Table of contents
Radiometric Dating
- Recent studies revealed that Calcium-41 can be used in radiometric dating as Carbon-14 by a technique called Atom- Trap Trace Analysis.
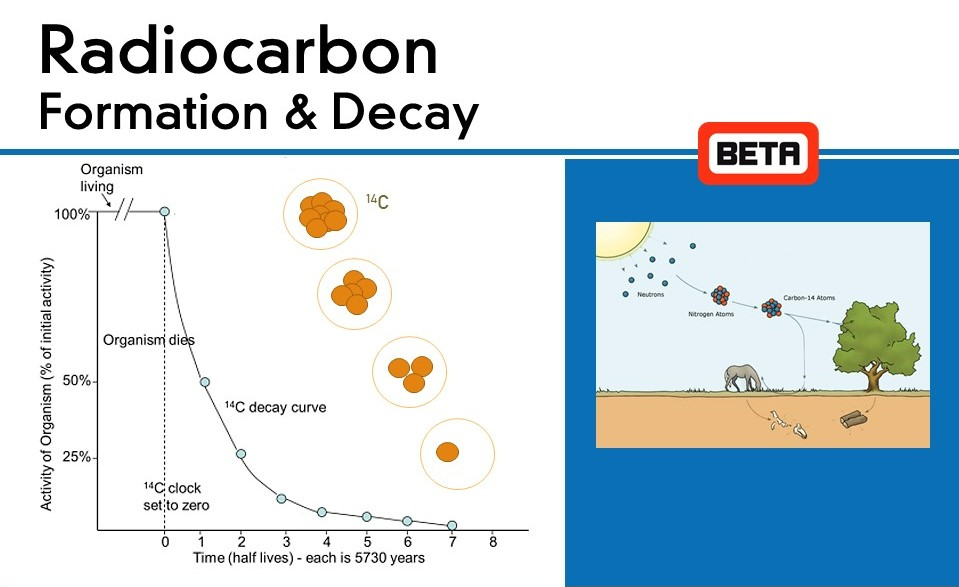
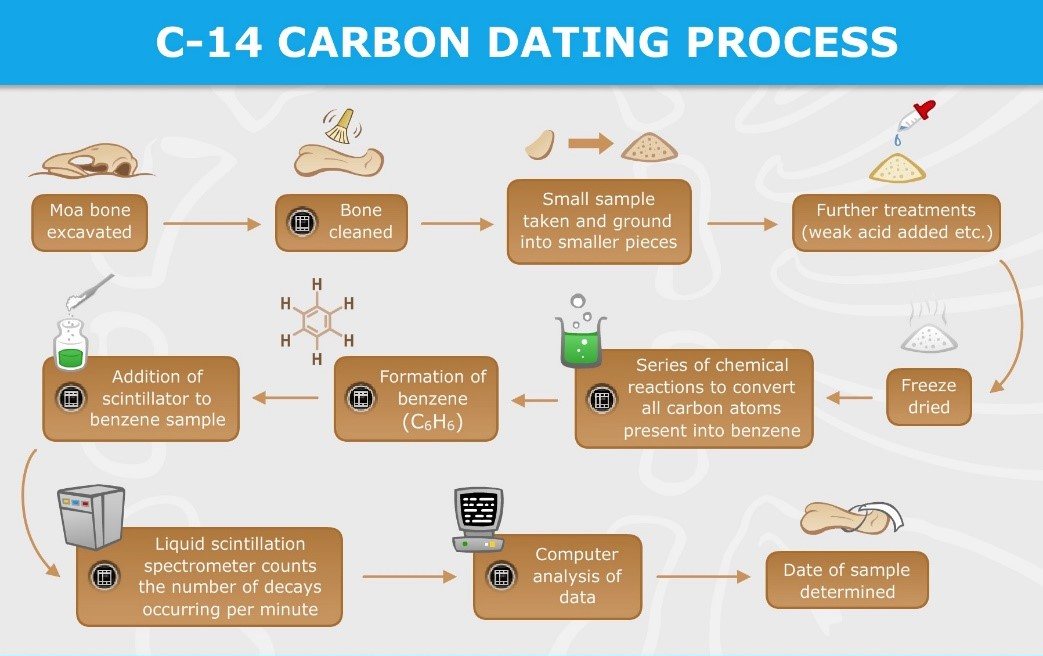
Radiometric dating is a method of finding out the age of something like a rock, or a fossil, which depends on radioactive isotopes like carbon-14, potassium- 14/argon-40 within that substance.
