Table of contents
Agnikul Cosmos successfully carries out a su-orbital test-flight of its home-built 3D-printed semi-cryogenic rocket Agnibaan from its own launch pad at Sriharikota.
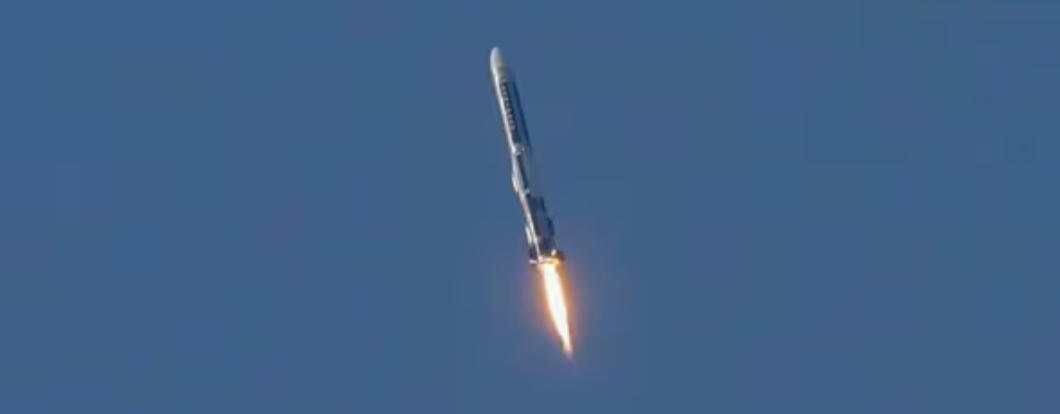


The successful launch of the Agnibaan rocket by Agnikul Cosmos marks a significant milestone in India's space sector.
- It highlights the growing role of private companies in space exploration and satellite launches.
Significance
- First Private Rocket Launch:
- Skyroot Aerospace: Launched the Vikram rocket in November 2022.
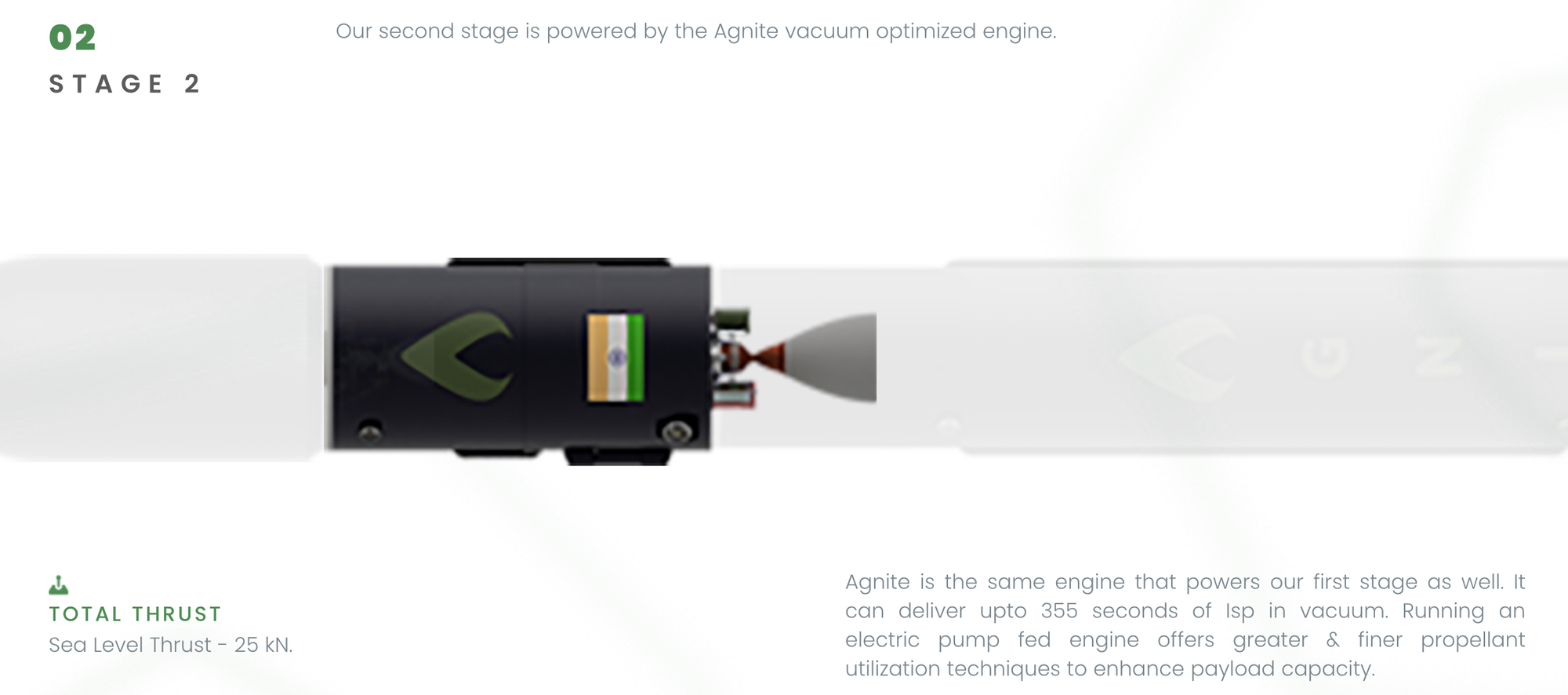
- Agnikul Cosmos: Launched the Agnibaan rocket, powered by the world’s first 3D-printed engine, from its own launchpad at ISRO’s Sriharikota facility.
- Engine: Semi-cryogenic engine named Agnilet, entirely 3D-printed.
- Launchpad: First privately owned launchpad in India.
What is Agnibaan?

