Table of contents
India’s Neighbourhood
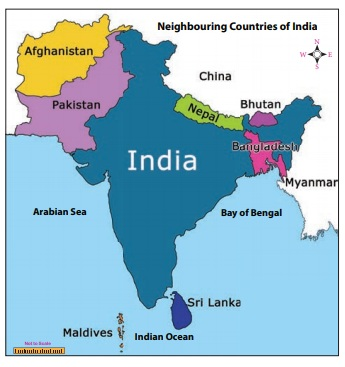
Immediate
- India shares its geographical land and maritime boundaries with its immediate neighbours in the South Asian region.
- These countries include Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, Maldives, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.
- India shares civilizational relations with these countries, which are marked by a shared history, culture, and extensive people-to-people contacts.
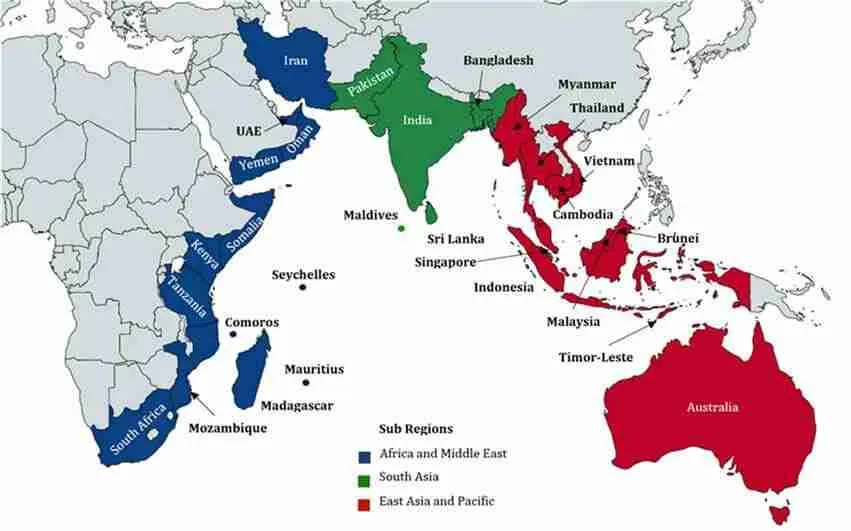
Extended
- Extended neighbours are countries that are geographically distant from India, such as those in the Indian Ocean Region, Southeast Asia, or West Asia, but maintain significant political, economic, cultural, and strategic ties with India.
Neighbourhood First Policy
India’s ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’ guides its approach towards the management of relations with countries in its immediate neighbourhood, that is, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
The Neighbourhood First policy, inter alia, is aimed at:
- Enhancing physical, digital and people-to-people connectivity across the region
- Augmenting trade and commerce
This policy has evolved into an institutional priority for all the relevant arms of the Government managing relations and policies with our neighbourhood.
India's Neighbourhood First Policy is a strategic initiative aimed at fostering better relations with its immediate neighbours. Introduced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the policy emphasizes the importance of regional cooperation and stability for India's national interests and global standing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Objectives
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Enhance political, economic, and cultural relations with neighbouring countries.
- Regional Stability: Promote peace and stability in the region, which is crucial for India's security and economic growth.
- Economic Integration: Boost trade and investment with neighbouring countries to create a more integrated regional economy.
- People-to-People Connectivity: Improve cultural and social ties through initiatives like visa liberalization, educational exchanges, and tourism.

Initiatives and Achievements
Energy Cooperation
Energy cooperation is crucial to India’s foreign policy, particularly with its neighbouring countries. India has entered into several agreements and initiatives focusing on the supply of electricity, the development of hydroelectric projects, and mutual energy security. Here are some key examples:
- India-Nepal Energy Cooperation


- Electricity Supply and Trade:
- Power Exchange Agreement: India and Nepal have signed agreements for the supply of electricity, facilitating the trade of power between the two countries. India exports electricity to Nepal to help meet its growing energy demands.
- Dhalkebar-Muzaffarpur Transmission Line: This cross-border transmission line enables the transfer of up to 600 MW of electricity from India to Nepal, enhancing energy security and grid stability in Nepal.
- Hydropower Projects:
- Arun III Hydropower Project: This is one of the largest projects being developed in Nepal with Indian investment. It aims to generate 900 MW of electricity, with a significant portion to be exported to India.
- Upper Karnali Hydropower Project: Another major project being developed by an Indian company, GMR Group, is expected to generate 900 MW of electricity, further boosting energy cooperation between the two nations.
- India-Bhutan Energy Cooperation


- Hydropower Projects:
- Tala Hydroelectric Project: This 1,020 MW project is one of the largest hydroelectric projects in Bhutan, constructed with Indian assistance. The power generated is exported to India, contributing to Bhutan’s revenue and India’s energy needs.
