Table of contents
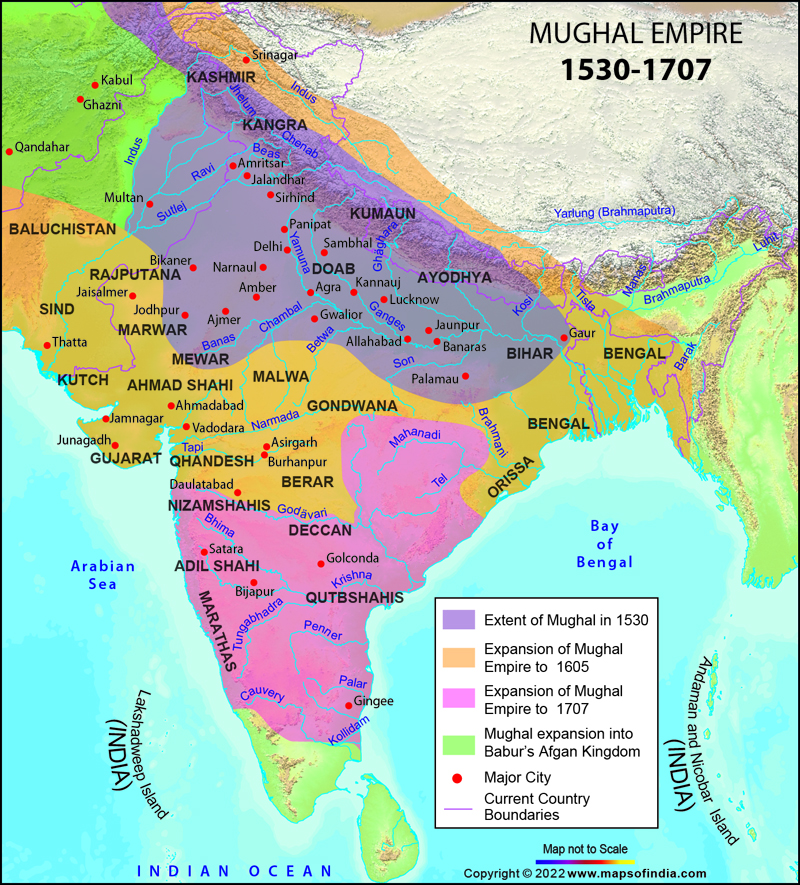
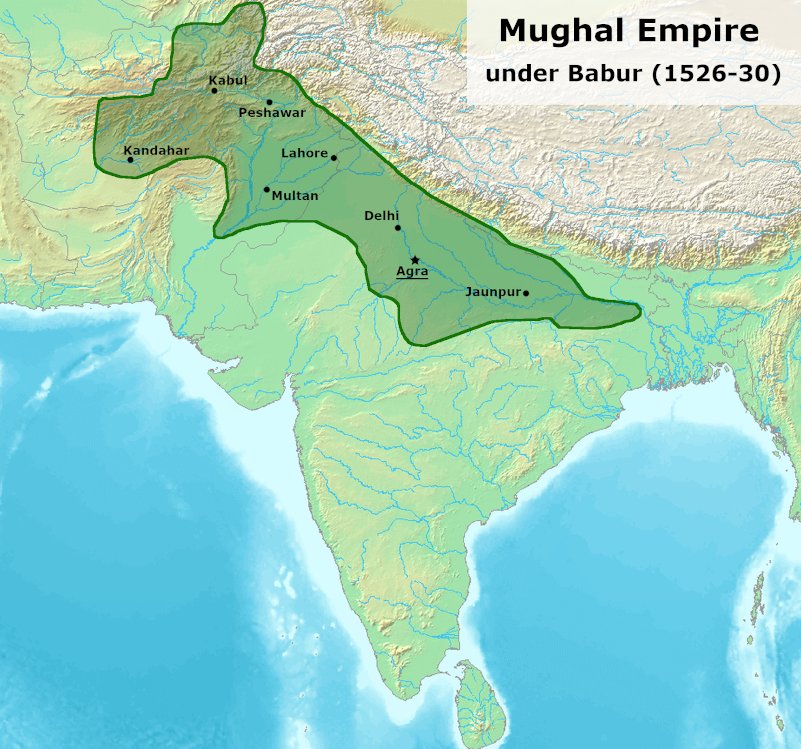
The rulers of the Mughal Empire were descendants of great rulers because Babur was related to Timur from his father’s side and to Chengiz Khan through his mother.
Babur's apprehension of a Uzbek attack and Rana Sanga's invitation forced him to look towards India.
-name-and-date.webp)
Babur
- Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodhi in the First Battle of Panipat in 1526.
- He then defeated Rana Sangha and assumed the title of Ghazi in the Battle of Khanwa (1527).
- In the Battle of Chanderi (1528), Medini Rai was defeated by Babur.
- He further defeated Mahmud Lodhi at the Battle of Ghagra (1529).
- These battles can be learnt by moving in a west to east direction in chronological order.
- Panipat to Khanwa to Chanderi and finally Ghagra.
- His cultural introductions include Charbagh style, compilation of Tuzuk-I-Baburi (Babarnama) & Masnavi.
- He popularized gunpowder, cavalry and artillery in India.

