Table of contents
What is CAR-T Cell Therapy?
CAR-T cell therapy, short for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell therapy, is a powerful form of immunotherapy for certain cancers.
- It is a type of immunotherapy that involves the engineering of a patient's immune system (T cells - genetically modified in a laboratory) to attack cancer cells.
Here's a breakdown of the process:
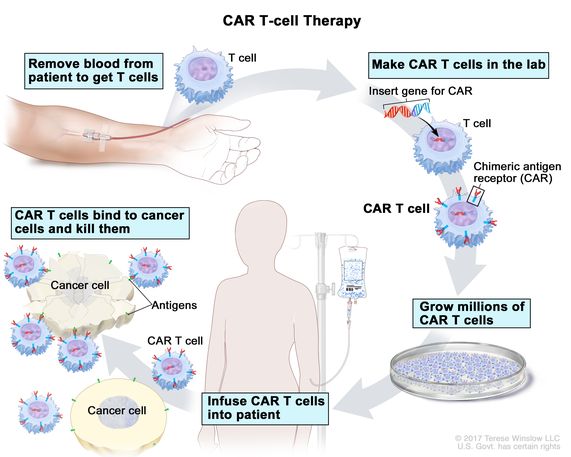
- T cell extraction: Doctors first draw blood from the patient to collect T cells, a type of white blood cell that fights infections.
- Genetic modification: In a lab setting, scientists genetically modify the extracted T cells. They equip them with a special receptor called CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor). Think of CAR as a GPS that helps T cells recognize specific proteins (antigens) on the surface of cancer cells.
- T cell expansion: Once equipped with the CAR, the T cells are multiplied in millions in a controlled laboratory environment.
- Reinfusion: The engineered T cells are then infused back into the patient's bloodstream. These supercharged T cells, now programmed to identify and target cancer cells, can launch a targeted attack on the tumor.
Points to remember about CAR-T cell therapy:
- It's a personalized therapy - the treatment uses a patient's own modified T cells to fight cancer.
- It targets specific cancers - CAR-T cell therapy is currently approved for certain types of blood cancers, like leukemia and lymphoma.