- Chukha Hydroelectric Project: With a capacity of 336 MW, this is one of the earliest and most successful projects developed with Indian cooperation. It plays a significant role in Bhutan’s economy through the export of electricity to India.
- Punatsangchhu-I and II Projects: These ongoing projects, with capacities of 1,200 MW and 1,020 MW respectively, are being developed with Indian assistance and are expected to significantly increase the power export from Bhutan to India.
- Electricity Trade:
- Long-Term Power Purchase Agreements: India has signed long-term agreements to purchase electricity from Bhutan, ensuring a stable revenue stream for Bhutan and a reliable supply of clean energy for India.
- India-Bangladesh Energy Cooperation
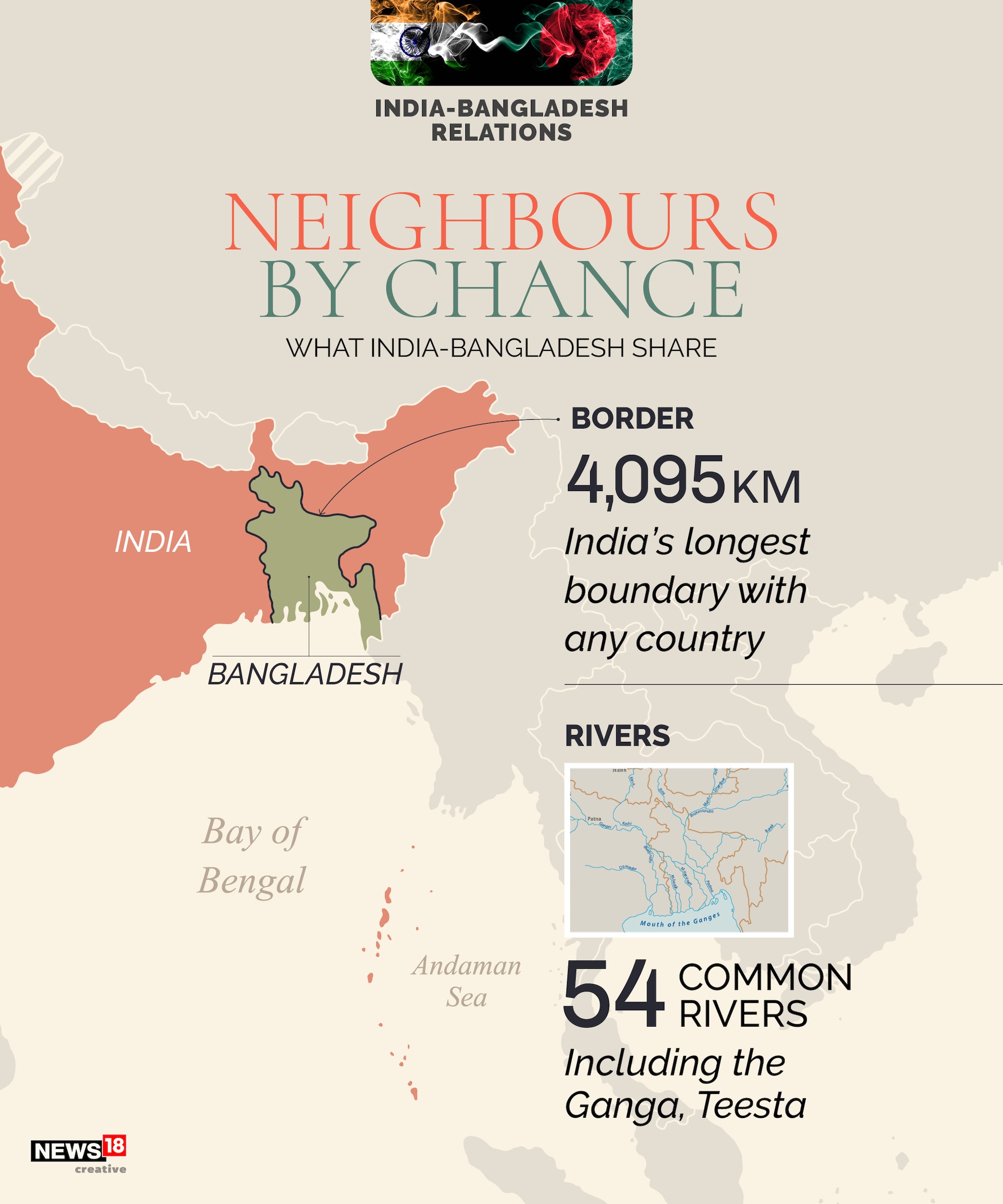
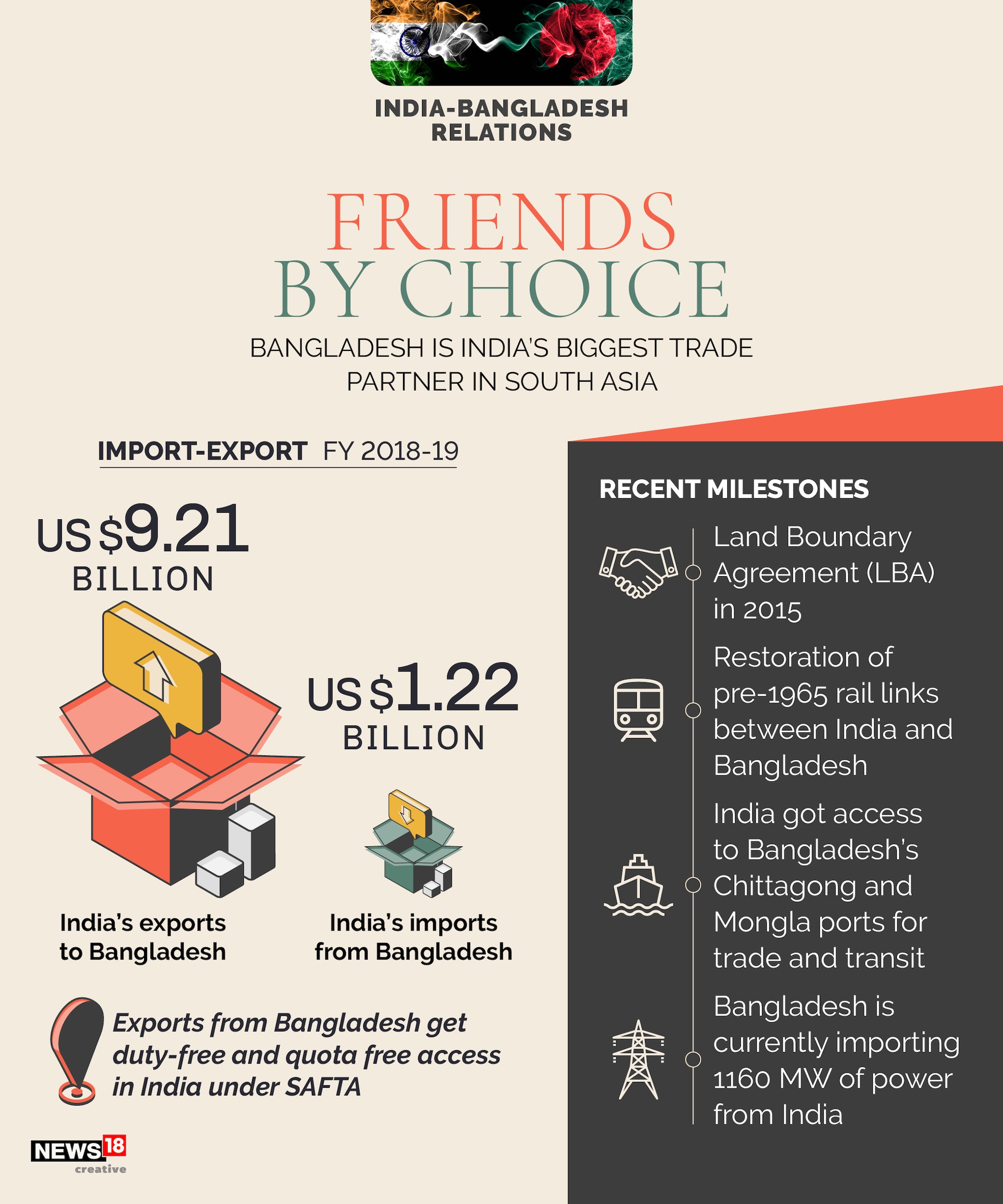

- Cross-Border Electricity Supply:
- Bheramara-Baharampur Transmission Line: This transmission line facilitates the export of electricity from India to Bangladesh. Currently, India supplies around 1,160 MW of electricity to Bangladesh through various cross-border connections.
- Tripura-Bangladesh Power Supply: India supplies 160 MW of power from its northeastern state of Tripura to Bangladesh, further strengthening energy cooperation.
- India-Myanmar Energy Cooperation


- Hydropower and Renewable Energy Projects:
- Tamanthi and Shwezaye Hydropower Projects: India has been involved in the development of these hydropower projects in Myanmar, aimed at generating renewable energy and enhancing regional cooperation in the energy sector.
- Solar Energy Projects: India is exploring opportunities to develop solar energy projects in Myanmar, promoting the use of renewable energy sources.
