Table of contents
8 Must-Know Economy Concepts for UPSC Prelims
Acing the UPSC Prelims requires a strong foundation in core subjects like Economics. But don't worry, aspirants! This guide tackles eight essential economic concepts that frequently appear in the exam. Understanding these concepts will not only strengthen your overall economic knowledge but also equip you to tackle related questions with confidence.
GDP and GDP deflator
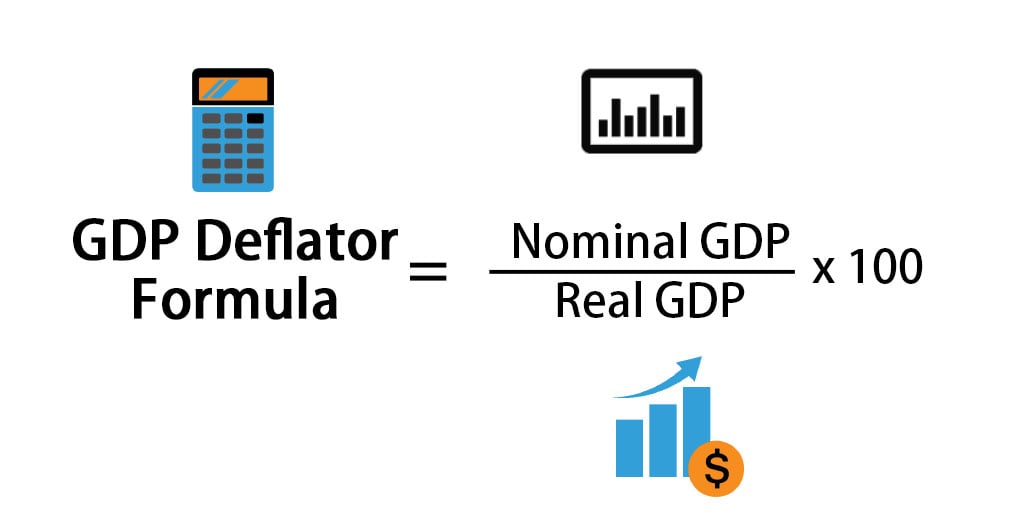
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the measure of the value of the economic activity within the country.
- It is the sum of the final prices of the goods and services produced in an economy in a given period.
- The government moved to a new base year of 2011-12 from earlier 2004-05 for national accounts, in January 2015.
- Also, the Central Statistics Office adopted the international practice of using gross value added at basic prices rather than using Gross Domestic Product at factor cost.
- GDP Deflator is a gauge of inflation which measures the average price changes in all components of GDP across the entire economy. A rising GDP Deflator indicates inflation, which can affect purchasing power of consumers.
Inflation
- A sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time.
- It reflects the rising cost of living and indicates the expensiveness of a set of goods and services over a specified period.
- There are many types of inflation based on different parameters. Like cost push and demand pull inflation, headline and core inflation, and based on intensity, it includes Stagflation, creeping inflation, galloping inflation, hyper inflation etc.
Unemployment
- Unemployment is a condition where individuals capable of working are actively seeking employment but are unable to secure it.
- The Periodic Labour Force Survey by NSSO gives key employment indicators like the Labour Force Participation Rates, Worker Population Ratio, Unemployment Rate etc.
- India’s unemployment rate has dropped to 3.1% in 2023 from 3.6% in 2022 and 4.2% in 2021.
- There are many types of unemployment like structural, cyclical, frictional, disguised, seasonal and technical.
We can't clear UPSC for you.
But with our personalised mentor support, you'll be ready to do it yourself.
Fiscal Policy
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-fiscal-policy-types-objectives-and-tools-3305844-final-5b4e4a59c9e77c005bbfde3a.png)
- Fisc means a state treasury or exchequer and Fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection (mainly tax and non-tax sources such as divestment, loans) and expenditure to control the economy.
- Health of fiscal policy depends on surplus and deficit. If revenue is more than expenditure, there is a surplus while if expenditure is more than revenue, there is a deficit.
- Fiscal policy and monetary policy plays an important role in managing the economy.
