Questions
- Social Movements have been studied differently by different scholars. Examine. 20
- Marriage as an institution is losing its ground and people are in search of alternatives for the same. What, according to you, are the reasons for it?
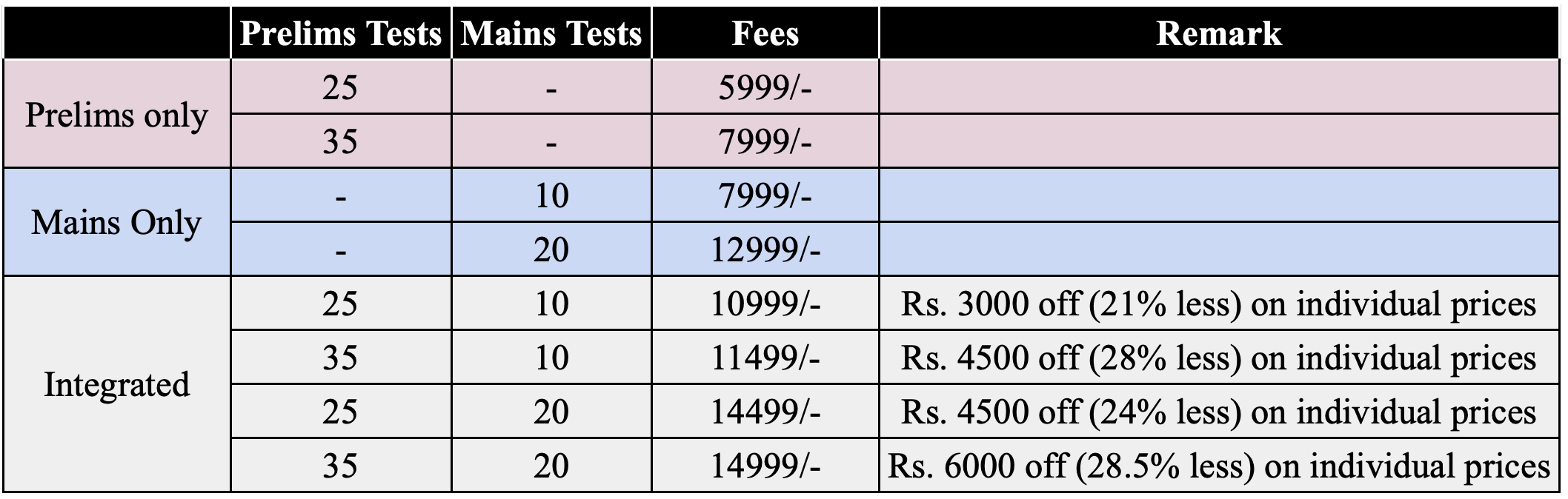
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023
Model Solutions
Q1. Social Movements have been studied differently by different scholars. Examine. 20
Model Structure
Introduction
- Social movements are defined as sustained collective action, aimed at bringing or resisting social change outside the sphere of established institutions.
- Requires sustained collective action. Collective action must be marked by some degree of organisation and also has a certain ideology.
Main Body
Various theories about the origin of social movements are discussed by few theorists:
- Structural Strain Theory :
- This theory, given by Neil Smelser, talks about factors that encourage social movement like structural conduciveness, structural strain, growth, and spread of a solution, precipitating factors, lack of social control, and mobilisation.
- Resource Mobilisation Theory:
- The theory was given by McCarthy and Zald. It explains movement success in terms of the ability to acquire resources and mobilise individuals.
- It further emphasises the importance of resources in social movement development and success. Resources are understood here to include: knowledge, money, media, labour, solidarity, legitimacy, and internal and external support from a power elite.
- It argues that social movements develop when individuals with grievances are able to mobilise sufficient resources to take action.
- The emphasis on resources is the reason why some discontented/deprived individuals are able to organise while others are not.
- Resource mobilisation theory also divides social movements according to their position among other social movements.
- Relative deprivation theory:
- The experience of being deprived of something to which one feels to be entitled is the genesis of it.
- It refers to the discontent felt by people when they compare their positions to those around them.
- Relative deprivation is a potential cause of social movements and deviance.
- Collective action theory:
- It is an action taken together by a group of people whose goal is to enhance their condition and achieve a common objective.
- Revitalisation theory:
- Wallace argues that though these movements express dissatisfaction and dissent against the system, they may offer positive alternatives.
- Status inconsistency theory:
- Broom and Lenski argued that discrepancy in status and ranking may lead to tensions and strife in society leading to discontent and protest.
Conclusion
- Thus, these theories of social movements help in understanding the causal factors and the journey of social movements until its dissolution or institutionalisation.
Q2. Marriage as an institution is losing its ground and people are in search of alternatives for the same. What, according to you, are the reasons for it? 10
Model Structure
Introduction
- According to Horton and Hunt, “Marriage is the approved social pattern, whereby two or more persons establish a family”.
- Family and marriage are considered to be the most basic and fundamental institutions in the subsystems of the society.
Main Body
- Family norms are undergoing certain changes in contemporary times and so is the case with marriages.
- Weiten observed the following threats to the institution of marriage
- Increasing acceptability of singlehood
- Increasing popularity of cohabitation
- Increasing rate of divorce.
- Along with these new forms like live-in relationships, contractual marriage etc are on rise.
- Many reasons for the rise of alternatives to marriage are discussed, out which few are mentioned below:
- Values attached to the institution of marriage have changed. Earlier marriage was considered a sacred institution and was mandatory for everyone, today, has given way to marriage being reduced to choice.
- Further, with the spread of rational education, globalisation and industrialization, people have become more broad minded which further weakened the institution. This has also led to reduction of backing to marriage by religion.
- Women's voice came to be heard due the rise of feminist movement. The violence which women suffered and the strains in the institution of marriage were known to everyone. This reduced the desirability of marriage among Youth gradually started getting aloof from marriages..
- The rise of individualism has led to an increase in conflict between couples.
- With the concept of equality gaining its ground, both partners have gained more aspirations, which further increases conflicts. The husband’s former role as leader, provider and protector is rapidly diminishing.
- Weakening of affinal bond; Husbands and wives may share a home, but not their lives. This is leading to a strained relationship between the partners.
- Reduction in stigma for divorce, has in return led to a high rate of divorce. This has led to reduction in stability of marriage, which was an important factor for people marrying.
Conclusion
- Though marriage as an institution has weakened due to certain factors, the argument that it is disintegrating is not true. Jennifer Somerville argues that changes in the institution of marriage have been exaggerated. Marriage as an institution has been affected to a limit as a result of its alternatives, but it cannot be said to be disintegrating.