- India-Sri Lanka Energy Cooperation
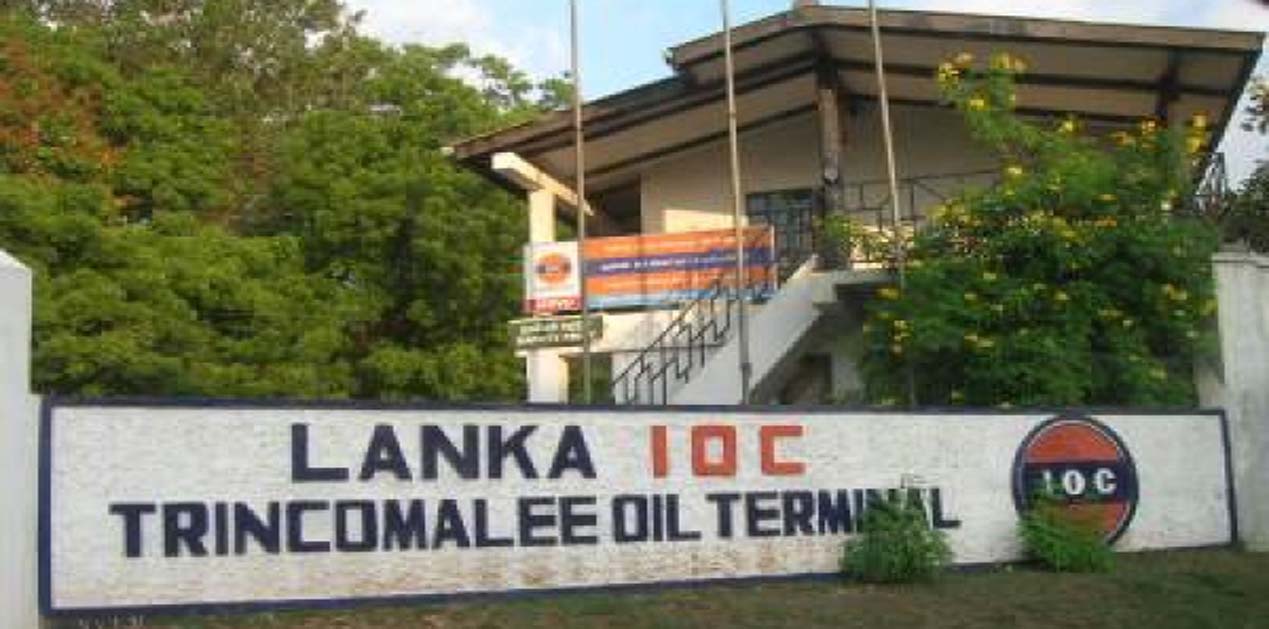


- Renewable Energy Initiatives:
- Solar and Wind Projects: India and Sri Lanka have agreed to collaborate on developing renewable energy projects, including solar and wind farms, to promote sustainable energy sources.
- Trincomalee Oil Tank Farm: India and Sri Lanka are working together to develop and modernize the Trincomalee oil tank farm, enhancing energy storage and security.
Infrastructure and Connectivity Projects
Significant investments in infrastructure projects like roadways, railways, and ports to improve connectivity.
- India-Nepal:
6.png)

- Integrated Check Posts (ICPs): India has established ICPs at key border points to facilitate smooth trade and movement of people.
- Motihari-Amlekhgunj Petroleum Pipeline: This pipeline project aims to enhance the fuel supply to Nepal, marking the first cross-border petroleum pipeline in South Asia.
- India-Bangladesh:

- Maitree Express and Bandhan Express: These train services have been established to improve connectivity between India and Bangladesh.
- Agartala-Akhaura Rail Link: This project aims to connect Agartala in India with Akhaura in Bangladesh, boosting trade and people-to-people contacts.
