Table of contents
The Indian banking sector serves as the backbone of the nation's financial system. Its stability and efficiency are paramount for fostering economic growth and development.
However, the banking sector has undergone significant transformations over the years to adapt to evolving economic landscapes and address emerging challenges. Here is a gist:
First Narasimham Committee Report – 1991
- It was formed to find out ways to ensure healthy development of the financial sector.
- The recommendations include-
- Establishing a 4 tiered bank hierarchy with 3 to 4 large banks at the top.
- Phased reduction in statutory liquidity ratio and 8% capital adequacy ratio.
- Responsibility of supervisory functions over financial institutions be assigned to an RBI sponsored quasi-autonomous body.
- Deregulation of Interest rates.
- Standardized classification of assets and full disclosure of accounts of banks and financial institutions.
- Setting up an Asset Reconstruction fund to take over unrecorded loan portfolios of banks.

Second Narasimham Committee Report – 1998
- Government appointed another committee under Mr Narsimham in 1998 to review the banking reform progress and recommend for more strengthening of the financial system.
- The focus was on areas such as capital adequacy, bank mergers, bank legislation, etc.
- The recommendations include-
- The committee suggested better domestic liquidity and exchange rate management for a stronger banking system and Current Account Convertibility.
- For this, it suggested merger of strong banks for ‘multiplier effect’.
- For a strong banking system, raising of the prescribed capital adequacy norms was suggested.
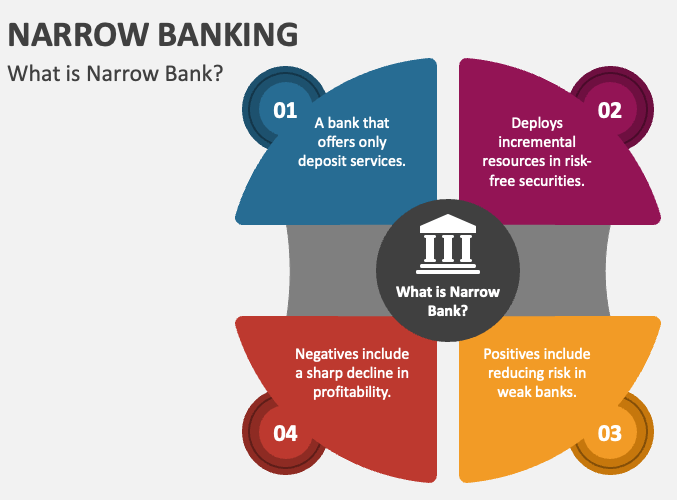
- Another suggestion was ‘Narrow Banking’ for rehabilitation of banks having high Non-performing assets by allowing banks to place their funds only in the short term and risk-free assets.
- Additional recommendations include technology upgrade, computerization, staff training, depoliticizing of banks, professionalism etc.
- The committee suggested reviewing and amending banking laws like the RBI Act, State Bank of India Act, Banking Regulation Act, Bank Nationalization Act, etc to align with the banking sector's present needs.


Nachiket Mor Committee
- Also known as the Committee on Comprehensive Financial Services for Small Businesses and Low-Income Households.
- Its main aim was framing a clear and detailed vision for financial inclusion and financial deepening.
- The Committee outlined six vision statements for full financial inclusion:
- Access to payment services and deposit services at a reasonable cost.
- Access to affordable formal credit.
- Universal Electronic Bank Account above the age of 18.
- Universal access to a range of deposit and investment products.
- Universal access to a range of insurance and risk management products.
- Right to suitability i.e low income households have the right to be offered suitable financial service.
P J Nayak Committee
- Also known as the Committee to Review Governance of Boards of Banks in India, it was established by the RBI in 2014.
- It reviewed the regulatory compliance requirements of banks' boards of directors.
- Another objective was to investigate the board representation in banks, board's compensation, combination of skills and the independence to govern.
- The strategy, governance, growth, and risk management of banks' boards was examined.
- To investigate any additional issues with regard to operation and governance like conflict of interest.
Bimal Jalan Committee
- Formally called the “Expert Committee to Review the Extant Economic Capital Framework of the RBI”, its recommendations are -
- It proposed Expected Shortfall methodology under stressed conditions instead of extant Stressed-Value at Risk for measuring the RBI’s market risk to ensure risk provisioning for market risk.
- It pointed out a clear distinction between the two components of RBI’s economic capital (realized equity and revaluation balances).
- Surplus distribution policy was recommended to be maintained by the RBI and only if realized equity is above its requirement, it can be transferred to the Government.
- The committee recommended maintaining a Contingent Risk Buffer within a range of 6.5 % to 5.5 % of the RBI’s balance sheet.
- Periodic review of RBI’s economic capital framework after every five years was recommended.
Enhanced Access & Service Excellence
- These reforms aimed at expanding the portfolio of Regional Rural banks (RRBs) by adding new segments.
- This expansion can be done by asking Rural banks to look beyond crop loans in areas like loans for tractors, housing, small businesses and education loans.
- The plan is to improve the profitability of RRBs.
- There is a proposal to raise the guarantee limit for education loans from Rs 7.5 lakh to Rs 10 lakh for more lending activity.
- The impact was visible in a consolidated net profit of Rs 1,682 crore in FY21, with 30 out of 43 RRBs reporting net profits, after two consecutive years of losses during covid.
- It was followed by EASE 2.0 which aimed at introducing reform action points across six themes like-
- Customer Responsiveness.
- Credit Off-take.
- Responsible Banking.
- Financial Inclusion & Digitalisation.
- PSBs as UdyamiMitra (SIDBI portal for credit management of MSMEs).
- Governance and HR.
- Then, EASE 3.0 was released to enhance ease of banking in all customer experiences by using technology. Themes include-
- Partnerships with FinTechs and E-commerce companies.
- Dial-a-loan and PSBloansin59 minutes.com.
- Tech-enabled agriculture lending.
- Credit at a click.
- EASE Banking Outlets.
- After this, EASE 4.0 was launched with a reform agenda for PSBs by institutionalizing clean and smart banking. Main themes include-
- Focus on North-East.
- Bad Bank.
- 24x7 Banking.
- Export Promotion.
- Leveraging the Fintech Sector.
- Latest EASE 5.0 reforms are aimed at-
- Invest in cutting technologies to further the reforms and respond to evolving competition, customer needs and the technology environment.
- Digital customer experience is at the center by promoting integrated and inclusive banking.
- The initiatives will be focussed on profitability, risk, business growth, customer service, operations and capability building.

