Topics of interest for CSE
- Population size, growth, composition, and distribution.
- Components of population growth: birth, death, migration.
- Population policy and family planning.
- Emerging issues: ageing, sex ratios, child and infant mortality, reproductive health.
DATA
Census Year | Population | Growth Rate |
1951 | 361,088,000 | - |
1961 | 439,235,000 | 21.6 |
1971 | 548,160,000 | 24.8 PEAK DECADE |
1981 | 683,329,000 | 24.7 PEAK DECADE |
1991 | 846,387,888 | 23.9 |
2001 | 1,028,737,436 | 21.5 |
2011 | 1,210,726,932 | 17.7 |
Period | Births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR | CDR | NC | TFR | IMR |
1995–2000 | 27,443,000 | 9,458,000 | 17,985,000 | 27.2 | 9.4 | 17.8 | 3.31 | 68.9 |
2000–2005 | 27,158,000 | 9,545,000 | 17,614,000 | 25.3 | 8.4 | 16.9 | 3.14 | 60.7 |
2005–2010 | 27,271,000 | 9,757,000 | 17,514,000 | 22.9 | 7.9 | 15.0 | 2.80 | 52.9 |
2010–2015 | - | - | - | 20.4 | 7.4 | 13.0 | 2.48 | 37.8 |
Crude Birth Rate (per 1000) | Crude Death Rate (per 1000) | Natural Change (per 1000) |
TFR is used instead of simple birth rates as it takes into account the size of the generational group. Avoids the Malthussian trap.
MIGRATION Stats: https://www.prsindia.org/theprsblog/migration-india-and-impact-lockdown-migrants
Targets: According to SDGs now.
- Achieve zero growth rate of population by 2045. (estimated peak at 2047 - 1.6 Bn)
- Achieve universal immunization of children against all vaccine preventable diseases. (Vaccines added for J-Encep, pneumonococcal conjugate vaccine and MR)
- Promote delayed marriage for girls, not before 18 and preferably after 20 years.
- Prevent and control communicable diseases.
- Universal access to information/counselling, and services for fertility regulation and contraception with a wide basket of choices.
- 80% institutional deliveries and 100% deliveries by trained persons. Taken up under the Janani Suraksha Yojana.
- Achieve 100% registration of births, marriage and pregnancy.
New Interventions under Family Planning Programme (2015 onwards)
- Scheme for home delivery of contraceptives by ASHAs at doorstep of beneficiaries.
- Scheme for ASHAs to ensure birth spacing. ASHAs to be incentivised for success.
- Emphasis on Post-Partum Family Planning (PPFP) services to capitalise on the cases coming in for institutional delivery under Janani Suraksha Yojana.
- Increasing male participation and promotion of Non Scalpel Vasectomy.
Problems:
- ASHA workers over stretched due to added responsibilities.
- Low ratio of ASHA workers to population they serve.
- Patriarchal society. Difficult for ASHA workers to communicate as mostly female.
EMERGING ISSUES IN POPULATION
Demographic dividend and transition
- Population estimated at 1350 million people in 2020. Current TFR - 2.1
- UNDP: India to peak at 1.6 billion in 2047 and decline to 1 billion by 2100.
- Lewis Turning point. When all surplus labour has been absorbed and further increase in employment would lead to a consequent rise in wages due to supply-demand based movement.
Ageing (MAPP-SU)
- Aging is a biological, psychological and socio-cultural phenomenon.
- 700% growth in senior citizens by 2050.
- In 2020 India's population would be 29. US/China 37, Japan 48.
- India's population is rapidly ageing. The numbers of people in 60+ age group jumped from ~7 crores in 2001 to more than 10 crores in 2011.
- In KA, TN, and GA aged (60+) outnumber the children below 6 as per census 2011.
- NSS surveys report that the number of 60+ women is higher than men at 1033 women per 1000 men. Feminisation of ageing. Trend in both rural & urban areas.
- 70% of these women dependents. Issues about their ill treatment and exploitation.
- With the decline of the institution of joint family old age care (geriatrics) is increasingly becoming a lucrative field of business.
Sex Ratios (MAPP-SU)
- National child sex ratio has gone down from 927 to 919 from 2001 to 2011.