- India-Myanmar:
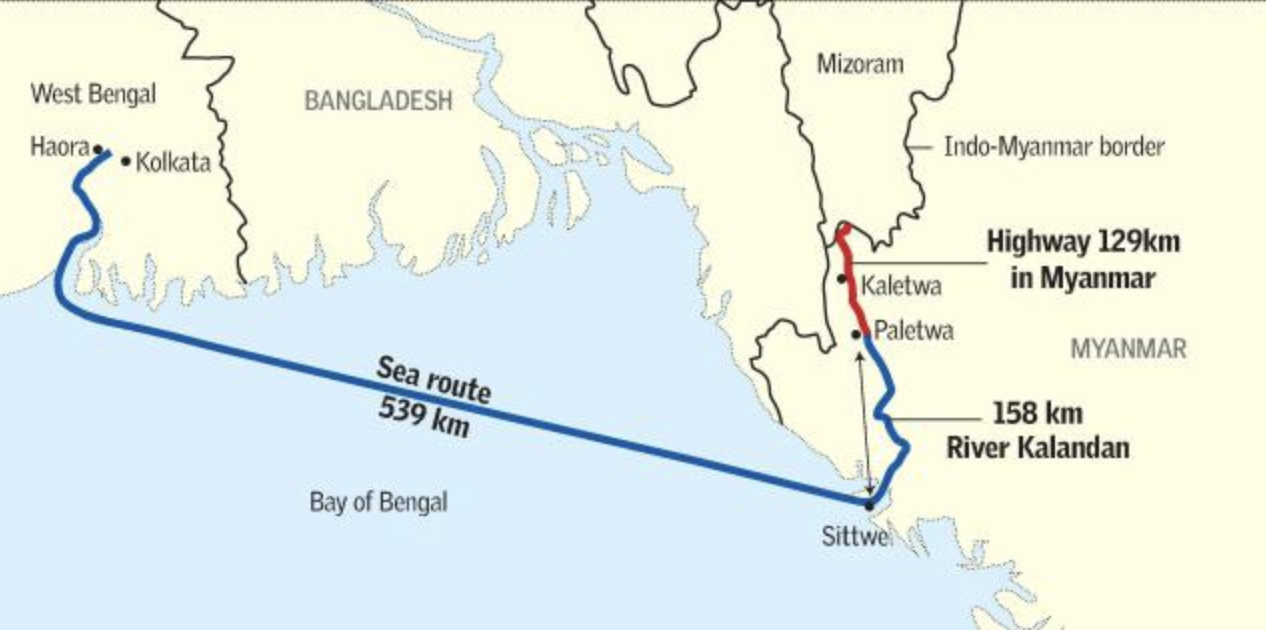
- India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway: This highway project aims to enhance connectivity between India, Myanmar, and Thailand, facilitating trade and economic integration.
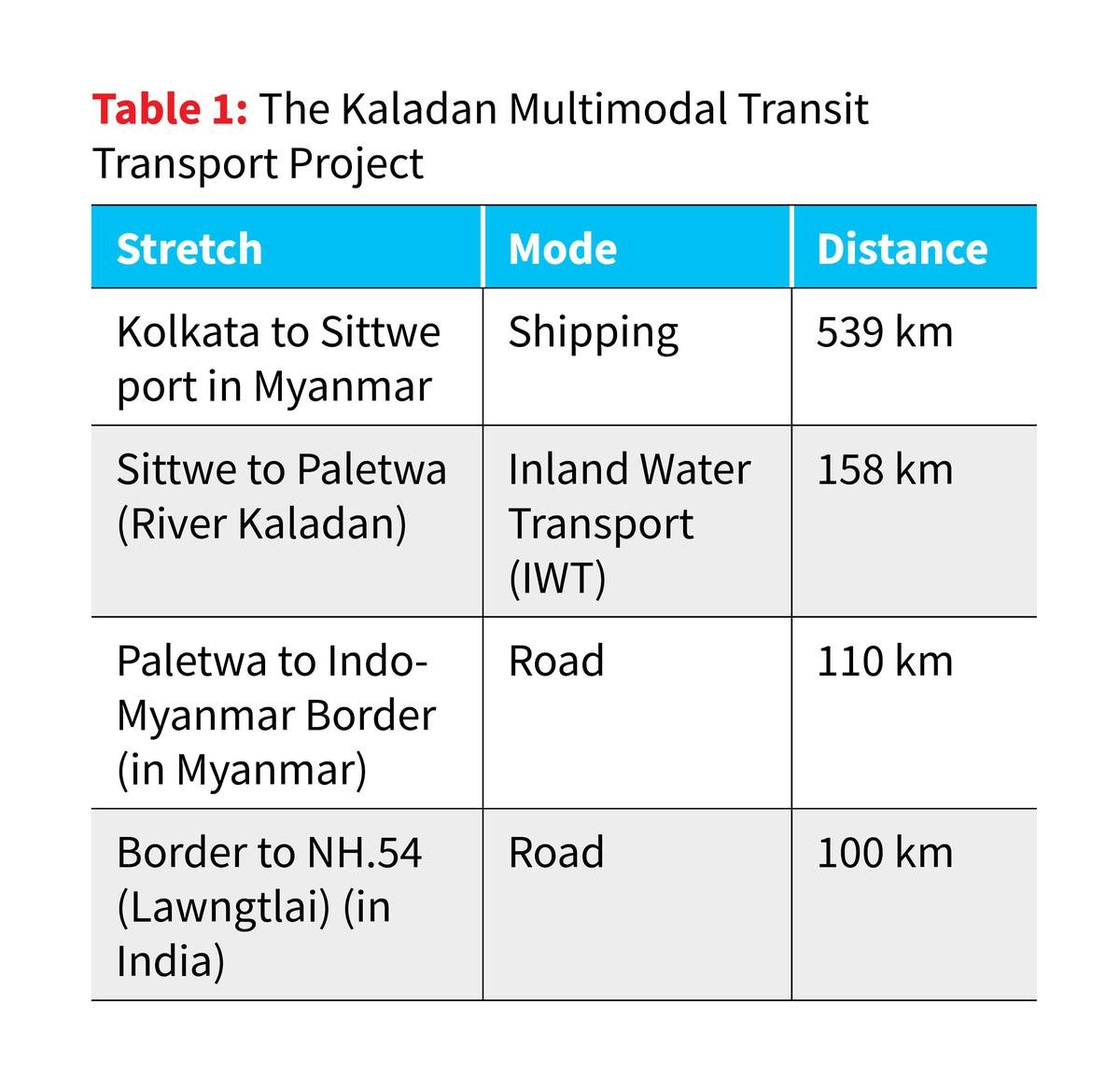
- Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project: This project connects the Indian port of Kolkata with Myanmar's Sittwe port, further linking to India's northeastern states.
