Table of contents
Relevance to UPSC CSE
-
UPSC Prelims: General issues on Environmental Ecology, Biodiversity and Climate Change
-
UPSC Mains (GS-3): Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment.
What is Climate Anxiety?
Climate anxiety, or eco-anxiety, is distress related to worries about the effects of climate change. It is not a mental illness. Rather, it is anxiety rooted in uncertainty about the future and alerting us to the dangers of a changing climate.
It is also called ‘climate change crisis’, ‘eco-angst’, ‘eco-trauma’ and ‘ecological grief’.
According to The Lancet, Climate anxiety and dissatisfaction with government responses are widespread among children and young people in countries across the world and impact their daily functioning.
Is it common to face climate anxiety?
- More than two-thirds of Americans experience some climate anxiety. (Source - A survey by the American Psychological Association)
- 84% of children and young adults ages 16 to 25 are at least moderately worried about climate change, and 59% are very or extremely worried (Source-The Lancet)
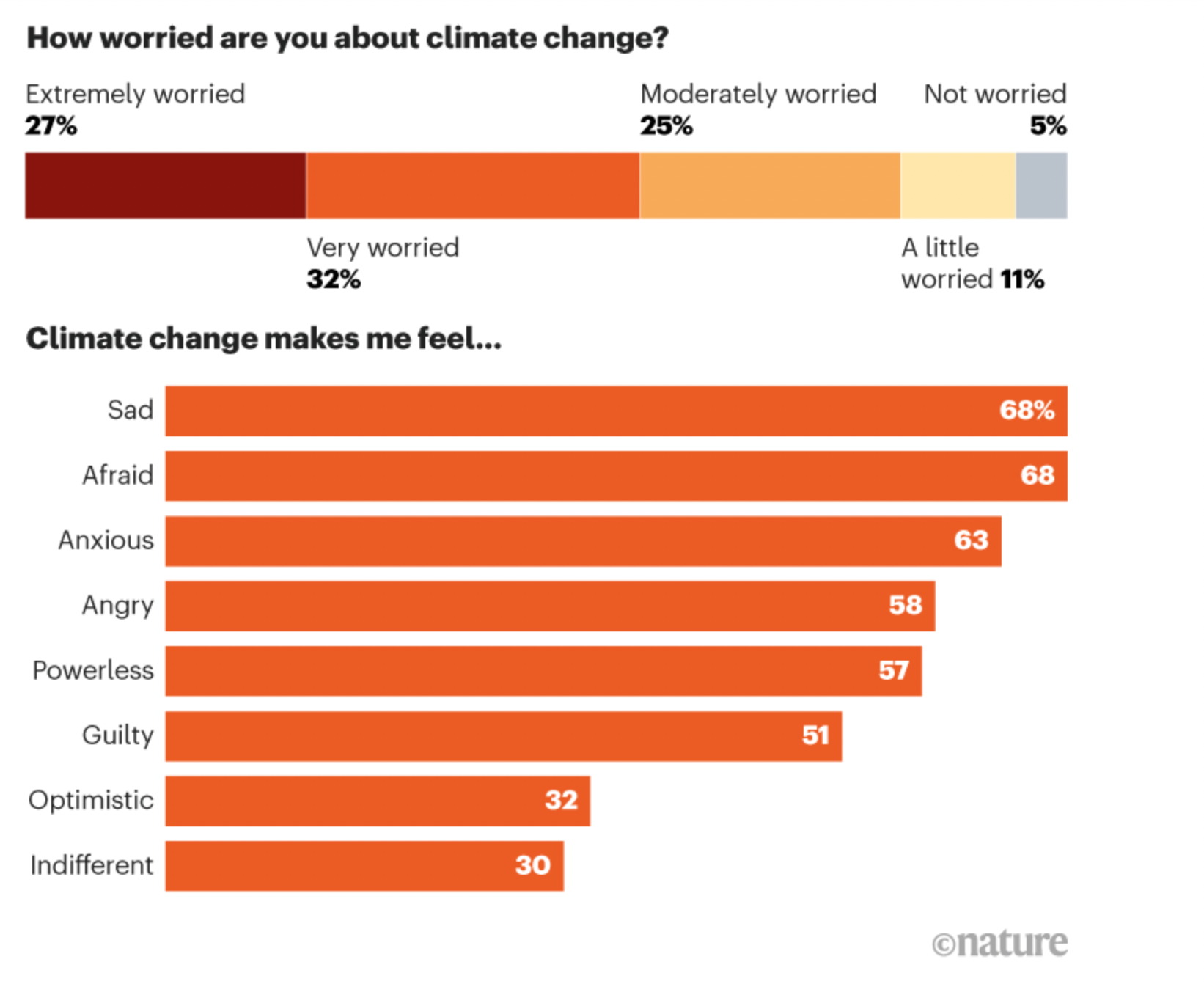
Here are the figures on climate anxiety published in The Nature Magazine -
Why climate anxiety is more in children/young adults?
- Children and young adults will disproportionately suffer the consequences of environmental changes.
- Children and young adults are also particularly vulnerable to chronic stress in general. Climate worries add to it
Symptoms of Climate Anxiety
- Grief and sadness over the loss of natural environments or wildlife populations
- Anger or frustration- Specifically toward people who don’t acknowledge climate change or towards older generations for not making more progress
- Obsessive thoughts about the climate
- Guilt or shame related to your own carbon footprint
- After experiencing effects of climate change - Post-traumatic stress (eg. Psychosomatic stress experienced by people of Kerala after floods)
- Feelings of depression, anxiety, or panic
- An existential dread - feeling as if you’ve reached a standstill
These feelings can contribute to secondary issues, like:
- Difficulty in focusing
- Appetite changes
- Sleep problems
How to manage Climate Anxiety?
- Best treatment is to take action against climate change, pollution, etc.
- On an individual level, it’s therapeutic to share your worries and fears with trusted friends, a therapist, or by joining a support group.
- Make changes to your lifestyle consistent with your values.
Examples
- Using eco-friendly products such as steel straw instead of plastic straw
- Choosing physical commuting, such as biking or walking, over driving can improve your physical and mental health while reducing carbon emissions.
- Active participation in Environmental protests/movements. Eg. Save soil movement or contribute in increasing public awareness about climate change through advocacy.
- Joining an organization like The Good Grief Network. It can help you process feelings related to climate anxiety and connect with others to take meaningful action.
- Talk about climate anxiety
Conclusion
Emotional turmoil related to climate change may seem less pressing than the tangible, serious damage many people already face around the world. But it’s still essential to take notice of these feelings instead of blocking them out. Awareness, after all, is the key to change.
Previous Post
