Table of contents
Protecting India's rich biodiversity and ensuring sustainable development requires a dedicated institutional framework. This section sheds light on some of the key environmental institutions in India, helping you understand the intricate web of organizations working to preserve our environment.
From government bodies like the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) to research institutions like the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), we'll explore their mandates and their contributions to environmental protection in India.
WILDLIFE CRIME CONTROL BUREAU (WCCB)
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau is a statutory body set up under the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972.
- It has five regional offices at Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai and Jabalpur and aims to combat organized wildlife crime.
- WCCB is the nodal point for SAWEN (South Asia Wildlife Enforcement Network) in India.
- It has conducted important operations like Save Kurma, Lesknow, Birbil, ThunderBird, Wild-Net and Clean Art.


NATIONAL TIGER CONSERVATION AUTHORITY (NTCA)
- It was established in 2006 as a statutory body constituted under the WPA, 1972.
- The chairperson is the Minister of Environment.
- NTCA provides statutory authority to Project Tiger and addresses the livelihood interests of local people in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
- The State level Steering Committees set up in the Tiger States is formed under the Chairmanship of respective Chief Ministers.


BOTANICAL SURVEY OF INDIA (BSI)
- It was established in 1890 with headquarters in Kolkata
- The body is the apex taxonomic research organization in India and it manages gene banks of threatened and endangered plant species.
- It surveys and documents traditional knowledge (ethno-botany) associated with plants, biosystematics research, floristic studies, digitization of herbarium specimens etc.
- BSI publishes ‘Red Data Book of Indian Plants’.


ZOOLOGICAL SURVEY OF INDIA (ZSI)
- The objective of this body is to promote the survey, exploration and research of the fauna.