Humayun
- Humayun succeeded Babur and had to deal with the power of the Afghans and Bahadur shah of Gujarat.
- Sher Shah defeated Humayun at the Battle of Chausa (1539) and Battle of Kanauj (1540), and forced him to flee India.
- After the breakup of the Suri Empire in 1555, he recaptured Delhi.
- He built a city in Delhi named “Dinpanah” and built mosques like Jamali mosque and mosque of Isa Khan at Delhi.
- Humayun’s tomb was built by his widow Hamida Benu Begum and his sister, Gul Badan Begum wrote “Humayun-Nama”.
- The foundation for the Mughal painting was laid by Humayun as he brought Mir Sayyid Ali and Abdal Samad to India.


Akbar
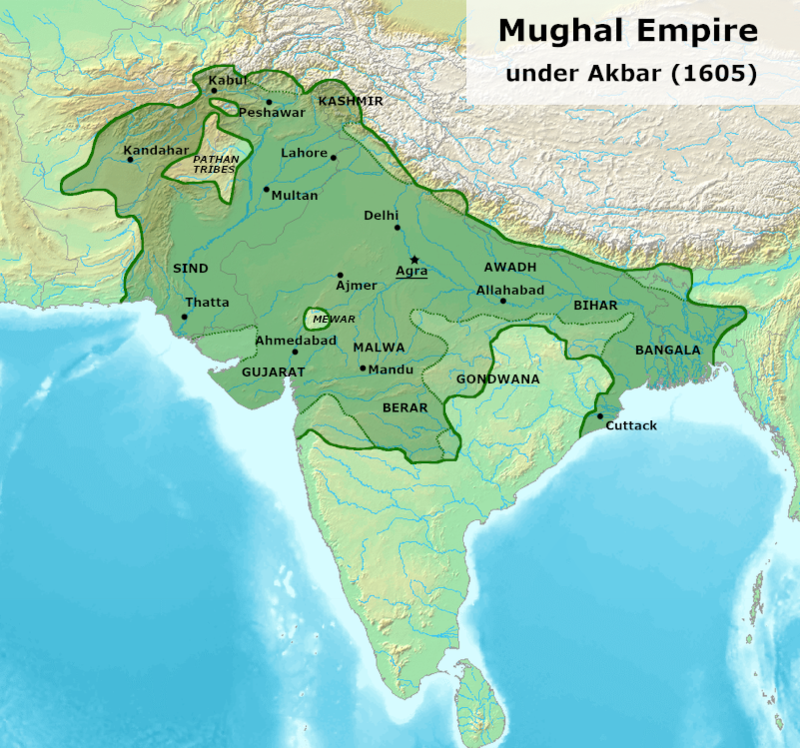
- He succeeded after Humayun’s death and defeated Hemu (Sur’s wazir) in the second battle of Panipat.
- Akbar defeated Rana Pratap in the Battle of Haldighati (1576) and Gujarat ruler Muzaffar Shah and to commemorate it, he built Buland Darwaza at Fatehpur Sikri.
- The European style of painting was introduced by Portuguese in his court and Jaswant & Daswan were famous painters in his court.
- Important terms-
- Jagir land was allotted to nobles & members of the royal family).
- Khalisa was a tract reserved for royal exchequer
- Inam land given to religious leaders, half of it was uncultivated.
- Amalguzar was land assessment and revenue collection officers.
- The revenue was fixed on the average yield of land measured on the basis of the previous ten years under the Dahsala System
- Revenue on the basis of what peasants had been paying in the past was based on the Nasdaq/kankut system.
- Land categorization involved Polaj (cultivated every year), Parati (once in two years), Chachar (once in three or four years) and Banjar land (once in five or more years).
- Maktab Khana or translation bureau was also established at Fatehpur Sikri for translation of many Sanskrit works into Persian.