Monetary Policy

- It is a policy to regulate the money supply and interest rates to achieve economic stability.
- The policy is regulated by the central bank of a country by controlling the interest rates and the money supply.
- Its main objective is to maintain price stability and ensure growth is not affected by it.
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 was amended by the Finance Act, 2016 for a statutory and institutionalized framework by the Monetary Policy Committee.
- It's a six member committee headed by the RBI governor.
Balance of Payments
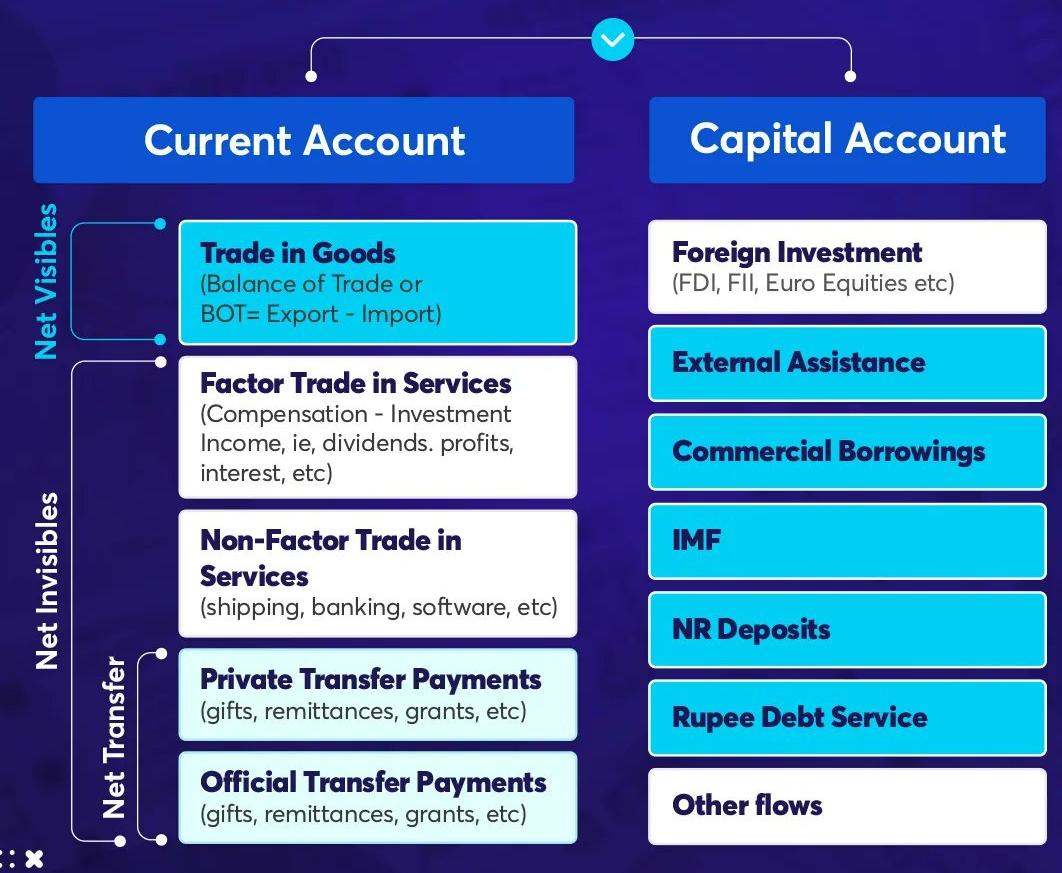
- It is simply the balance of exports and imports from a country and into the country respectively, of the goods and services.
- Balance of payments data for Q3FY23 reveals a significant improvement in the current account deficit reducing to 2.2% of GDP from the previous quarter’s 3.7%.
- This is driven by decrease in merchandise trade deficit and an increase in services trade and remittances.