- It's a developing field - While CAR-T therapy shows promise, it's a relatively new treatment and research is ongoing to improve its effectiveness and reduce side effects.
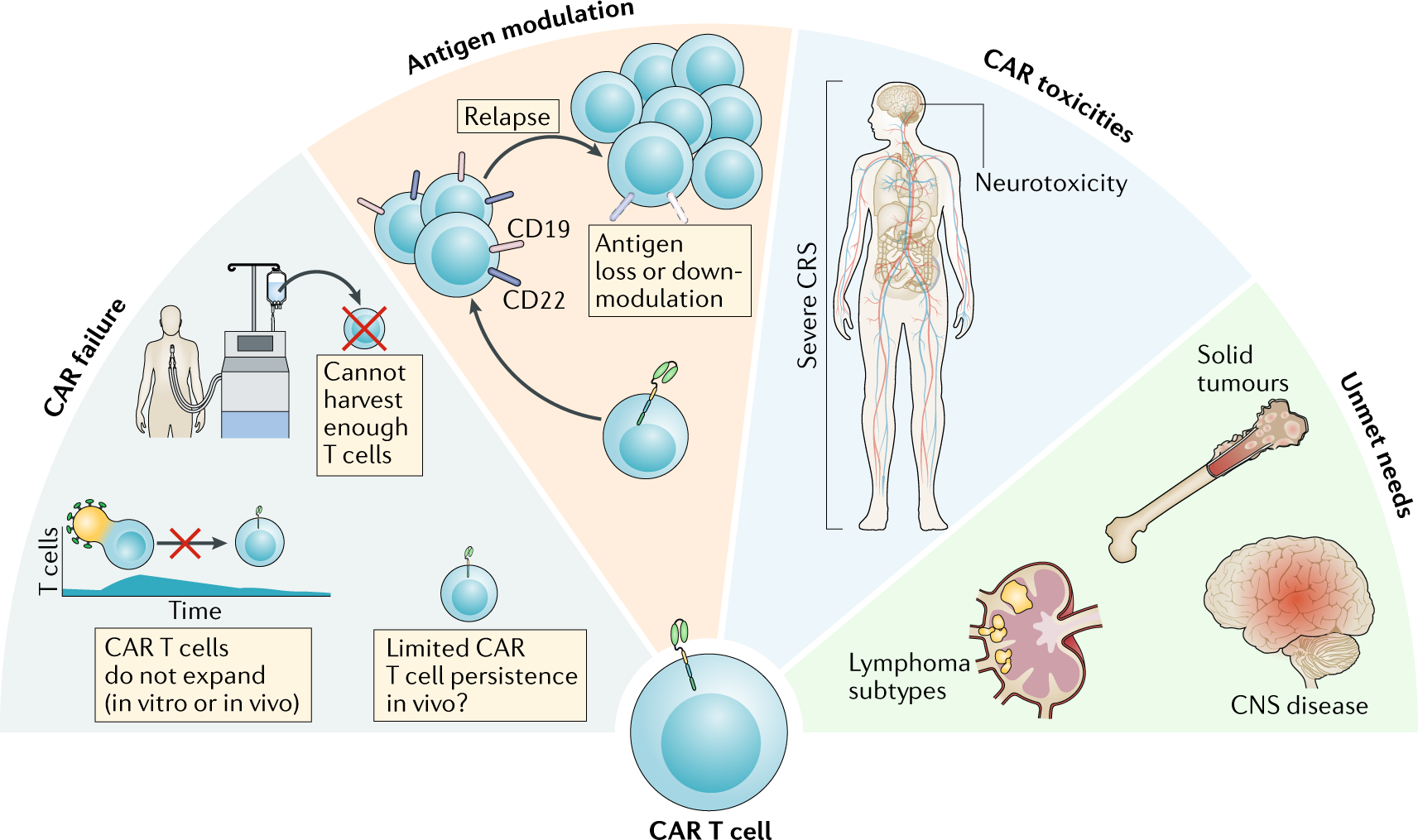
Challenges of CAR-T Cell Therapy
We can't clear UPSC for you.
But with our personalised mentor support, you'll be ready to do it yourself.
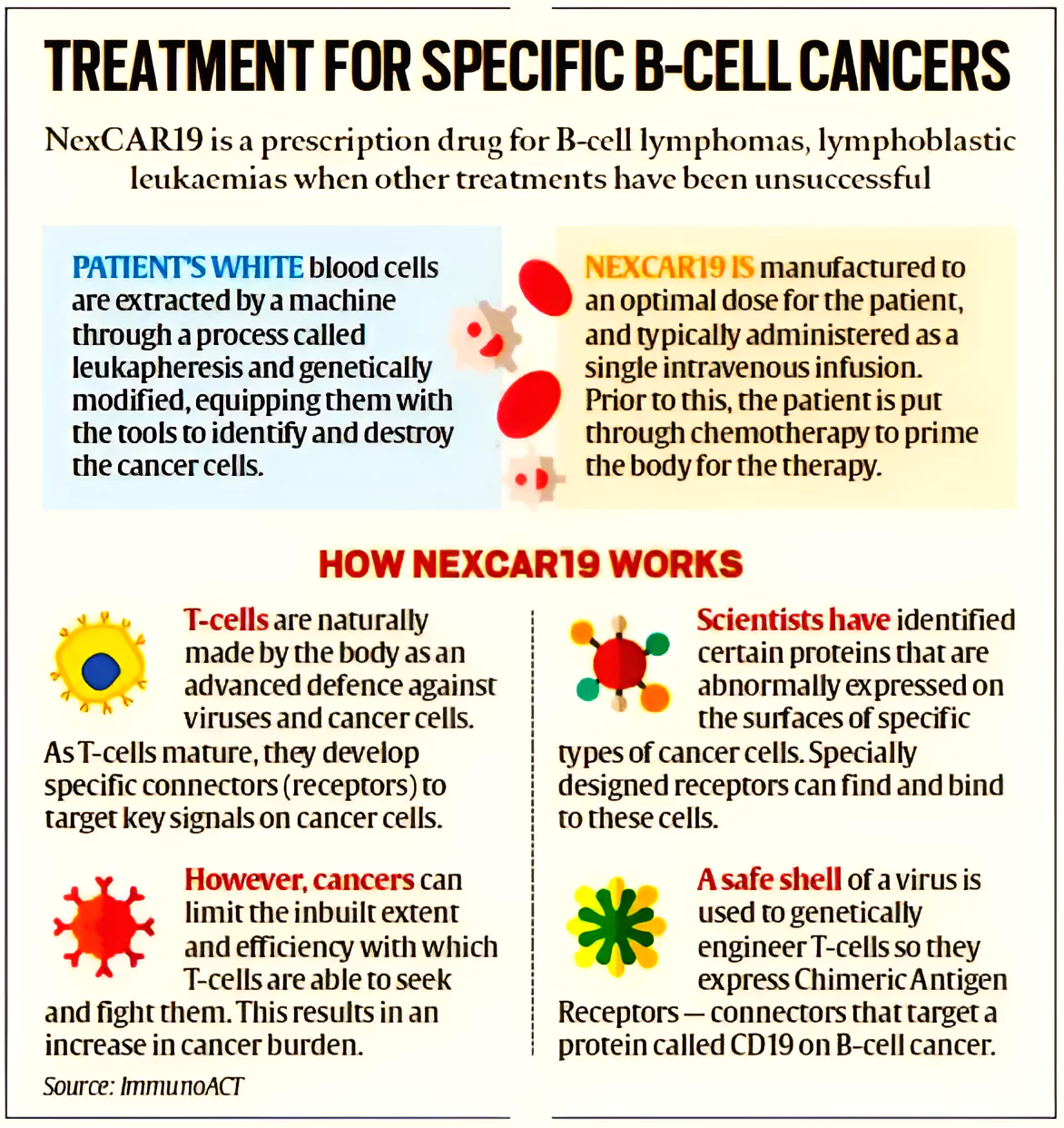
What is NexCAR19?
NexCAR19 is a CAR-T cell therapy developed in India that is more affordable than similar treatments from the US.
- It is designed to treat relapsed or refractory B-lymphomas and B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL).
The story of NexCAR19 is one of perseverance and collaboration.
Advantages of NexCAR19
NexCAR19 is a game-changer for several reasons:
- Effectiveness: Approximately 70% of patients respond to NexCAR19 treatment, with some achieving complete remission.
- Unique Feature: Lab and animal studies indicate lower drug-related toxicities, including reduced neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS).
- NexCAR19 uses a "humanized" CAR, potentially reducing the side effects often associated with CAR-T therapy.
- Affordability: Existing CAR-T therapies are exorbitantly priced. NexCAR19, however, is significantly cheaper, making it a more realistic option for many patients in India.
- Hope for aggressive cancers: NexCAR19 targets relapsed or refractory B-cell lymphomas and B-ALL, offering renewed hope for patients who haven't responded to conventional treatments.
Trials for paediatric patients are underway at Tata Memorial Hospital, ensuring broader applicability.
Challenges of NexCAR19
- Cost remains a hurdle: While more affordable than other options, NexCAR19 is still a relatively expensive treatment.
- ImmunoACT is in the process of securing licenses and partnering with hospitals, including Tata Memorial, Nanavati, Fortis, and Jaslok, across multiple cities.
- Initially priced at Rs 30-40 lakh, ImmunoACT aims to eventually reduce the cost to Rs 10-20 lakh, making the therapy more accessible.
- Side effects: CAR-T therapy, including NexCAR19, can cause side effects. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), an inflammatory response, is a common one.
- Limited access: Specialized medical facilities are crucial for managing potential side effects of CAR-T therapy. Access to such facilities remains a challenge in some parts of India.
- Early stage: NexCAR19 is a relatively new treatment. More research is needed to determine its long-term efficacy and explore further cost-reduction methods.
NexCAR19 represents a significant breakthrough in India's fight against cancer. It offers a promising, potentially life-saving treatment option for patients battling aggressive B-cell malignancies. However, improving affordability, ensuring wider access to specialized care, and conducting further research are crucial steps for maximizing its impact.
Previous Post