- The organic body keeps absorbing and losing carbon-14 atoms when it's alive and when it dies, it stops absorbing resulting in decay of carbon-14.
- The difference between the presence of these atoms and the number that should’ve been there, time of death can be found.
Gene-Drive Technology
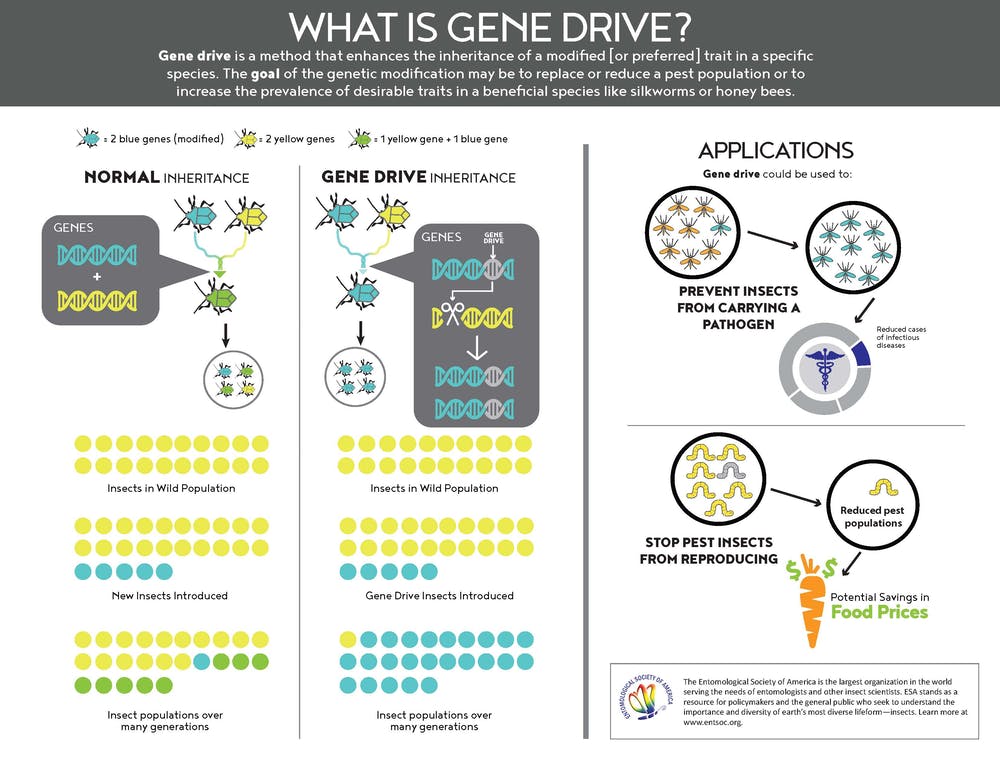
- Gene-drive Technology is a genetic engineering technique that alters genes to change patterns of how traits are passed from parents to offspring (Mendelian inheritance).
- Gene-drive Technology has applications like reduction in mosquito populations due to the production of sterile offspring.
- 3 Key Components of Gene Drive technology include:
- Gene
- Cas9 enzyme as a molecular scissor
- CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats).

