Table of contents
Introduction
The National Testing Agency (NTA) is an autonomous and self-sustained premier testing organization established by the Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India. It was created to conduct entrance examinations for higher educational institutions in India, ensuring standardized and transparent testing processes.
Establishment and Purpose
- Union Budget Announcement (2017-18): The proposal for the establishment of the National Testing Agency was announced in the Union Budget 2017-18 by the Finance Minister of India. This marked the beginning of the conceptualization and formation of the NTA.
- Approval by the Union Cabinet: The Union Cabinet approved the establishment of the NTA as an autonomous and self-sustained premier testing organization to conduct entrance examinations for higher educational institutions.
Administrative Framework
- Ministry of Education (formerly Ministry of Human Resource Development): The NTA operates under the Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education. It functions as a society registered under the Indian Societies Registration Act, 1860.
Articles and Regulations
- Article 246: Under this article, the Parliament has the power to make laws concerning any of the matters enumerated in List I (Union List) in the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution, which includes education.
- Article 265: This article ensures that no tax shall be levied or collected except by the authority of law, which indirectly impacts the funding and financial regulations of autonomous bodies like the NTA.
- Societies Registration Act, 1860: The NTA is registered under this act, which provides the legal framework for the registration and functioning of societies in India.
- Central Educational Institutions (Reservation in Admission) Act, 2006: This act, which mandates reservations in admissions to central educational institutions, also impacts the examination and admission processes managed by the NTA.
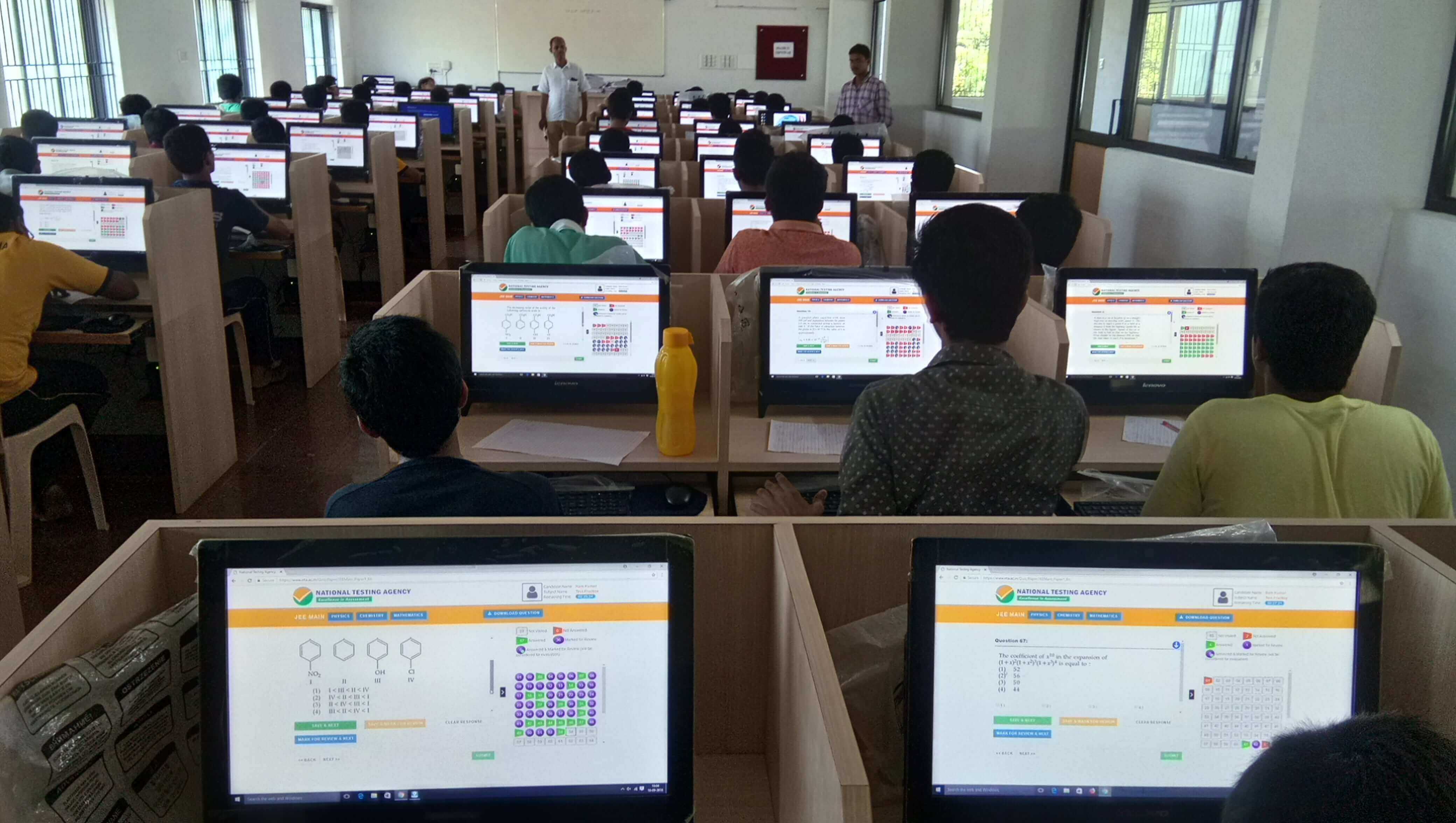

Objectives of NTA
- Standardized Testing: To provide a single, standardized platform for conducting entrance exams.
