Table of contents
Humanoid robots have been a subject of fascination and development for decades.
Context: Recently NASA shared a visual of its humanoid robot Valkyrie performing tasks at the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas.
Valkyrie is designed to operate in “degraded or damaged human-engineered environments,” like areas hit by natural disasters, as well as handle risky tasks like cleaning solar panels or inspecting malfunctioning equipment outside spacecraft.
What are Humanoid Robots?
Humanoid robots are robots that resemble and act like humans. Typically engineered to imitate authentic human expressions, interactions and movements, these robots are often outfitted with an array of cameras, sensors and, more recently, AI and machine learning technologies.
What is the fascination for Humanoid Robots all about?
A humanoid robot is a type of robot designed to resemble the human body in appearance and mechanics. These robots often have a torso with a head, two arms, and two legs, although some models might have only part of the human body structure.
Humanoid robots captivate people because they blur the line between the animate and the inanimate, they challenge our understanding of intelligence and life, and they promise a future where the boundaries of human capability are significantly expanded.
Technology Behind Humanoid Robots:
- Bipedal Locomotion: Humanoid robots use various technologies to achieve bipedal walking and balance. This includes gyroscopes, accelerometers, and other sensors to maintain stability and orientation.
- Actuators: These are the "muscles" of robots. Hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric actuators are common, and they allow the robot to move and perform tasks.
- AI and Machine Learning: To process information and learn from their environment, humanoid robots use AI algorithms and machine learning. This enables them to perform complex tasks and improve over time.
- Computer Vision: Cameras and other sensors allow robots to perceive their surroundings. Advanced image processing algorithms enable them to recognize objects and people.
- Speech Recognition and Natural Language Processing (NLP): These technologies allow robots to understand spoken language and communicate with humans.
- Haptic Feedback: This technology gives robots a sense of touch, allowing them to manipulate objects with precision.
- Control Systems: Humanoid robots are often controlled through advanced computer systems that coordinate all aspects of their operation, from movement to decision-making.
- Teleoperation: Some humanoid robots are controlled remotely by humans, often through motion capture or other interfaces that allow for nuanced control.
Applications
Robots serve a multitude of functions across various industries. Here are some of their key applications:
- Manufacturing: Performing assembly, welding, painting, and material handling.
- Healthcare: Assisting in surgeries, patient rehabilitation, and dispensing medication.
- Agriculture: Harvesting crops, monitoring fields, and automating irrigation.
- Defense: Reconnaissance, diffusing bombs, and unmanned surveillance.
- Logistics: Sorting packages, managing inventory, and delivering goods.
- Home Assistance: Cleaning, lawn mowing, and performing household chores.
- Space Exploration: Conducting research, collecting samples, and maintaining equipment.
- Entertainment: Performing in shows, simulating rides, and interacting with guests.
- Education: Teaching assistance, language tutoring, and educational demonstrations.
- Customer Service: Providing information, guiding users, and automating check-ins.
- Search and Rescue: Locating individuals in disaster zones and inaccessible areas.
- Underwater Exploration: Mapping the sea floor, monitoring marine life, and inspecting infrastructure.
- Research and Development: Prototyping, testing theories, and laboratory automation.
- Construction: Fabricating structures, heavy lifting, and precision tasks.
- Environmental Monitoring: Sampling air and water quality, and wildlife tracking.
- Security and Surveillance: Monitoring areas, detecting anomalies, and reporting incidents.
- Elderly Care: Assisting with mobility, social interaction, and daily living activities.
These functions underline the versatility of robots and their growing significance in advancing human efficiency and capabilities across sectors.
We can't clear UPSC for you.
But with our personalised mentor support, you'll be ready to do it yourself.
Here’s a list of some popular humanoid robots from around the world, along with a brief explanation of the technology that powers them:
Popular Humanoid Robots:
- ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility): Developed by Honda, ASIMO was one of the world's most advanced humanoid robots, known for its ability to walk, run, and climb stairs.
- Sophia: Created by Hanson Robotics, Sophia is known for its human-like appearance and behavior, which is powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
- Atlas: Developed by Boston Dynamics, Atlas is a highly advanced humanoid robot capable of a range of physical activities, including running, jumping, and performing backflips.
- Nao: Aldebaran Robotics (now SoftBank Robotics) developed Nao, a robot often used in education and research.
- Pepper: Also from SoftBank Robotics, Pepper is designed to recognize human emotions and interact with people.
- Robonaut: Developed by NASA, Robonauts are designed to work alongside humans in space, equipped to handle tools and perform tasks that are risky for astronauts.
- HRP-4C: A humanoid robot created by AIST in Japan, designed to resemble a young Japanese female, and can simulate certain human movements and sounds.