- It is headquartered at Kolkata with 16 regional stations located in different geographic locations.
- It owes its genesis to the Asiatic Society of Bengal founded by Sir William Jones in 1784.




FOREST SURVEY OF INDIA (FSI)
- This organization is headquartered in Dehradun and functions under MoEF & CC.
- It conducts survey and assessment of forest resources and the forest cover.
- The Forest Survey Report is a biennial pubication released by FSI since 1987.



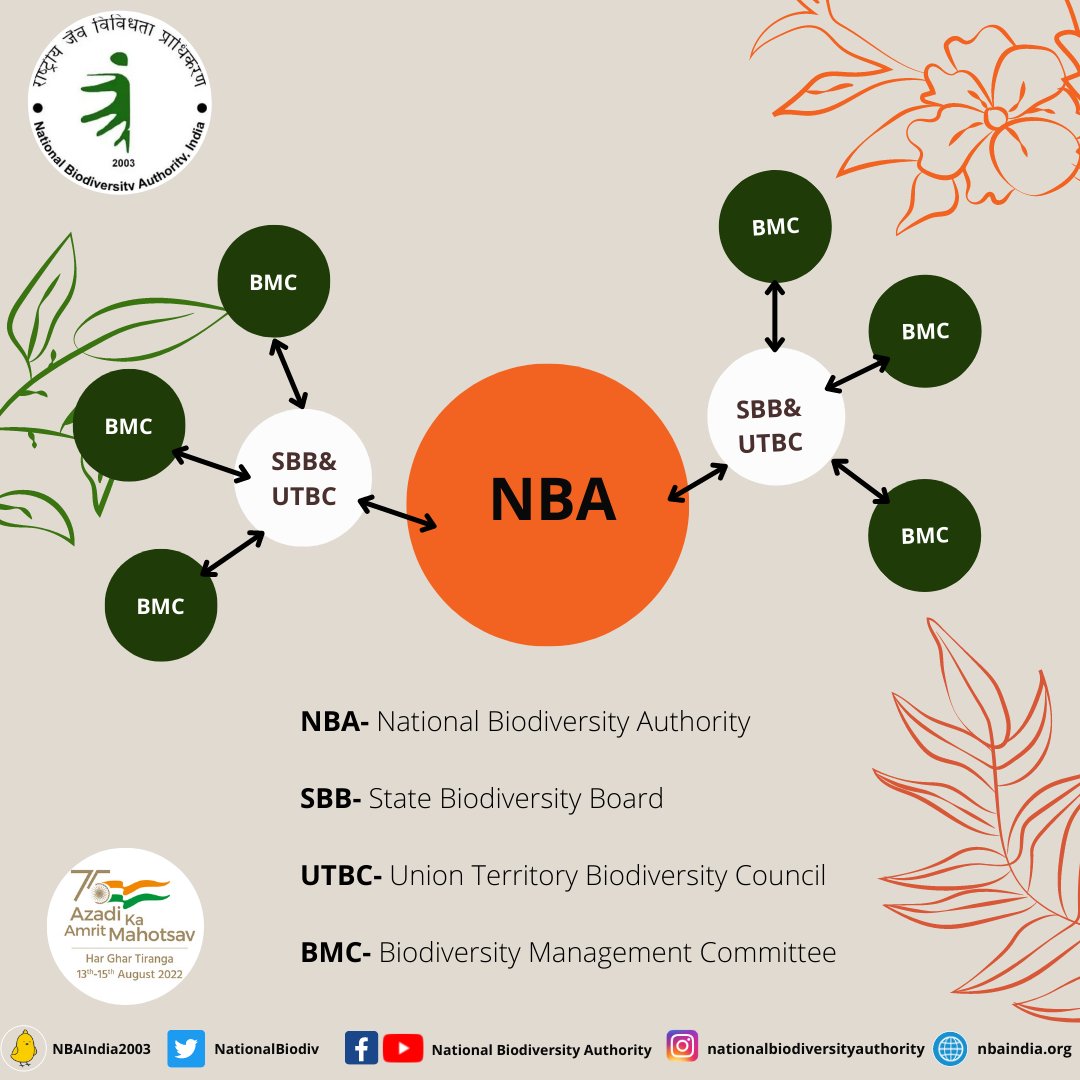
NATIONAL BIODIVERSITY AUTHORITY (NBA)
- NBA is a statutory body under the Biological Diversity Act, 2002.
- It is in line with the Convention on Biological Diversity which India signed it in 1992
- It was established in 2003 with headquarters at Chennai.
- The body performs regulatory & advisory functions on issues of conservation, sustainable use of biological resources.
- It prmotes creation of State Biodiversity Boards and Biodiversity Heritage Sites.

ANIMAL WELFARE BOARD OF INDIA (AWBI)