- Currently stands at 899 females /1000 males as per SRS data in 2018.
- Major cause of the fall in sex ratio at birth is the female foeticide/infanticide.
- HR showing a decreasing trend in the population of women (2011).
- KL and PU have positive sex ratios while TN and AP are close to a balanced sex ratio.
- However, all states including KL & PU have adverse child sex ratios with HR again being the lowest at 834/1000.
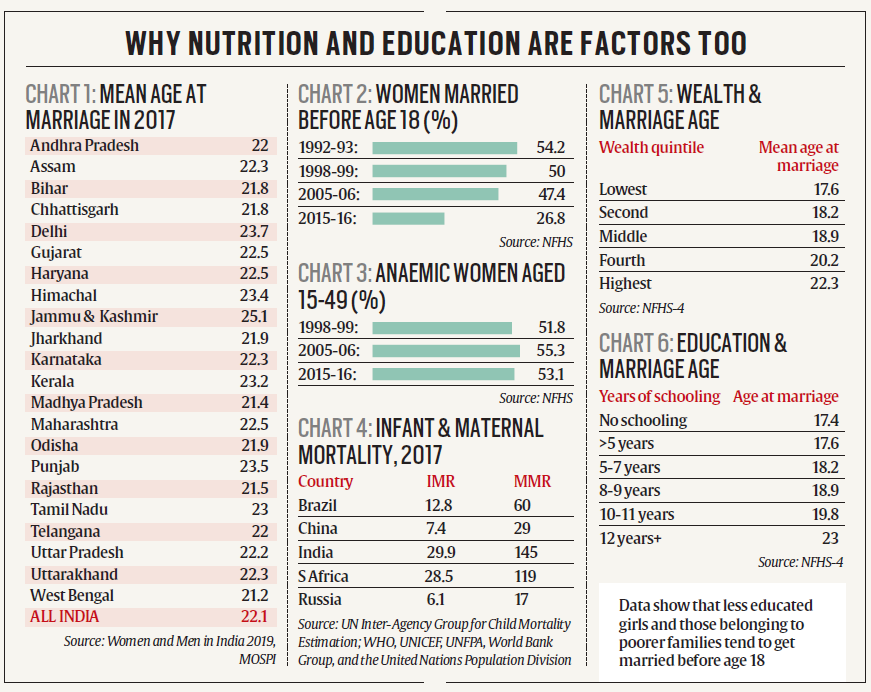
Child and IMR
- NFHS 5 data shows that under nutrition on the rise in India.
- Consistent decline in IMR and U5MR in India. Incremental rate of decline.
- Six states of India set to achieve the IMR and U5MR target of SDG4: TN, KR, MH, WB, PB, and HP.
- SDG target is 26 but India had an average IMR 37 with the lowest being in A&N Is at 10 and the highest being in MP at 51.
- Presence of several risk factors significantly associated with IMR and U5MR:
- Low levels of maternal education (less than class 8).
- Early childbearing (earlier than 20 yrs).
- Inadequate birth spacing (less than 24 months).
- Anemic pregnancies. 53% of all pregnant women anemic.
- Stagnation of early neonatal mortality in most of the states highlights the importance of improving quality of perinatal care for improving child survival.
- Eco Survey: Developmental support at birth has most impact on better future development.
- ICDS, MDM scheme should be strengthened.
Fertility Rates
- Mission Parivar Vikas launched in 145 High Focus districts for improved family planning services with focus on 7 states with highest TFR, to reach the replacement level fertility goals of 2.1 by 2025.
- The TFR in some states like GA and WB has fallen to nearly European levels.
- BH, RJ and UP (30 per cent of India’s population) are responsible for most growth.
- New Interventions under Family Planning Programme (2015 onwards)
- Scheme for home delivery of contraceptives by ASHAs.
- Scheme for ASHAs to ensure birht spacing. ASHAs to be incentivised.
- Emphasis on Post-Partum Family Planning (PPFP) services to capitalise on the huge cases coming in for institutional delivery under Janani Suraksha Yojana.
- Increasing male participation and promotion of Non Scalpel Vasectomy.