- Fedora: Developed in Russia, this robot is aimed at replicating the appearance and some functions of the human body.
- T-HR3: Developed by Toyota, this robot can be remotely controlled by a human operator and is designed to assist in the home and healthcare settings.
- Surena: Surena is a humanoid robot series developed by the University of Tehran, Iran, which has seen several iterations with progressively advanced features.
Robotics in India
India has been making significant strides in the field of robotics, including the development of humanoid robots and other robotic innovations.
Humanoid Robots from India:
- Vyommitra: Developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Vyommitra is a female humanoid robot prototype unveiled as part of India's Gaganyaan space mission. It is designed to simulate human functions and can interact with the environment, recognize humans, and respond to their queries.

- AcYut: Created by students from BITS Pilani, AcYut is a series of humanoid robots capable of walking, dancing, and performing complex movements.
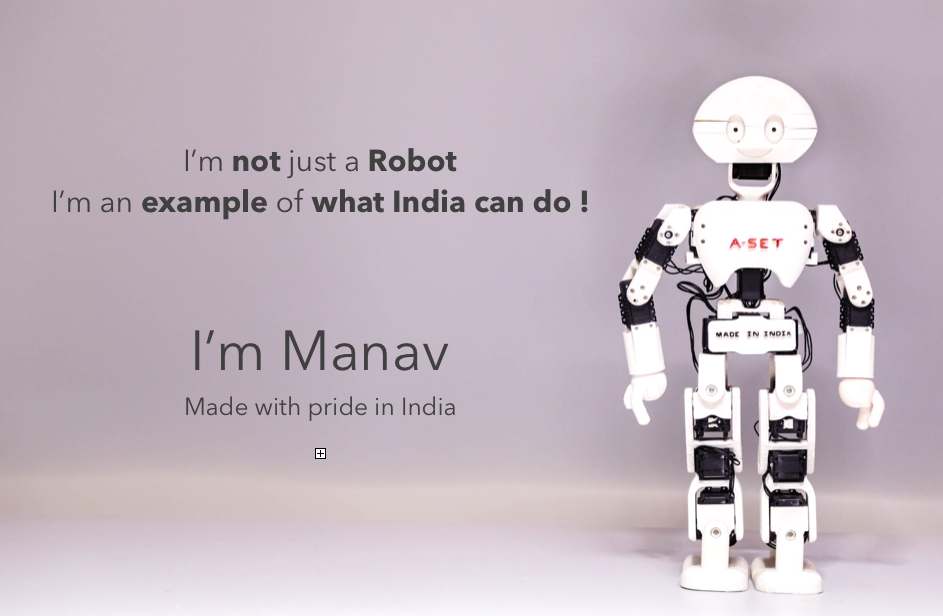
- Manav: Developed by A-SET Training and Research Institutes, Manav is India's first 3D-printed humanoid robot, capable of dancing, soccer playing, and performing other activities.
- Kempa: Greets passengers at the Kempegowda International Airport, Bengaluru, offering directions and information about flights, tourist places, and heritage in Karnataka.
- Shalu: The first female humanoid robot in India made from 100% waste materials, multilingual and educational, capable of speaking 47 languages and recognized for educational interactions.
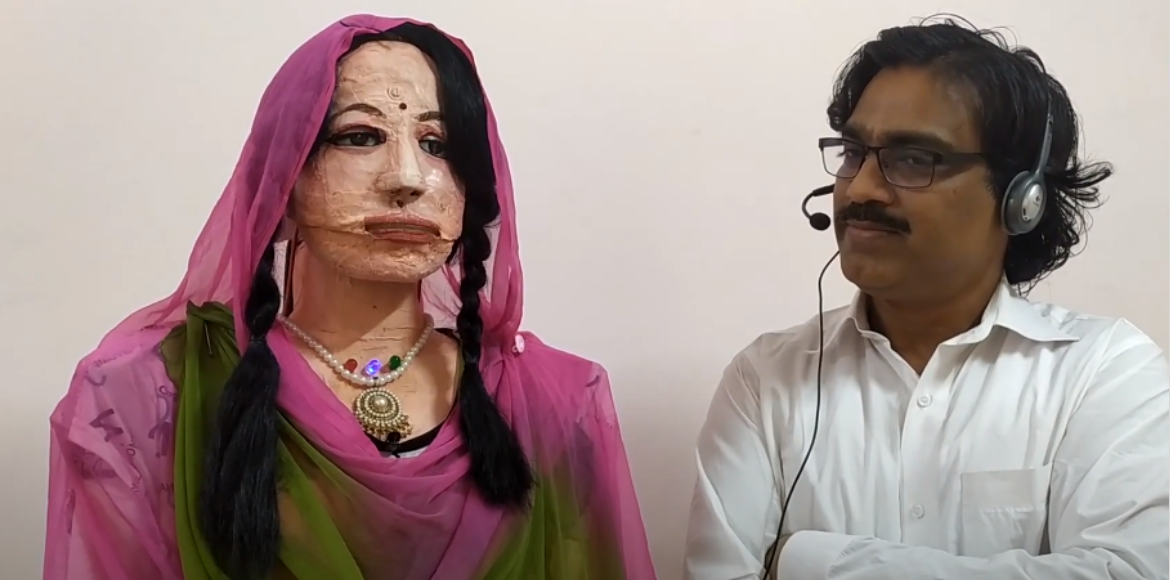

- Sandy: An android-supported humanoid robot created by i-Brain Robotics, designed for companionship with true emotion sensory units and self-learning capabilities.