- It was established in 1962 with a headquarters in Ballabgarh, in Haryana.
- Rukmini Devi Arundale was the first chairperson of AWBI.
- AWBI is a statutory body established under The Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960.
- It administrative ministry is the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.

CENTRAL ZOO AUTHORITY (CZA)
- Central Zoo Authority is a statutory body established under the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972.
- It is headquartered at New Delhi with Ministry of Environment Forest & Climate Change being the administrative authority.
- Its objective is conservation of wildlife, maintaining Indian Zoos on par with International standards and animals exchange.
- Environment minister is the chairperson of this body.


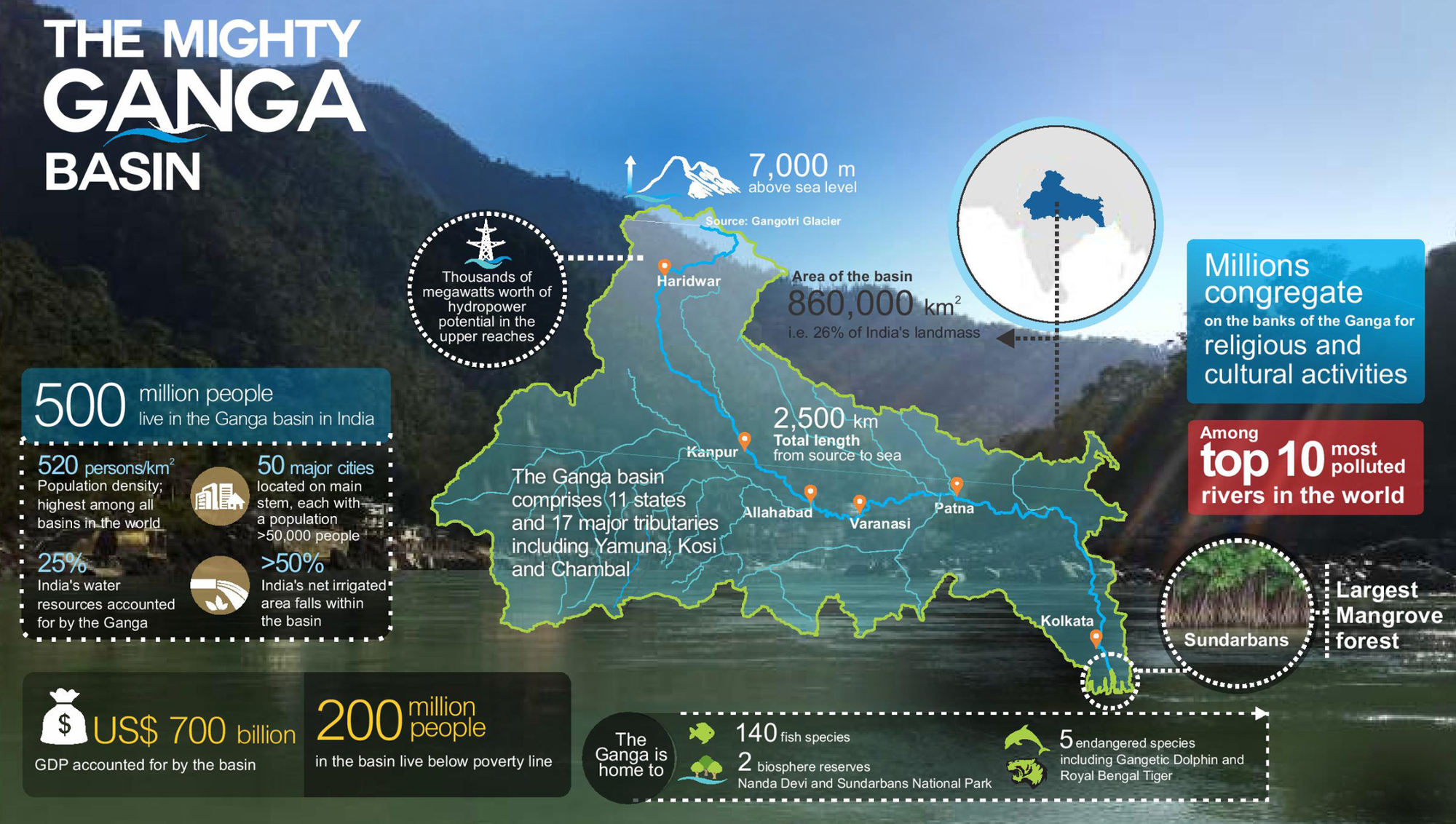
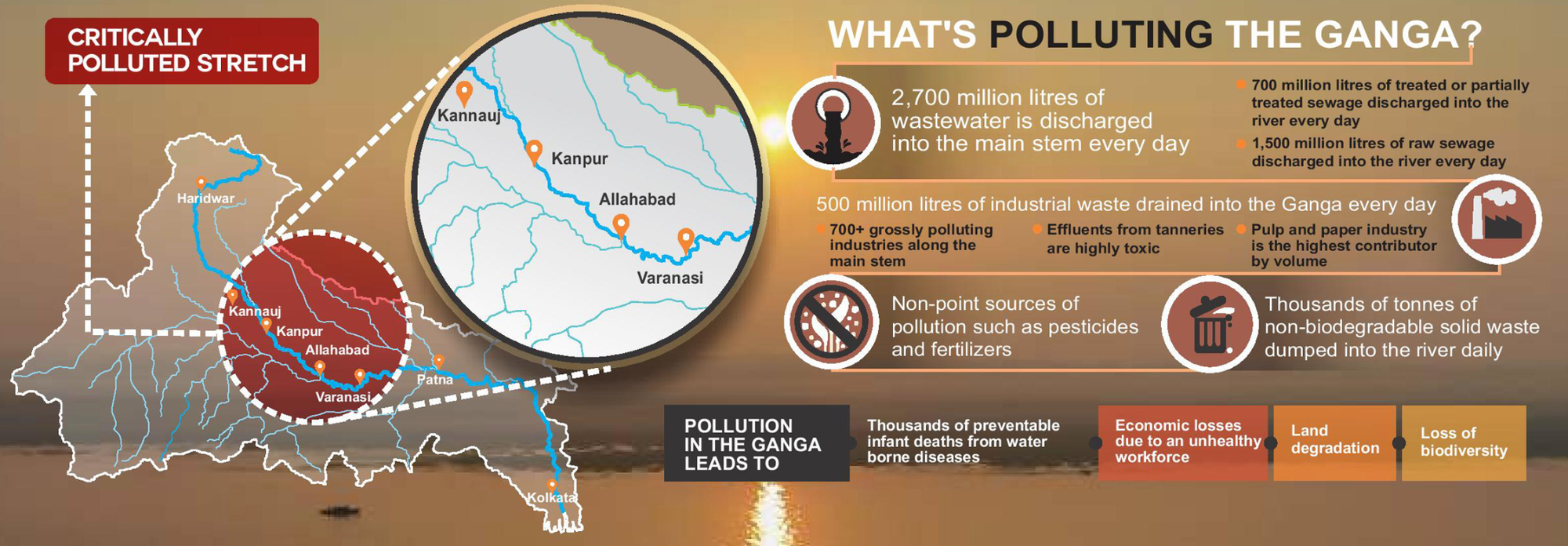
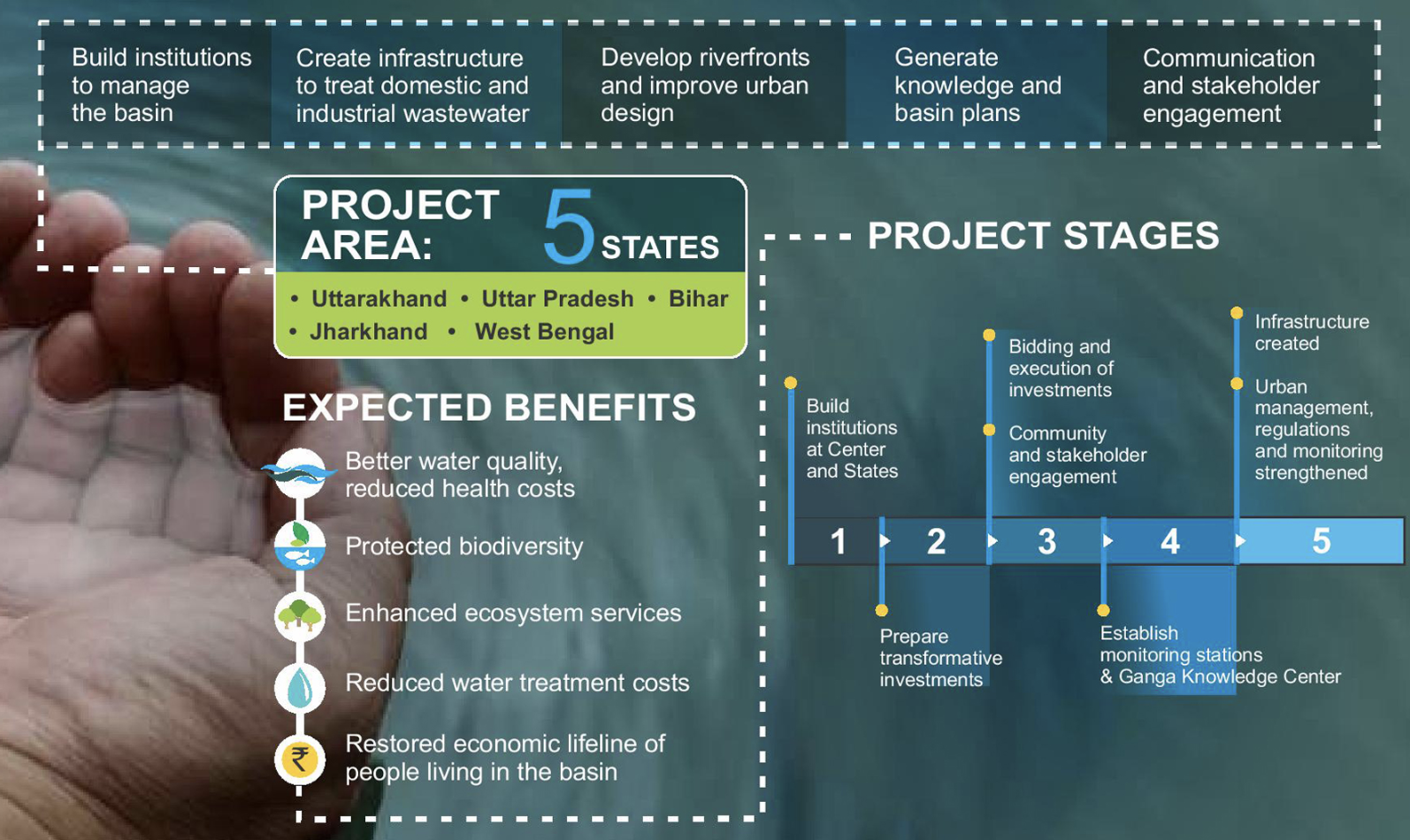
NATIONAL GANGA RIVER BASIN AUTHORITY (NGRBA)
- The authority was established in 2009 and works under the administrartive control of the under Ministry of Jal Shakti.
