry and crop growth to meet nutritional requirements considering agro-ecological zones and the changing climate.
- Shift from incentivising production of few crops through MSP to encouraging production of pulses, oilseeds, poultry products etc. as well.
- Public distribution system should be further strengthened and the basket of commodities should be increased to include millets, pulses and oils.
- Increasing the quality of agricultural products through
- Increased expenditure on agriculture research.
- Stringent enforcement of regulations.
- Collaboration with the private sector.
- Extensive use of digital technologies.
- Raise fortified staples and micronutrient content in the food basket of the Mid-Day Meals.
- Serving nutritious breakfast to elementary school students should be a part of the scheme, as envisioned by the National Education Policy 2020 on a priority basis.
- Increase frequency of awareness campaigns such as ‘Eat Right India initiative’.
- Unhealthy food and drinks should be highly taxed and advertisements should be discouraged.
- To create an eco-system for collection and conversion of UCO(used cooking oil) into Biodiesel so that UCO is not used for edible purposes.
- Nutrition dimension should be mainstreamed into national missions like Food Security Act, National Health Mission etc.,
Conclusion:
- The National Nutrition Mission and Integrated Child Development Services are important measures taken by the government in this context. These should be complemented by large-scale expansion of food fortification programmes, equitable food distribution, proper maternal, infant and childcare practices, maintenance of adequate hygiene and sanitation etc.
Daily Answer Writing Initiative
Build your Mains muscles with daily answer writing practice.

