Table of contents
Let us look into a few dynasties from the early medieval Indian history which are important for Prelims 2024.
Here are few PYQs:


Pratiharas (8th-10th CE)
- The Pratiharas or Gurjara-Pratiharas ruled over western and northern India.
- Nagabhata-I was the founder but the most important king was Mihira Bhoja.
- They had an ongoing conflict with the Palas of eastern India and the Rashtrakutas of southern India.
- Nagabhata II defeated Pala king Dharmapala and fought Rashtrakuta king Govinda III.
- Mihira Bhoja was a devotee of Vishnu and adopted the title of Adivaraha. He built the Telika Temple located within the Gwalior Fort.
- Pratihara is derived from the Sanskrit word which means "doorkeeper".

The Palas (8th-11th CE)
- After the death of Harsha, the Pratiharas, Palas and Rashtrakutas were engaged in a tripartite struggle for the control of the Ganga–Yamuna doab.
- Pala empire was founded by Gopala and was one of the most powerful Buddhist imperial powers in the Indian subcontinent.
- Gopala founded the monastery at Odantapuri, which is India's second oldest Mahaviharas.
- Dharampala founded the Vikaramasila monastery in the Bhagalpur district and built Somapura Mahavihara in present-day Bangladesh.
- Next important ruler was Mahipal who checked the invasion of northern India by Rajendra Chola.
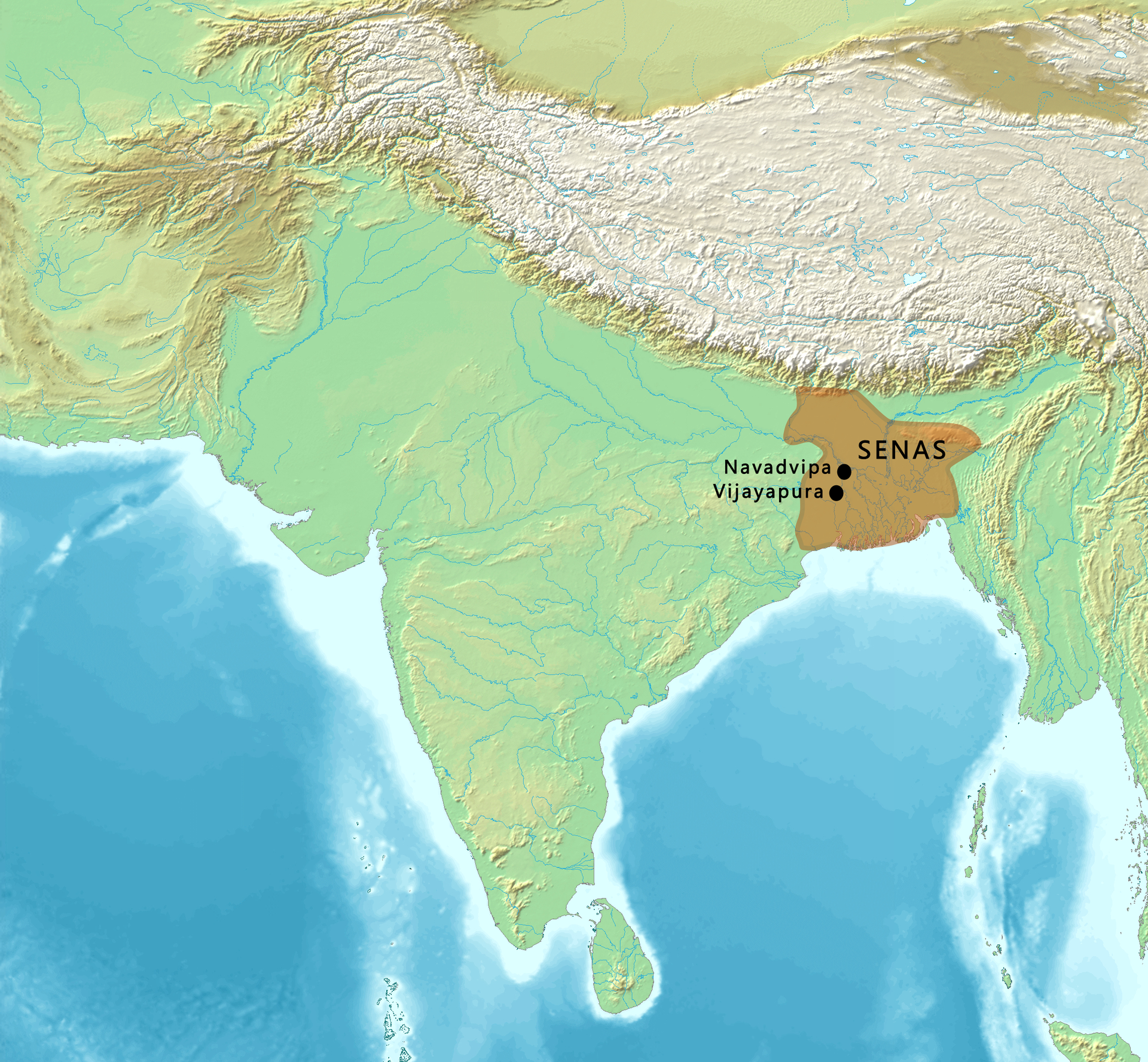
Sena Dynasty (11th-12th CE)
- The Sena dynasty rulers were devout Hindus who ruled the Indian subcontinent's northeast region.
- The dynasty was founded by Samantha Sen in southern India but his successor Vijaya Sena was the real founder in North East India.
- Deopara Prashasti commissioned by Lakshmana Sena described the Senas as migrant Brahmaksatriyas from Karnataka.
- Vijayasena defeated the last ruler of the Pala dynasty, Madanapala, and established the Sena dynasty.
- Next ruler was his son, Ballala Sena who introduced social reforms known as Kulinism in Bengal.
- He was succeeded by Lakshamanasena, the greatest ruler of this dynasty, who was finally defeated by Muhammad Bhaktiyar Khalji and the dynasty ended.