- Its objctive is to address the pollution and conservation of the river Ganga.
- The chairma of NGRBA is the Prime Minister.
- The members include related union ministers and the Chief Ministers of the States through which Ganga flows.
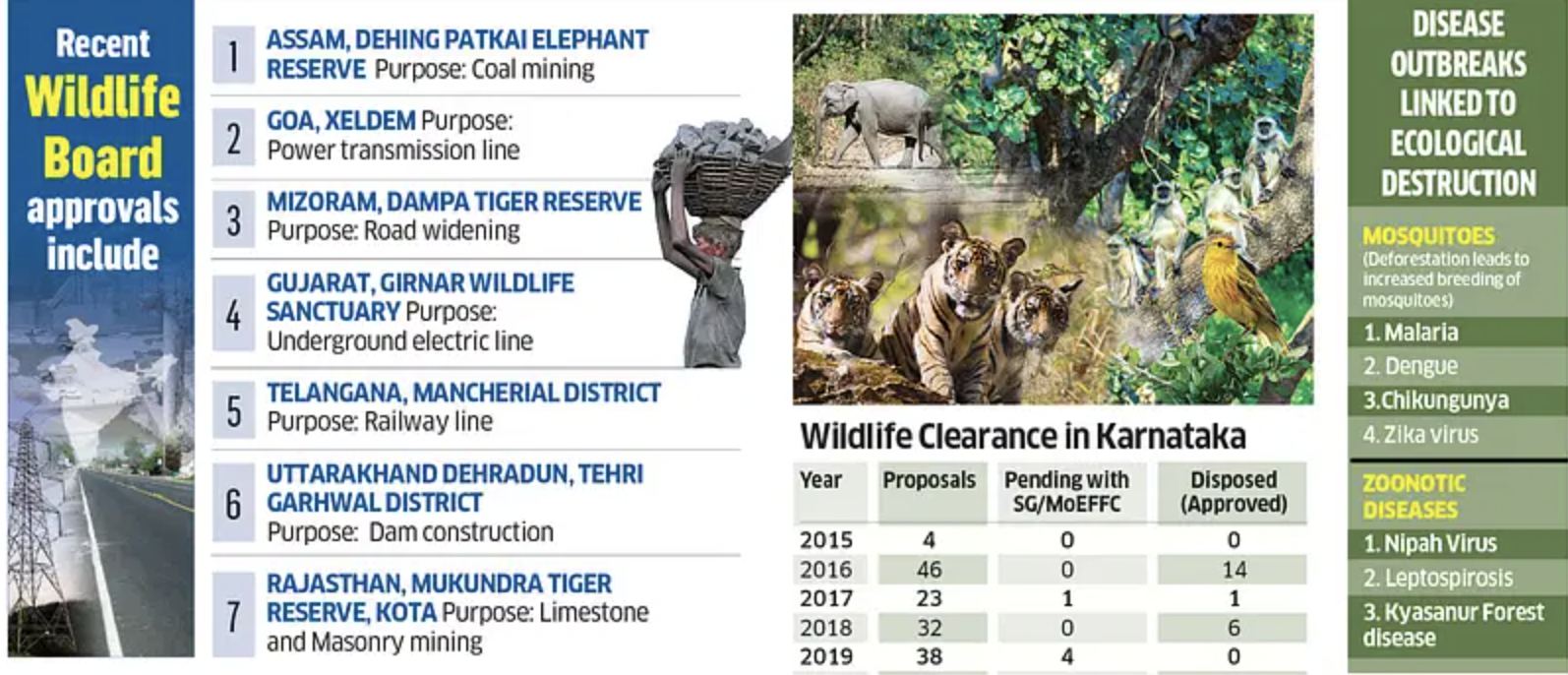
NATIONAL BOARD FOR WILDLIFE (NBWL)
- Formed it 2003, it replaced the ‘Indian Board for Wildlife’ which was formed in 1952.
- It is a statutory body constituted under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
- The NBWL is composed of the Prime Minister as chairperson and the Minister of Environment as vice chairperson.
- It aims to promote the conservation and development of wildlife and forests.
- No alteration of boundaries in National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries can be done without approval of the NBWL.