- Efficiency and Transparency: To ensure efficient, transparent, and error-free examination processes.
- Research and Development: To conduct research on educational testing and assessment.
- Capacity Building: To build capacities of educational institutions in India for conducting online and offline exams.

Key Examinations Conducted by NTA
- Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) Main: For admission to undergraduate engineering programs.
- National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET): For admission to undergraduate medical programs.
- Common Management Admission Test (CMAT): For admission to management programs.
- Graduate Pharmacy Aptitude Test (GPAT): For admission to pharmacy programs.
- University Grants Commission-National Eligibility Test (UGC-NET): For determining eligibility for college and university level lectureship and for the award of Junior Research Fellowship (JRF).
Recent Issues and Allegations
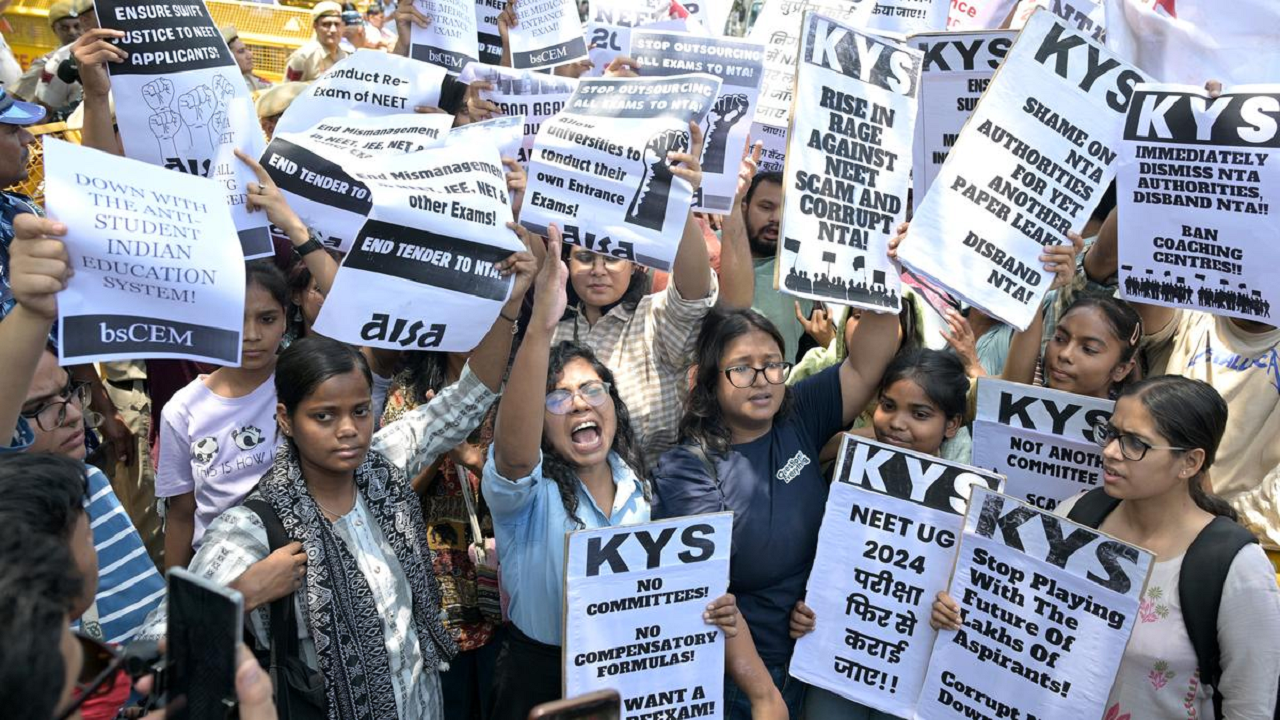

- NEET Irregularities: Allegations of irregularities in the NEET exam, including question paper leaks and malpractices.
- UGC-NET Cancellation: The UGC-NET exam was cancelled due to the alleged leak of question papers on the dark net, as reported by the Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C).