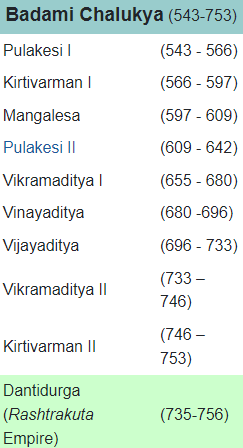
Chalukyas (6th-12th CE)
- After the downfall of the Gupta dynasty, Chalukyas rose to power.
- There are three closely related but individual Chalukyas dynasties.
- The Chalukyas of Badami were the successors of Vakatakas' in western Deccan.
- In the eastern Deccan, Eastern Chalukyas became independent after the death of Pulakesin II, with the capital at Vengi.
- The Western Chalukyas ruled from Basavakalyan after the fall of Rashtrakutas.
- It was the first time that a South Indian kingdom seized control of the entire region between the Kaveri and Narmada rivers.
- A new style of architecture called Vesara developed and Kannada literature was patronized.
- Also, Telugu literature under the patronage of the Eastern Chalukyas was developed.
- Sources include inscriptions like in Badami cave, Kappe Arabhatta record, Peddavaduguru inscription, Kanchi Kailasanatha inscription and Pattadakal Virupaksha Temple inscriptions.

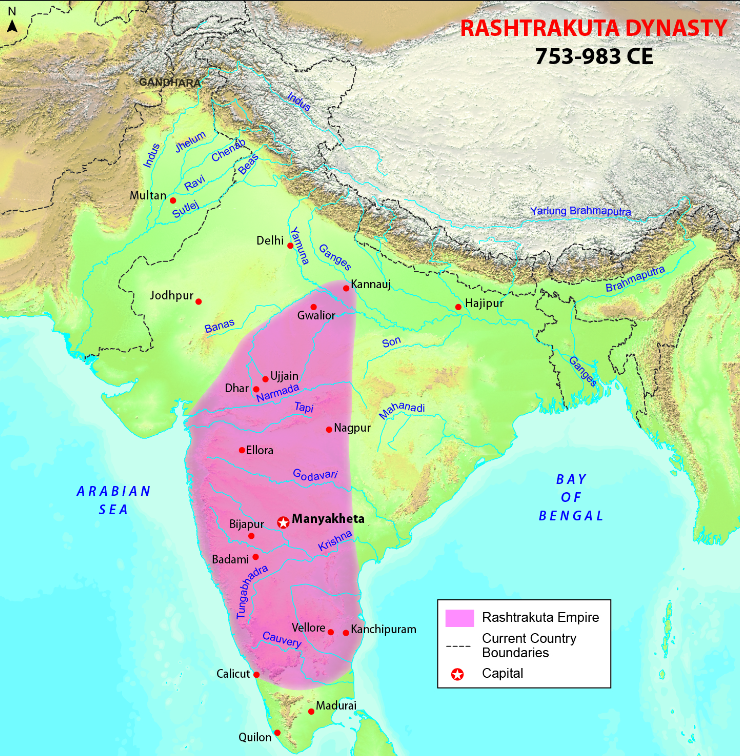
Rashtrakutas (750-900 CE)
- Dantivarman or Dantidurga was its founder with capital at Malkhed near Solapur, by overthrowing the Chalukyas.
- Krishna I was the greatest ruler who defeated the Pallavas and established dominance over parts of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- He started the art of sculpting and built the largest rock-cut Hindu structure at Ellora.
- Amoghvarsha was the next greatest ruler who contributed to Literature by writing Kavirajamarga and Prasnottara Malika.
- Next ruler was Indra III who was called the greatest Indian King by Al Masudi.
- Krishna III fought against Paramaras of Malwa, eastern Chalukya of Vengi and Cholas of Tanjore.
- He patronized poets Pampa and Ponna who were called Ratnatraya along with Ranna.
Cheras (9th-12th CE)
- The Cheras were a Dravidian sovereign dynasty who ruled in two periods. The early Chera between the 4th and 5th centuries BC and the Later Chera (Kulasekharas) between 8th and 12th centuries AD.
- The Cheras were one of the three major powers of ancient Tamilakam, alongside the Cholas of Uraiyur and the Pandyas of Madurai.
- Also referred to as 'Keraputras,’ Uthiyan Cheralathan was the founder and is mentioned in Sangam literature.
- The later Cheras were dominated by the Kulasekhara Dynasty with Mahodayapuram or Kodungallur as their capital, under whom Vaishnavism spread.
- The Kollam Era (a Malayalam calendar system) was initiated by Kulasekhara Cheras which marked the foundation of Kollam city.