- Agnibaan is a highly customizable 2 stage launch vehicle.
- Variants: Capable of carrying payloads between 30 kg and 300 kg to lower Earth orbits, around 700 km high.
- Agnibaan can access both low and high-inclination orbits
- It is completely mobile—designed for accessing more than 10 launch ports.
- Driven by LOX/Kerosene engines in all its stages, Agnibaan is configurable by the customer.
- Agnibaan doesn’t fly with the same number of engines all the time.
- The mission, the satellite and the launchport itself would decide how many engines go on the first stage.


Small Satellite Market
What is Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)?


- Definition: SSLV is a type of launch vehicle designed to carry small payloads, typically up to 500 kg, to low Earth orbits.
- Features:
- Cost-Effective: Lower launch costs compared to larger launch vehicles.
- Flexibility: Can be launched on-demand, catering to the needs of small satellite operators.
- ISRO’s SSLV: Developed to meet the growing demand for launching small satellites for various applications like communications, disaster management, and scientific research.
- Payload Capacity: Up to 500 kg.
- Launches: Flown twice, with one successful launch.
Both Agnikul and Skyroot are targeting the small satellite market to meet the growing demand for space-based applications.
- Future Prospects: ISRO is developing a second space port at Kulasekarapattinam, Tamil Nadu, primarily for SSLV launches.

3D Printing in Space Sector
What is 3D Printing and its Usage?
- Definition: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file by layering materials.
- Usage in Space Sector:
- Prototyping: Rapid creation of prototypes for testing and validation.
- Manufacturing: Production of complex parts that are difficult or impossible to make with traditional methods.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces material waste and production costs.
- Customization: Allows for the creation of customized parts tailored to specific missions.
- Advantages:
- Efficiency: Faster production times and reduced material waste.
- Cost Reduction: Lower manufacturing costs.
- Customization: Ability to produce complex and customized parts.
- Reliability: Potentially fewer points of failure due to fewer assembled parts.
- Disadvantages:
- Material Limitations: Limited to materials that can be 3D printed.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality and reliability can be challenging.
- Initial Costs: High initial investment in 3D printing technology.
Private Sector Participation
- Opportunities:
- Innovation: Increased innovation and technological advancements.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced costs through competition and private investment.
- Job Creation: Generation of new jobs and skill development.
- Global Competitiveness: Enhances India's position in the global space market.
- Challenges:
- Regulation: Need for robust regulatory frameworks to ensure safety and compliance.
- Funding: Securing adequate funding and investment.
- Technology Transfer: Ensuring effective technology transfer and collaboration with public sector entities like ISRO.
- Market Risks: Navigating market risks and uncertainties.
Initiatives by Government
Initiatives by Government to Promote the Privatization of the Space Sector include:
- IN-SPACe: Establishment of IN-SPACe to regulate and promote private sector participation.
- Policy Reforms: Introduction of new policies to facilitate private sector involvement in space activities.
- Collaboration with ISRO: Encouraging collaboration between private companies and ISRO for technology transfer and joint missions.
- Funding and Support: Providing financial support and incentives to private space companies.
- Infrastructure Development: Development of infrastructure like launchpads and spaceports to support private launches.
What is IN-SPACe?
- Definition: Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) is an autonomous agency under the Department of Space, Government of India.
- Purpose:
- Regulation: Authorizes and regulates private sector activities in space.
- Promotion: Facilitates private sector participation in space missions.
- Support: Provides technical and financial support to private space companies.
Conclusion
The launch of the Agnibaan rocket by Agnikul Cosmos signifies a turning point in India's space sector, showcasing the potential of private companies to contribute to space exploration and satellite launches. This development aligns with the government's initiatives to promote privatization and innovation in the space sector, paving the way for a more competitive and dynamic space industry in India.
Previous Post