Jehangir
- Built Moti Masjid at Lahore and Shalimar and Nishant gardens in Kashmir.
- Decoration of walls with floral designs made of semi-precious stones called Pietra Dura and use of Halo or Divine lights behind the king’s head was started during his reign.
- Captain Hawkins and Thomas Roe (got the Farman for setting up an English factory at Surat) visited his court.
- Jahangir built Zanjr-i-adal at Agra fort for royal justice and wrote the autobiography Tuzuk-i- Jahangiri in Persian.
- He introduced the “du-aspah-sih-aspah” system later modified to Mansabdari system.


Shah Jahan
- Initial reign was not successful as the campaign to seize Balkh from the Uzbeks failed in the north-west and Qandahar was lost to the Safavids.
- His Deccan policy was successful as he defeated Ahmednagar, Bijapur and Golconda.
- The capital shifted from Agra to Shahjahanabad in 1638, with the Red Fort, the Jama Masjid and Chandni Chowk.
- Salutations under him included Chahar, Taslim and Zaminbos (kissing the ground).
- A war of succession among his sons broke out and after the battle of Dharmat, Samugarh, Khajwa and Deorai, Aurangzeb emerged victorious.
- He built the Taj Mahal, Moti Masjid, Sheesh Mahal and Musamman Burj at Agra, Jama Masjid, Red Fort with its Rang Mahal, Diwan-i-Am and Diwan-i-Khas at Delhi.


Aurangzeb
- Aurangzeb took the title Alamgir which means ‘World Conqueror’ and was also called Zinda Pir.
- He took the Mughal Empire to its greatest extent ruling over almost the entire Indian subcontinent.
- He annexed Bijapur (1686) & Golkonda (1687) and extended the Mughal Empire further south.
- He was conservative and forbade painting, music and other cultural things.
- He issued Zawabit-i- Alamgir (decrees of Aurangzeb) and appointed Muhtasibs to enforce its moral codes.
- He built Bibi Ka Maqbara for his first wife Dilras Bano Begum.


Later Mughals
Jahandar Shah
- He introduced Ijarah i.e Revenue Farming and tried to establish friendly relations with Maratha and Rajputs.
- He abolished Jizya and granted Sardeshmukhi and Chauth of Deccan to Shahu.
- Title of Mirza Raja Sawai to Jai Singh of Amber and Maharaja to Ajit Singh was given by him.
Farruk Siyar
- He abolished Jizya completely but was a puppet of the Sayyid Brothers.
- Policy of religious tolerance was adopted.
- He gave a royal farman to the British in 1717.
Muhammad Shah Rangeela
- He was incompetent and pleasure loving. Many autonomous states like Deccan under Nizam-ul-Mulk, Awadh under Saadat Khan and Bengal under Murshid Quli Khan emerged under his reign.
- During his reign, Nadir Shah invaded India, looted Delhi and took away the Kohinoor Diamond and peacock throne.
- Nadir Shah defeated him in the Battle of Karnal in 1739 and Ahmad Shah Abdali also raided Delhi for the first time during his reign.
Shah Alam II
- During his reign, the third Battle of Panipat was fought between Marathas and Ahmad Shah Abdali.
- Took part in the Battle of Buxar (1764) along with Mir Qasim and Shuja-ud-Daula against the British East India Company.
- Was defeated and was forced to sign the Treaty of Allahabad (1765).
Akbar II
- Gave the title of ‘Raja’ to Ram Mohan Roy.
- Introduced Hindu-Muslim unity festival Phool Walon ki Sair which starts from Yogmaya temple and ends at Kaki Dargah.
Bahadur Shah II
- He was the last Mughal Emperor and he participated in the revolt of 1857.
