Table of contents
Introduction
The MSME sector constitutes a vast network of over 60 million units and employs 120 million people, contributing around 30 percent to the GDP. It accounts for about 45% of manufacturing output and around 40 % to total exports.
Definition of MSMEs
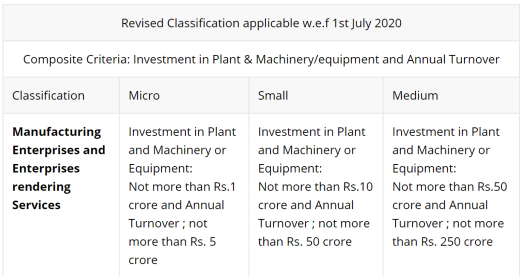
Manufacturing/Service Enterprise (Investment)
- Micro: upto 1 Crore
- Small: upto 10 Crore
- Medium: upto 50 crore
Turnover (5 times investment)
- Micro: upto 5 Crore
- Small: upto 50 Crore
- Medium: upto 250 Crore
Significance of MSMEs Sector
- Employment generation: employs about 120 million people
- MSME sector accounts for 30% of India’s GDP
- 45% of exports
- Income augmentation,
- Building rural infrastructure,
- Women empowerment (14% MSMEs are women led)
- Promotion of traditional goods, innovation etc.
Challenges
- Limited capital and knowledge
- Technological Backwardness
- Inadequate infrastructure facilities including access to power, water, & road
- Low production capacity and constraints in modernisation & expansions which inhibits the sector to profit from ‘economy of scale’
- Ineffective marketing strategy
- Non-availability of skilled labour at affordable cost
- High competition from cheap import
- Lack of adequate forward and backward linkages
- Financial constraints
- Poor access to formal capital: Only about 8 percent of MSMEs are served by formal credit channels.
- Low financial and digital literacy
- Limited funding capacity and accessibility of NBFCs and SFBs
Recent initiatives for MSMEs Sector
- In-principle approval for loans up to Rs. 1 crore within 59 minutes
- Interest subvention of 2%
- All CPSUs to compulsorily procure through GeM portal (25% target)
- 4% SC/ST led MSMEs and 3% from women led
- Technology Centres (TCs) and Extension Centres (ECs)
- Equity infusion for MSMEs through Fund of Funds
- Use of Fintech is being encouraged
- MUDRA Loans
U. K. Sinha Committee Report
(Expert committee on MSMEs) Report by RBI. Recommendations:
- Review the MSME Development Act as a comprehensive and holistic MSME code
- Change definition from current investment based to turnover based
- Strengthening government e-market portal.
- State Finance Commission and Khadi and Village Industries Commission should redirect their focus in promoting the MSME sector
- Exit policy should be their for out-of-court assistance to MSMEs
- Market support to MSMEs. Eg. External service provider giving customised solutions to struggling enterprise
- Improving access to technology
- Setup a National Council for MSMEs to facilitate coherent policy outlook & Unity of monitoring
Rainbow reforms for MSMEs
Access to credit, access to market, technology upgradation, ease of doing business and a sense of security for employees are five key aspects for facilitating MSME sector.
These reforms are for both manufacturing and service sector.
Easy access to credit
- loans of up to Rs 1 crore will be sanctioned in 59 minutes through a special portal as part of the Centre’s Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Support and Outreach programme.
- GST-registered MSMEs will get two per cent interest subvention
Easy access to market
- public sector companies will hav to compulsorily procure 25%, instead of 20%, of their total purchases from the MSMEs.
- Of the 25% procurement mandated from the MSMEs, 3% must now be reserved for women entrepreneurs
Technology Upgradation
- 20 tool hubs would be formed across the country, and 100 spokes in the form of tool rooms would be established.
Ease of doing business
- inspections of factories in the sector will be sanctioned only through a computerised random allotment and inspectors will have to upload reports on the portal within 48 hours.
- MSMEs will have to file just one annual return on eight labour laws and 10 central rules (earlier it needed to filed twice annually)
- Environment clearance under Air and water act on self certificate of MSME. Only 10% industries to be inspected
Social security to employees of MSMEs
Campaign to ensure all MSMEs are covered under social security schemes.
Concerns
- Risk of credit stimulus is the mis-allocation of productive economic resources
- Likely deterioration in credit standards as the financial institutions are pushed to lend aggressively to MSMEs
Important for Prelims -
- MSME Sambandh Portal - To monitor the implementation of the Public Procurement from MSEs by Central Public Sector Enterprises. (Mandatory 25% from SMEs)
- Udyami Mitra Portal - To provide ‘End to End’ solutions not only for credit delivery but also for the host of Credit-plus services by way of hand holding support, application tracking, and multiple interfaces with stakeholders. It was launched by SIDBI. It provides a unique match making platform to MSME loan seekers, lenders as also handholding agencies.
- MSME Sampark portal- To bridge gap between the Recruiters and Job Seekers.
- Samadhan Portal – It enables the MSMEs to directly register their cases relating to delayed payments by Central Ministries/Departments/CPSEs/State Governments. The information on the portal will be available in public domain, thus exerting moral pressure on the defaulting organizations.
Previous Post