Economic Assistance and Development Aid
Bhutan:
- Economic Assistance: India provides significant economic aid to Bhutan for its five-year plans, supporting various developmental projects and infrastructure improvements.
Sri Lanka:
- Housing Projects: India has funded housing projects in Sri Lanka, particularly for the rehabilitation of Tamil refugees in the Northern and Eastern provinces.
- Emergency Aid: India has provided emergency relief assistance to Sri Lanka during natural disasters and economic crises.
Maldives:
- Greater Male Connectivity Project: India is funding this project to build bridges and causeways linking the capital Male with surrounding islands, enhancing transport and economic activities.
- COVID-19 Assistance: India provided medical supplies, vaccines, and financial assistance to the Maldives during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Security Cooperation
Confidence-Building Measures: India has undertaken several confidence-building measures, including border agreements and non-reciprocal initiatives, to build trust among its neighbours.
Bangladesh:
- Counter-Terrorism Cooperation: India and Bangladesh have strengthened their cooperation in combating terrorism, with joint efforts to tackle cross-border terrorism and insurgent activities.
- Coastal Security: The two countries collaborate on maritime security to safeguard their coastal regions and ensure safe maritime trade routes.
Myanmar:
- Joint Operations: India and Myanmar have conducted joint military operations to target insurgent groups operating along the border, enhancing security and stability in the region.
Humanitarian Assistance
India has a long history of providing humanitarian assistance to countries in need, especially within its neighbourhood. These efforts demonstrate India's commitment to regional stability and goodwill. Here are some notable examples:
- COVID-19 Pandemic Assistance



- Vaccine Diplomacy: Vaccine Maitri Initiative: India supplied millions of doses of COVID-19 vaccines to countries around the world, including its neighbours like Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Sri Lanka, and Myanmar. This initiative was critical in helping these countries combat the pandemic.
- Medical Supplies: Emergency Medical Supplies: India sent essential medical supplies, including PPE kits, masks, ventilators, and medicines, to neighbouring countries during the pandemic.
- Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance


- Nepal: 2015 Earthquake Relief: Following the devastating earthquake in Nepal, India launched Operation Maitri, providing immediate rescue and relief efforts. India sent rescue teams, medical aid, and essential supplies, and helped in the reconstruction of infrastructure.
- Sri Lanka: Cyclone and Flood Relief: India has consistently provided aid to Sri Lanka during natural disasters. For instance, after the severe floods and landslides in 2017, India sent relief materials, including food, water, and medical supplies.
- Maldives: Water Crisis in 2014: When the Maldives faced a severe water crisis due to a fire at the Malé Water and Sewerage Company, India swiftly sent potable water and desalination plants to help alleviate the crisis.
- Bangladesh: Cyclone Amphan Relief: In 2020, India provided relief assistance to Bangladesh following the devastating impact of Cyclone Amphan, including essential supplies and support for rehabilitation efforts.
- Development Assistance and Capacity Building
- Bhutan: Hydropower Projects: India has funded and assisted in the construction of several hydropower projects in Bhutan, which are crucial for Bhutan’s economy and provide clean energy to India.
- Myanmar: Development Projects: India has undertaken numerous development projects in Myanmar, including road construction, schools, and hospitals, which help in improving the living standards of the people.
- Afghanistan: Infrastructure Projects: India has invested in key infrastructure projects in Afghanistan, such as the construction of the Afghan Parliament building, the Salma Dam, and road projects. India also provides educational scholarships and medical aid.
- Health Assistance
- Bhutan: Health Sector Support: India has supported Bhutan’s health sector through various initiatives, including the supply of medical equipment and vaccines.
- Sri Lanka: Cancer Hospital: India funded the construction of a 150-bed cancer hospital in Hambantota, enhancing healthcare infrastructure in Sri Lanka.