WPI
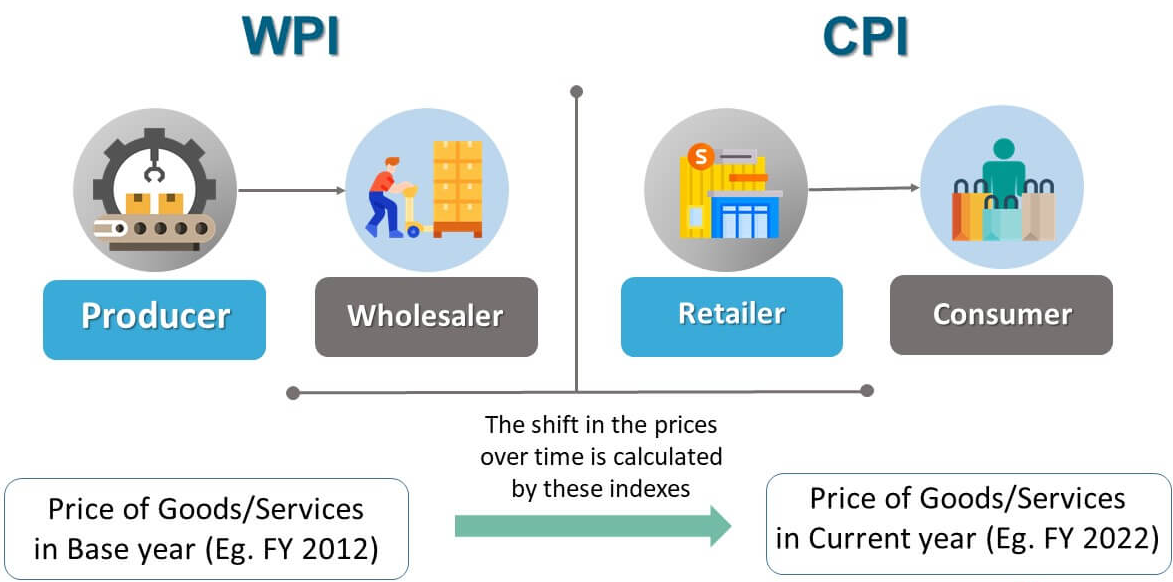
- The index is compiled by the Office of the Economic Adviser in the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, and is important for calculating inflation.
- It depicts the price of a basket of wholesale goods traded between corporations and not those goods purchased by the consumers.
- It also depicts demand and supply parameters in manufacturing, construction and industry.
- By this, it measures the macroeconomic as well as microeconomic conditions of an economy.
CPI

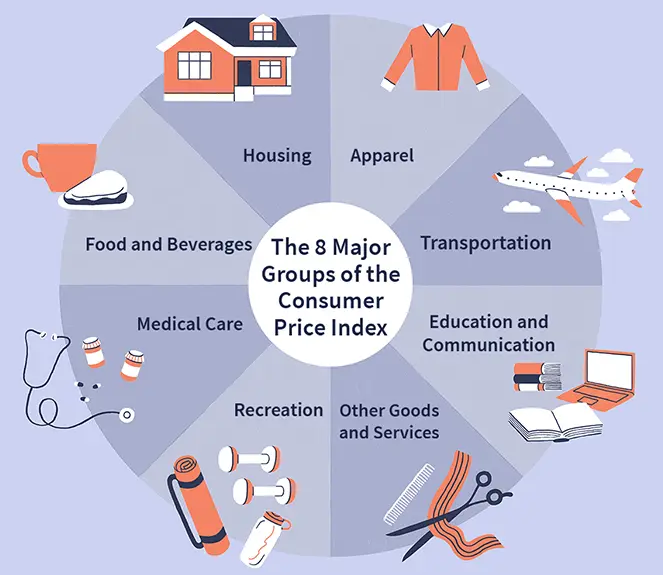
- The Consumer Price Index or market basket is used to calculate the retail inflation in the country as it measures the price changes of a basket of consumer goods and services bought by households.
- It is of four types viz-
- CPI Industrial Workers (CPI-IW)
- CPI Agricultural Laborers (CPI-AL)
- CPI Rural Labourer (CPI-RL)
- CPI Urban Non-Manual Employees (CPI-UNME)
- CPI can be used to regulate prices, find real value of wages, salaries, and pensions and to deflate monetary magnitudes.