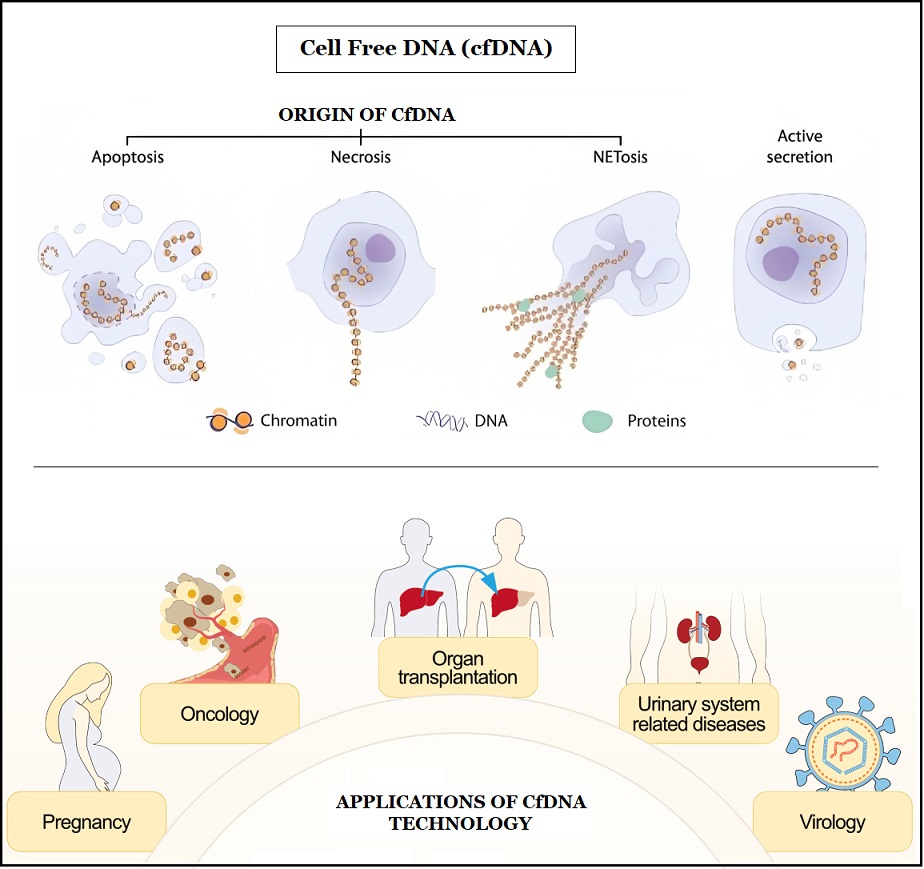
Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA)
- CfDNA are small fragments of nucleic acids released from cells in body fluids like plasma, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- Its quantity in the blood increases under pathological conditions such as cancer, auto-immune diseases etc.
- Its applications include-
- Early detection and treatment of cancers,
- Detecting genetic abnormalities in fetus
- As a biomarker.
- Monitor immune response after organ transplantation

NexCAR19
- NexCar19 (Actalycabtagene Autoleucel) is an indigenous CAR-T cell therapy approved by Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation.
- NexCar19 therapy is designed to target cancer cells that carry the CD19 protein, which is a biomarker for B lymphocytes.
A biomarker is a substance that provides information regarding a biological condition, process or treatment.
- The therapy targets B-cell lymphomas using genetically modified patient's T cells.
- Its advantages include single infusion treatment, high precision, and individualized treatment.
- But there are some challenges like proliferation of CAR T-cells leads to Cytokine Release Syndrome and there are chances of neurological Toxicity.

Tidal Locking
- Tidal locking involves a situation in which a planet in its orbit around a star keeps the same face towards the star because the rotation period of the planet around its own axis becomes equal to its revolution period around the star.
- One side is always facing a star while the other is in perpetual darkness on a tidally locked planet due to the gravitational force exerted by both the moon and the earth on each other.
- Because of tidal locking, only one side of the moon remains visible from the earth and the moon gets divided into two parts, during the ‘new moon’ phase-
- About 60% of the nearside of the moon is visible from Earth.
- The far side is never visible from the Earth.

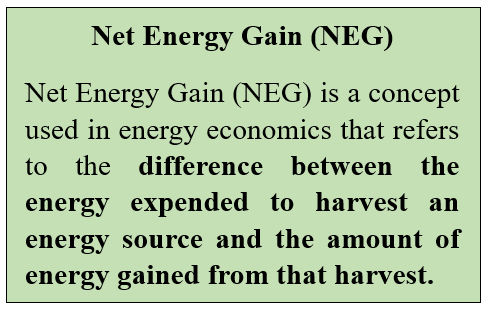
Net Energy Gain
- Net Energy Gain (NEG) is a term used in commercial fusion power which means that nuclear fusion processes generate more energy than it consumes.
- This is common in the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor project of which India is a part.
- India has also constructed its indigenous tokamak ADITYA and semi-indigenous Steady State Superconducting Tokamak (SST-1).

Giant Magnetoresistance
- Giant magnetoresistance is a property which is the result of electrical resistance of a conductor (sandwiched between two materials) affected by magnetic fields in adjacent materials.
- This is due to the fact that when materials are magnetized in same direction, electrical resistance in the conductor is low and vice-versa
- Graphene is an element which displays an anomalous giant magnetoresistance at room temperature.
- Applications of giant magnetoresistance include biosensors, automotive sensors, hard disk drives and magnetoresistive RAM in computers and medical imagers.
