Questions
- Migration brings plethora of problems to the labourers, discuss the problems faced by them and suggest solutions. 10
- “The major function of education is the transmission of society’s norms and values.” Analyse this statement of Durkheim. 10
Model Solutions
Q1. Migration brings plethora of problems to the labourers, discuss the problems faced by them and suggest solutions. 10
Model Structure
Introduction
- Everett Lee defines migration as a permanent or semi permanent change of residence.
Main Body
Voluntary migration finds its genesis majorly in poor economic conditions. It impacts labourers in following ways:
- Basic necessity: labourers have to face problems to fulfil basic necessities. For example, PDS is denied to migrants in many states.
- Migration which results in absence of the adult males for a long period of time may cause the dislocation of the family.
- Social status: As the labourers have left their place of origin, they do not hold any social status at the new place.
- Sustainability in terms of jobs
- Children’s education is affected the most. As there is non availability of formal education institutes around the settlements of labours.
- Labourers, though migrate to run from poverty, fall into the vicious cycle of debt and expenses.
- Regionalism – they face various discrimination on the grounds of non nativeness. This creates strife and conflicts between individuals.
- Slum and deprivation: They are forced to live in unhygienic conditions due to non availability of proper infrastructure.
- Violence and harassment is faced by women migrant labourers. Men are no exceptions to the violence too. They are vulnerable to multiple forms of exploitation.
Solutions - All india registers can be created to keep a record of the labourers.
- Improving educational and health opportunities in the states facing issues of migration
- Skill development plans can be developed.
- Allocation of resources and land to the migrant settlement by state governments.
- Legislative measures.
Conclusion
- Migrant labourers face problems at their homes and at places away from homes. It is therefore necessary to take measures to maintain a safe and healthy work environment for them.
Q2. “The major function of education is the transmission of society’s norms and values.” Analyse this statement of Durkheim. 10
Model Structure
Introduction
- Education is a social institution through which a society's children are taught basic academic knowledge, learning skills, and cultural norms.
Main Body
- According to Durkheim, education is an agent of transmission of social norms.
- By respecting rules in schools, children learn to respect norms of the society.
- Family and peers fail to provide certain functions which are then performed by education.
- He argues that education helps in transmission of both general and specific values.
- According to Durkheim ‘Society can survive only if there exists among its members a sufficient degree of homogeneity: education perpetuates and reinforces this homogeneity by fixing in the child from the beginning the essential similarities which collective life demands’. Education instils a sense of social solidarity.
- Durkheim also argued that a crucial function for education in an advanced industrial economy is the teaching of specialised skills required for a complex division of labour.
- His functional views on education were also supported by the studies of Parsons. He argued that schools are societies in miniature. Child learns universalistic values which are necessary for social integration.
Functionality of education was criticised: - Pierre Bourdieu argues that modern education perpetuates inequality. As unequal chances of education means unequal opportunities.
- According to Marx, education promotes ruling class ideology.
Conclusion
- Education has recently developed as a means of economic development. Sally Tomlinson says that education should be a liberalising, humanising and democratising force.
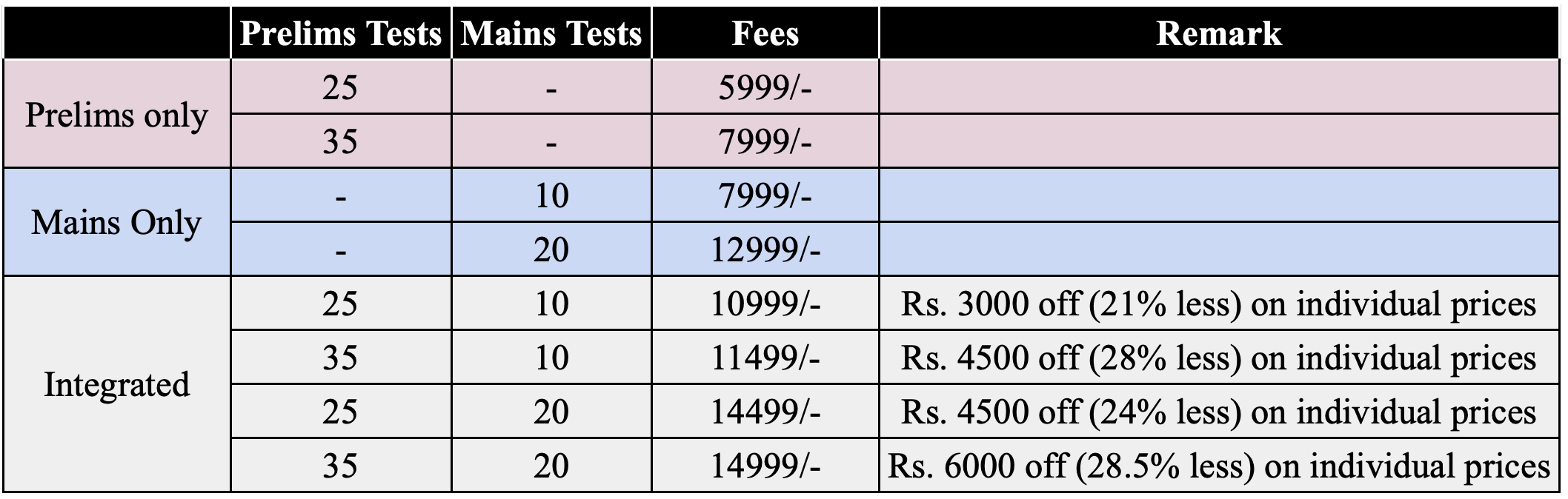
Integrated Prelims + Mains Test Series
For UPSC Prelims and Mains 2023