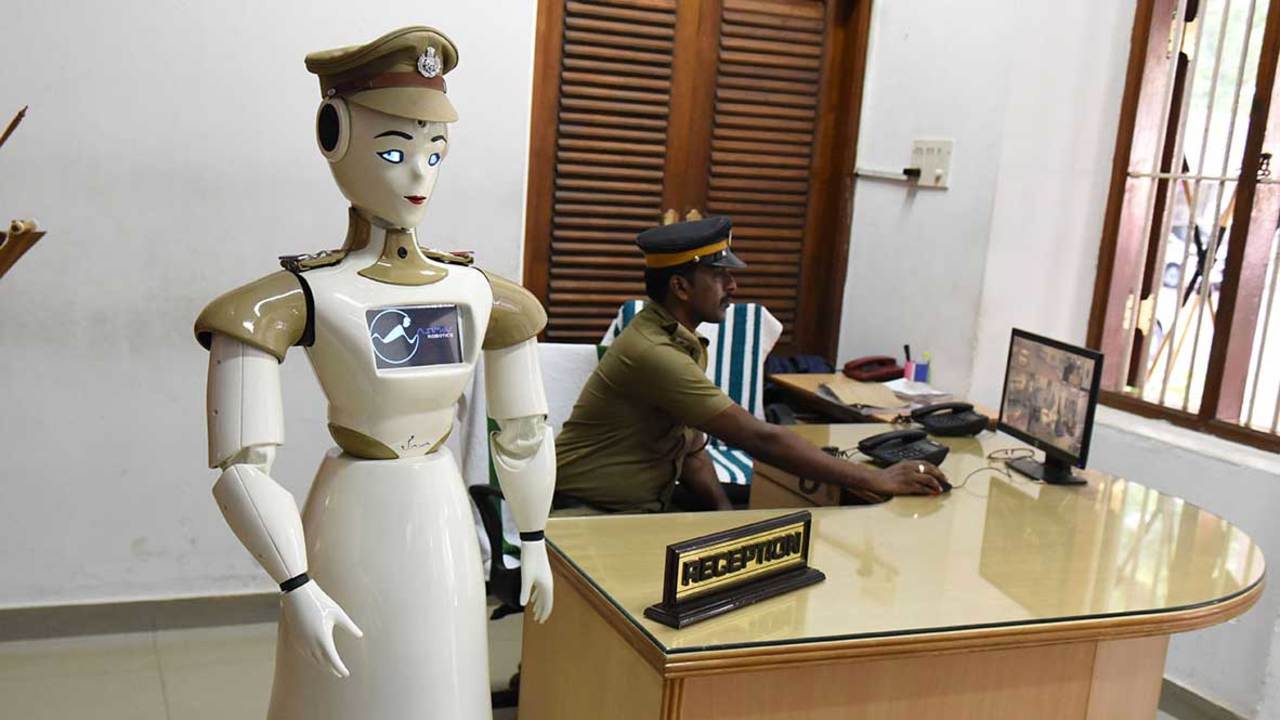
- RoboCop (KP-Bot): Deployed in Kerala, this robot can assist visitors, direct them to various places, and is known for saluting higher-level authorities, enhancing police force efficiency.

- Daksha: The first anti-terror robot developed by the DRDO, equipped for bomb disposal with a battery-powered system, cameras, X-ray devices, and a shotgun for breaching operations.
