Table of contents
Concepts
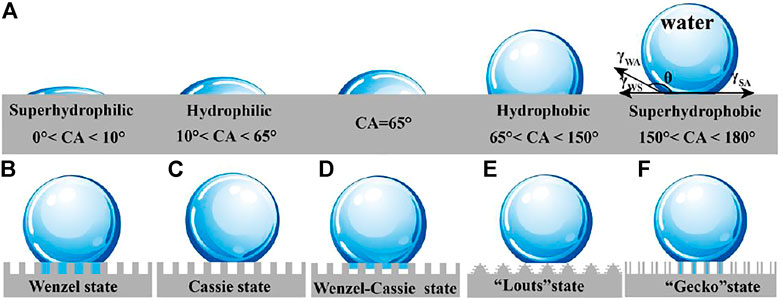
Superhydrophobicity
- Superhydrophobicity refers to the property of a surface that is extremely difficult to wet.
- Water droplets on a superhydrophobic surface will bead up and roll off, rather than spreading out.
- This is due to the surface having a very high contact angle with water, typically greater than 150 degrees.
Activated Carbon
- Activated carbon is a form of carbon processed to have small, low-volume pores that increase the surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.
- It is commonly used in water purification, air filtration, and as a catalyst support.

Superhydrophobic Activated Carbon Catalyst
- When activated carbon is modified to become superhydrophobic, it combines the high surface area and adsorption capabilities of activated carbon with the water-repellent properties of superhydrophobic materials.
- This combination can be particularly useful in catalytic processes where water presence can inhibit the reaction or where the catalyst needs to be protected from moisture.
Biodiesel Production

- Biodiesel is a renewable, biodegradable fuel made from a variety of feedstocks including vegetable oils, animal fats, and recycled cooking oils.
- The most common method of producing biodiesel is through a chemical process called transesterification, where triglycerides react with an alcohol (usually methanol) in the presence of a catalyst to form biodiesel and glycerol.
Catalysts in Biodiesel Production
Catalysts are crucial in the transesterification process as they speed up the reaction and improve yield. Traditionally, homogeneous catalysts like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH) are used. However, these catalysts have several drawbacks:
- They are corrosive.
- They require extensive purification steps.
- They generate waste products.

A Method for Cheaper Biodiesel Production
A team of scientists from India, China, and the U.K. has developed an innovative catalyst that significantly reduces the cost of producing environmentally friendly biodiesel.

- It is called Superhydrophobic Activated Carbon Catalyst.
What is this technology?
- Superhydrophobic Catalyst:
- Definition: The catalyst is described as "spherical superhydrophobic activated carbon," meaning it repels water, similar to surfaces like lotus leaves.
- Importance: The water-repellent properties prevent the poisoning of active sites by water during biodiesel production, ensuring the catalyst's effectiveness and longevity.

Cost Reduction
- Current Costs: The current cost of biodiesel in India is around ₹100 ($1.2) per liter.
- Projected Costs: Using this new catalyst can reduce the cost to about ₹30 (37 cents) per liter, making biodiesel more affordable and competitive with fossil fuels.
Production Efficiency
- Robustness: The catalyst can withstand the water by-product during biodiesel production, maintaining its activity and reusability over multiple cycles.
- Efficiency: This robustness and reusability make the biodiesel production process more efficient and cost-effective.
Environmental Impact
- Eco-Friendly: The catalyst is derived from biomass (cellulose), making it ecologically benign and abundant.
- Sustainable Energy: By lowering the production costs of biodiesel, the technology promotes the broader adoption of sustainable energy solutions.
Research and Development
- Techniques: Developed using methods like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to achieve superhydrophobic properties.
- Publication: The research has been published in the peer-reviewed journal "Advanced Functional Materials," highlighting its significance in the scientific community.
- Collaborators: The team includes scientists from the National Institute of Technology (NIT) in India, the University of Cambridge in the U.K., and Guizhou University in China.
Superhydrophobic Activated Carbon Catalysts
Advantages
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces purification needs and waste, lowering production costs.
- Efficiency: Better catalytic activity due to water-repellent properties.
- Environmental Impact: Uses renewable, non-toxic materials, reducing waste and environmental footprint.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Scalability: Developing large-scale production methods.
- Durability: Ensuring long-term stability and reusability.
- Feedstock Versatility: Testing effectiveness with various feedstocks.
Key Benefits
- Cost-Effective: Reduces biodiesel production costs significantly.
- High Efficiency: Ensures the catalyst remains effective and reusable.
- Environmentally Friendly: Uses biomass-derived, non-toxic materials.
- Sustainable: Encourages the use of renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
This breakthrough in biodiesel production technology represents a significant step towards making renewable energy more accessible and affordable, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future.
Previous Post