DEEP Project
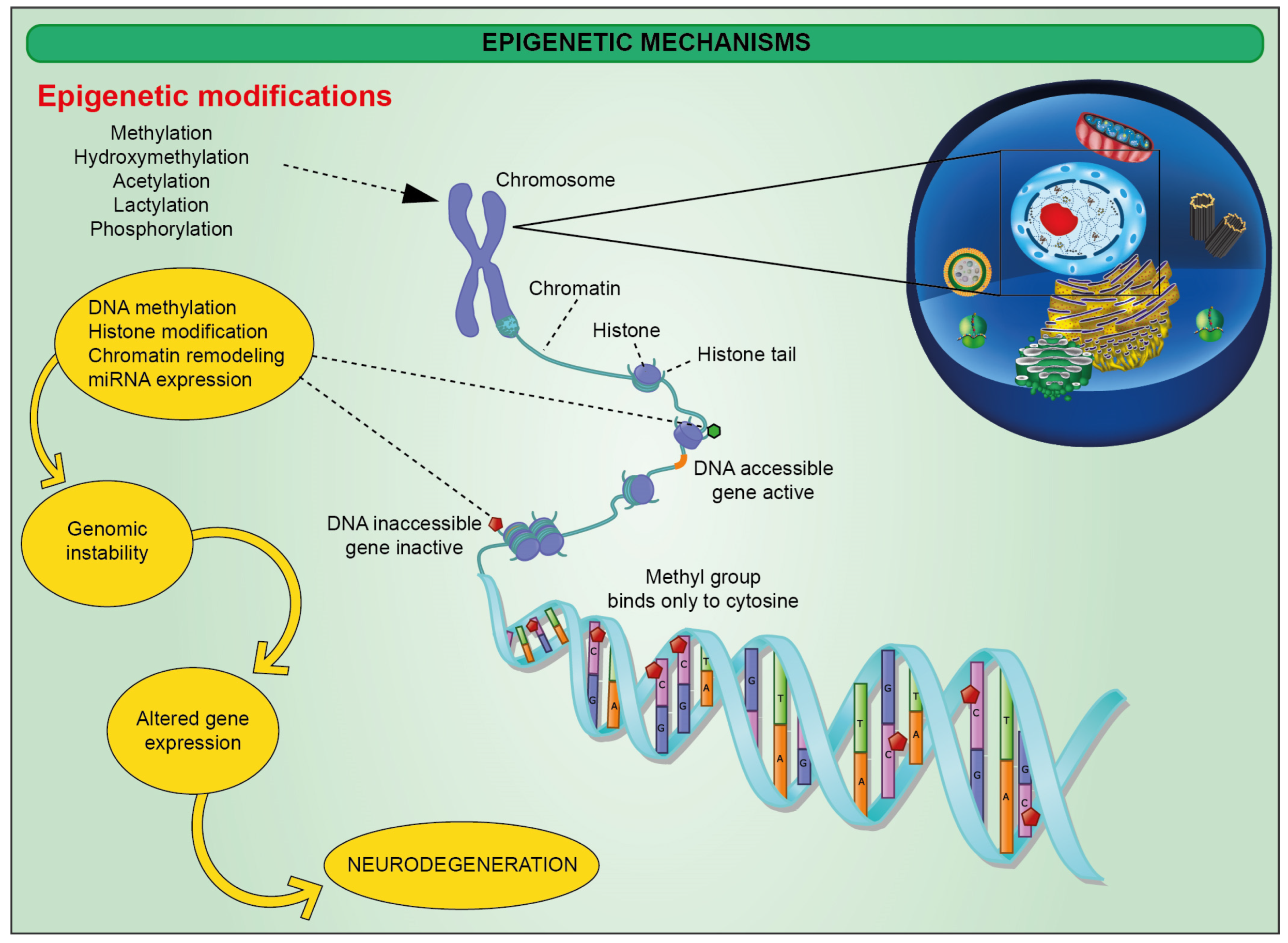
- Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology has collaborated with research groups on the five year Diverse Epigenetic Epidemiology Partnership (DEEP) project.
Epidemiology is the study of patterns and factors related to health and disease while epigenetics is the study of how behaviors and environment can cause changes that affect the way your genes work.
- Epigenetic changes are reversible unlike genetic changes and there is no change in the DNA sequence but they can change how the body reads a DNA sequence.
- DNA methylation is an example of epigenetic modification in which high DNA methylation leads to gene silencing.
- This is an important project because majority health research is mostly on people of white European origins and other communities are under-represented.