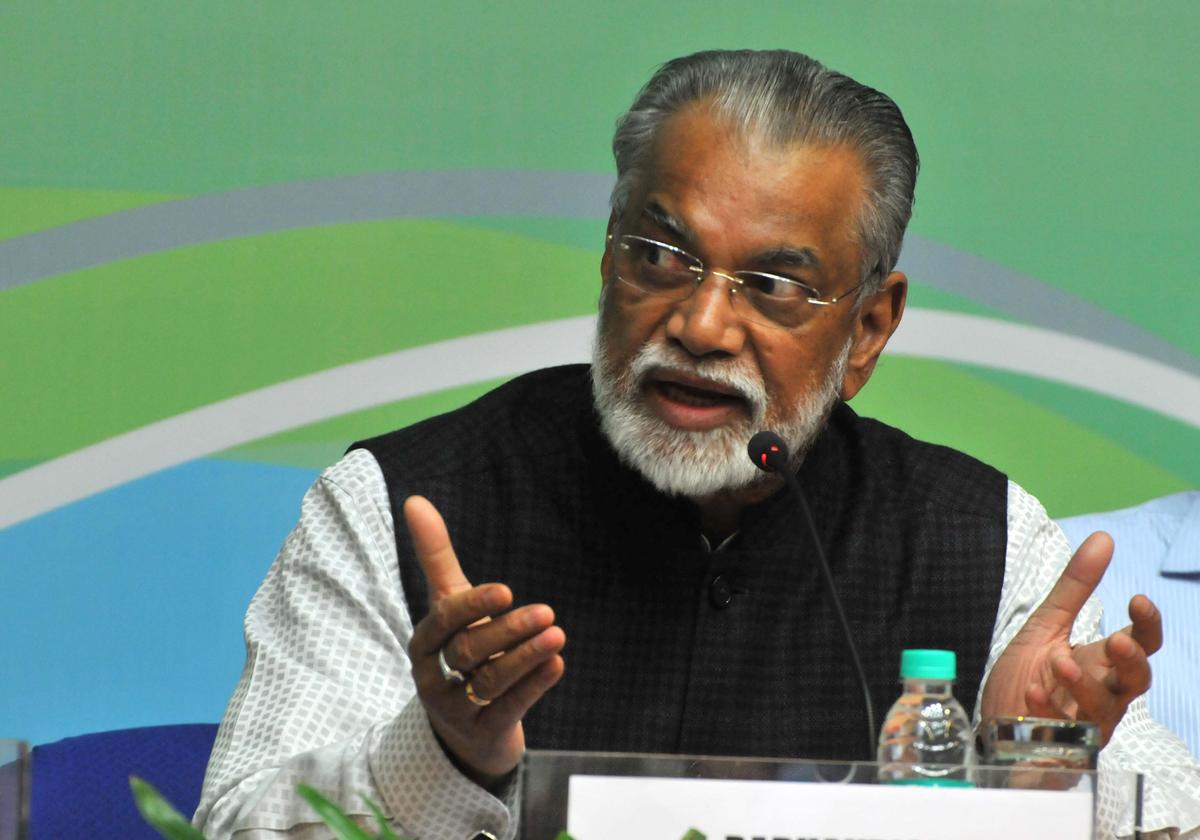
Government Response
- Institutional Failure: Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan acknowledged the irregularities as an institutional failure of the NTA.
- Reform Committee: A reform committee consisting of technocrats, bureaucrats, and scientists will be formulated to suggest improvements in the functioning of the NTA.



Challenges Faced by NTA
- Cybersecurity: Ensuring the security of examination data and preventing leaks.
- Operational Efficiency: Managing large-scale examinations with minimal errors.
- Transparency: Maintaining transparency in the examination process to build trust among stakeholders.
- Technological Upgradation: Continuously upgrading technology to handle the evolving challenges in online and offline examinations.
Future Directions
- Enhanced Security Measures: Implementing advanced cybersecurity measures to prevent data breaches and leaks.
- Process Improvements: Streamlining examination processes to enhance efficiency and reduce errors.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with educational institutions, students, and other stakeholders to address their concerns and improve the examination experience.
- Research and Innovation: Investing in research and innovation to develop better testing methodologies and assessment tools.
- Information Technology Act, 2000: As the NTA conducts online examinations, the provisions of the IT Act are relevant for ensuring cybersecurity, data protection, and the integrity of online testing processes.
Conclusion
The National Testing Agency plays a crucial role in the Indian education system by conducting various entrance examinations. However, recent issues highlight the need for reforms and improvements in its functioning. The establishment of a reform committee is a step in the right direction to address these challenges and ensure the integrity and efficiency of the examination process.
Note: This is a developing story.