- Maldives: Gift of a COVID-19 Testing Lab: India gifted a state-of-the-art COVID-19 testing lab to the Maldives, boosting their capacity to handle the pandemic.
- Food Aid and Agricultural Support
- Yemen: Food Aid: India has provided food aid to Yemen amidst the ongoing conflict and humanitarian crisis, helping to alleviate food shortages and malnutrition.
- Sri Lanka: Food Supplies: In 2022, India sent a large consignment of essential food items to Sri Lanka to help mitigate the impact of an economic crisis that led to severe food shortages.
- Myanmar: Rice and Pulses Supply: India has sent consignments of rice and pulses to Myanmar to support food security in the country.
Cultural and People-to-People Initiatives
Nepal:
- Scholarships and Educational Exchange: India provides scholarships to Nepalese students for higher education in Indian institutions, fostering educational and cultural ties.
- Bharat-Nepal Maitri Bus Service: This bus service connects various cities in Nepal and India, promoting tourism and people-to-people contacts.
Sri Lanka:
- Tourism Promotion: India promotes Buddhist tourism by facilitating pilgrimages to significant Buddhist sites in India, attracting tourists from Sri Lanka.
- Educational Grants: India offers scholarships and training programs to Sri Lankan students and professionals, enhancing educational and skill development ties.
Multilateral and Regional Cooperation
SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation):
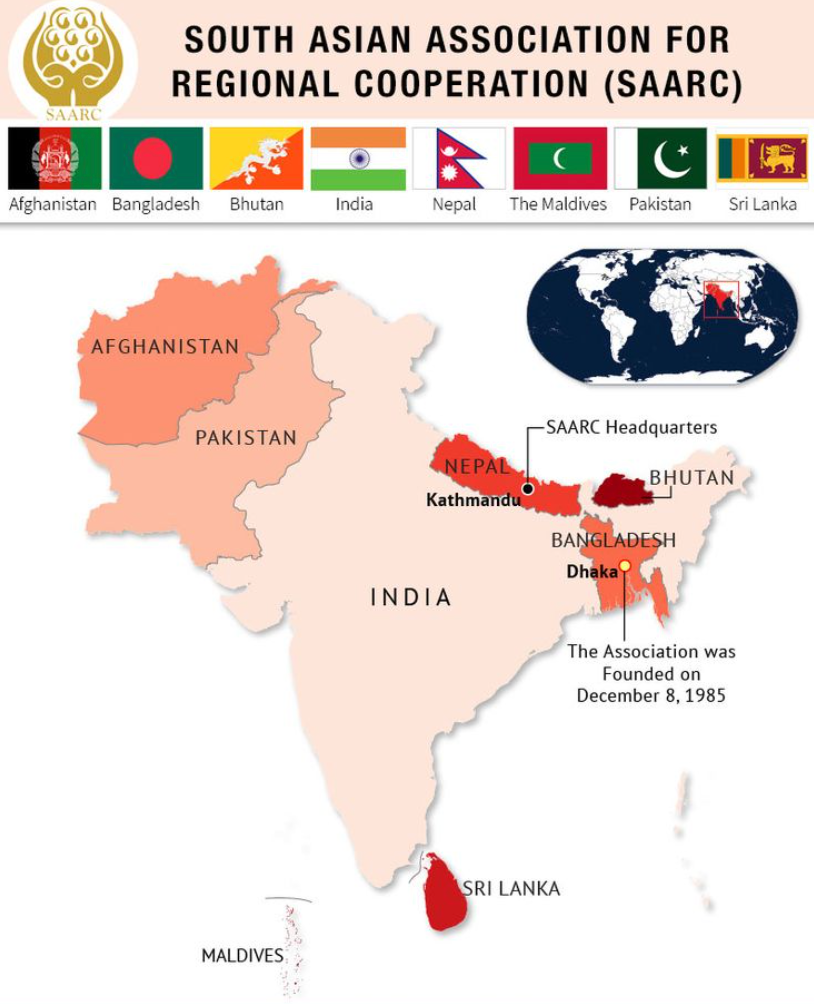

- SAARC Satellite: India launched the South Asia Satellite to provide communication and meteorological services to SAARC countries, enhancing regional cooperation in space technology.
BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation):
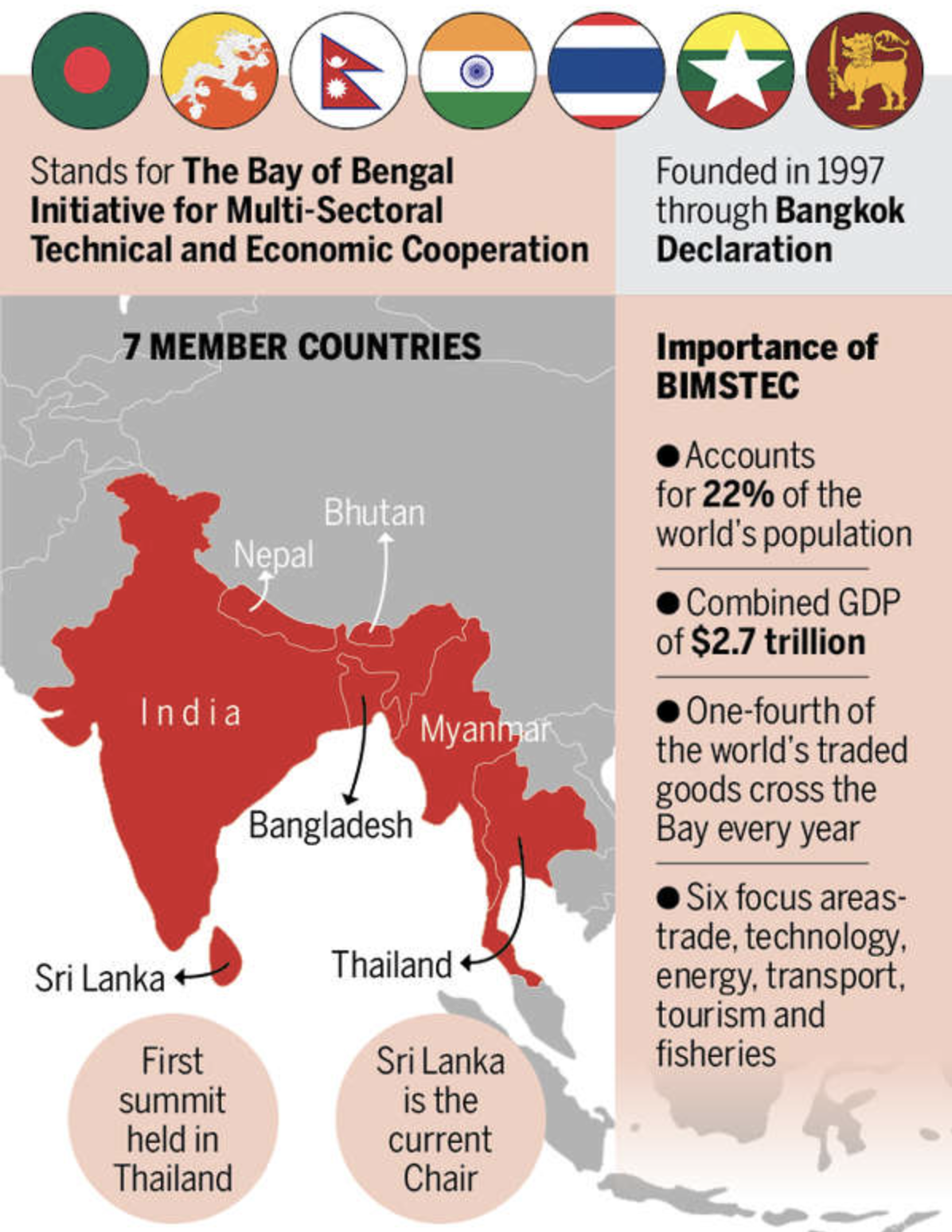

- Disaster Management Exercises: India hosts regular disaster management exercises under the BIMSTEC framework, improving regional coordination and response capabilities.
Challenges
- Rise of China: China's increasing influence in South Asia has posed significant challenges to India's relations with its neighbors. China's investments and strategic partnerships in countries like Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Nepal have complicated India's diplomatic efforts.
- Political Instability: Political instability in neighbouring countries can disrupt bilateral relations and cooperation.
- Border Disputes: Ongoing border disputes with countries like Pakistan and China continue to be a major challenge.
- Economic Disparities: Economic disparities between India and its neighbours can create friction and hinder cooperation.
Recent Developments
- Maldives: The complementarity of India's 'Neighborhood First' policy and the Maldives' 'India First' policy has advanced their special partnership.
- Nepal: Recent agreements include the initiation of an annual policy dialogue between NITI Aayog of India and the National Planning Commission of Nepal, and the construction of an Integrated Check Post (ICP) in Dodhara Chandani.
- Pacific Island Countries: At the third FIPIC Summit in 2023, PM Modi unveiled a 12-point development plan for the Pacific Island nations, covering areas such as healthcare, renewable energy, and cyber-security.
India's Neighbourhood First Policy is a cornerstone of its foreign policy, reflecting the importance of regional stability and cooperation for its national interests. Despite facing challenges, India remains committed to fostering strong and mutually beneficial relationships with its neighbours.
Previous Post