Questions
- Analyse the impact of legislation on marriage and inheritance in India. 10
- Explain the research of Human Relation School on the social organisation of the work. 10
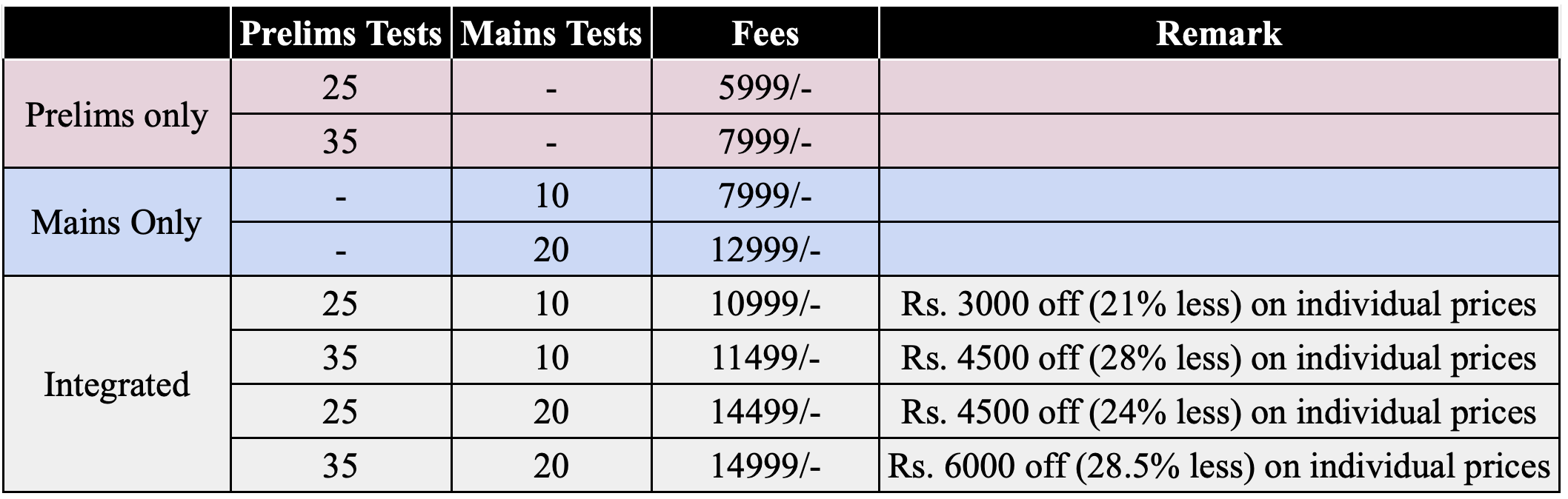
Courses for UPSC Prelims, Mains, Optional
Test Series courses live now.
1. Analyse the impact of legislation on marriage and inheritance in India. 10
Model Structure
Impact on marriages & divorces:
- The form of marriage changed from polygamous to monogamous because of legislations such as Hindu Marriage Act
- The 1869 Divorce Act and subsequent 2001 amendment made one of the grounds of divorce i.e., adultery more gender neutral
- With respect to Islamic personal laws, the recent Triple Talaq Act has made instant triple talaq illegal thereby enhancing security of Muslim women
- The age at marriage is impacted by legislations such as Child Marriage Act and Age of Consent Act (Current debate about raising minimum marriageable age of girls)
- Sati became obsolete because of legislative intervention
- Widow remarriage was promoted via Widow Remarriage Act enacted in the pre-independence era
- The provision of spousal maintenance after divorce came about because of legislations
- Special marriage act: provision for civil marriage irrespective of the religion or faith followed by either party → interfaith and inter-caste marriage
Impact on inheritance: - The Hindu Succession Act 1956 and subsequent 2005 amendment made the daughters equal coparceners. This resulted in improved bargaining power for Hindu women
- Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) has expanded the Hindu women’s right to be the coparcener (joint legal heir) and inherit ancestral property on terms equal to male heirs.
- The patrilineal systems of inheritances such as Mitakshara and Dayabhaga got supplanted with Bilineal inheritance systems
- Cardinality principle of inheritance also changed & all offspring are equal coparceners
Conclusion
- Demand for Uniform Civil Code (Art. 44) to ensure equal marriage, divorce and inheritance laws across different religions
2. Explain the research of Human Relation School on the social organisation of the work. 10
Model Framework:
Introduction:
- Research by Elton Mayo at the General Electric Company in Chicago which was named by him as a Hawthorne experiment concluded that group relationship and management worker communication is far more important in determining behaviour than physical condition.
Main body:
- Employee behaviour depends primarily on the social organisational circumstances of work. Leadership style, group cohesion and job satisfaction are major determinants.
- Employees work better if they are given tasks
- Standard set internally by working group influence more than by management
- Individual workers cannot be treated in isolation but to be seen as members of a group.
- Monetary incentives and good working conditions are less important than belonging to a group.
- Managers must be aware of the social needs of the employees and thus employees will collaborate with the official organisation rather than work against it.
- Criticism
- Study lacks scientific base
- Sample size was very small
- Employees were under observation might impact their behaviour
Conclusion:
- Human relations school approach and four sizes more on social conditions inside as well as outside the organisation
- Thus to establish emotional bonds with employees, today organisations arrange cultural festivals on lines of human relation schools suggestions.
Previous Post