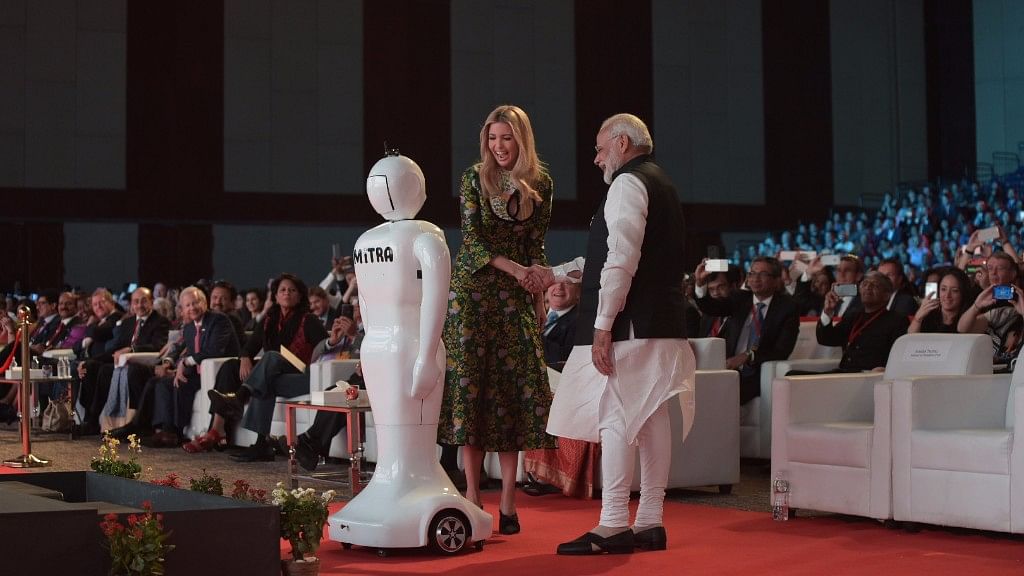
- MiTRA: Built by Invento Robotics, Mitra is an interactive humanoid robot that can converse with customers and visitors, often deployed in banks, airports, and events.

Other Robotic Innovations from India:
- iRASTE: An AI-powered road safety project developed by Intel India, INAI, IIIT Hyderabad, CSIR-CRRI, Mahindra & Mahindra, and NMC. iRASTE focuses on vehicle safety, road infrastructure safety, and vulnerable road user safety to reduce road accidents.
- eYantra: An initiative by IIT Bombay to spread education in embedded systems and robotics, eYantra provides hands-on learning with robots to engineering students across India.
- Agribot: A robot designed to assist in agricultural processes, including plowing, seeding, spraying, and weeding. It's a move towards precision agriculture to increase efficiency and reduce labor.
- EndoMaster: A medical robot co-developed by an Indian-origin scientist in Singapore, used to perform complex surgeries with minimal invasion.
- Genrobotic Innovations: A company known for its robot "Bandicoot", which is used for cleaning sewers and manholes, effectively reducing the need for manual scavenging and enhancing worker safety.
India's focus on robotics reflects its commitment to technology and innovation, and these developments are just the tip of the iceberg in terms of the potential for robotics in the country.
Government's Initiative and Support
The Government of India has initiated several programs aimed at encouraging robotics innovation in the country.
These programs are designed to support research and development in robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and related technologies.

Here are some of the key government initiatives:
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM): Launched by NITI Aayog, AIM includes the establishment of Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) in schools across India, where students have access to tools and equipment to create innovative solutions, including basic robotics.
- Digital India: This flagship program aims to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy. It encourages innovation in robotics as part of its focus on electronic manufacturing.
- Make in India: Launched to encourage companies to manufacture their products in India and incentivize dedicated investments into manufacturing, including robotics.
- Startup India: This initiative provides a platform for startups to access funds, mentorship, and various resources, which includes startups in the robotics sector.
- Skill India: Launched by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, it aims to train over 40 crore people in India in different skills by 2022, including robotics and AI.
- National Programme on AI: Guided by NITI Aayog, the program aims to harness the benefits of AI and robotics for the country's economic transformation.
- Robotics Education Programme: Some states in India have introduced robotics as part of their curriculum in schools and colleges to foster an interest in robotics from an early age.
- SMART India Hackathon: Organized by the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), it encourages students to solve problems with digital and hardware solutions, including robotics applications.
- DST & DBT Programs: The Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) fund research projects in robotics, biotechnology, and AI.
- NewGen IEDC: The New Generation Innovation and Entrepreneurship Development Centre (NewGen IEDC) is a program sponsored by the National Science and Technology Entrepreneurship Development Board (NSTEDB), aimed at inculcating the spirit of innovation and entrepreneurship among students, including robotics innovation.
- Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE): TIDE centers across India support ICT-based innovations, including robotics startups.
- Public Sector Research Funding: Government agencies like the Indian Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) fund and conduct research in robotics and automation.
These initiatives, often in partnership with academic institutions and industry leaders, have positioned India as an emerging hub for robotics and AI innovation.
The programs are not only providing the necessary financial support but are also creating an ecosystem conducive to the exchange of knowledge and fostering entrepreneurship in the field of robotics.
Previous Post