Table of contents
Here are the terms in the news involving "CARBON":
Carbon Sequestration
- Carbon sequestration is a technique of removing carbon from the atmosphere and its long-term storage in soils, geological formations, plants and the ocean.
- Carbon dioxide is naturally captured from the atmosphere via biological, chemical, and physical processes or it can be man made also.
- Sequestration can be accelerated by changing land use patterns and agricultural practices like converting crop and livestock grazing land to land for non-crop fast-growing plants.
- Artificial capture and sequestration of industrial carbon dioxide is done using subsurface saline aquifers, aging oil fields, reservoirs, ocean water etc.
Carbon Capture & Storage
- CCS involves different technologies that capture CO2 emissions from large sources like refineries or power plants and trap them beneath the Earth.
- It is different from the carbon dioxide removal process (CDR) in which CO2 is removed from the atmosphere.
- CCS is a three-step process viz capturing the carbon dioxide produced by industry, transporting it and storing it underground.
- It is done using three techniques:
- Post-combustion
- Pre-combustion
- Oxyfuel combustion
- Post-combustion involves the removal of CO2 after the fossil fuel has been burnt by using a chemical solvent.
- Pre-combustion involves removing CO2 before burning the fossil fuel or burning it partially to form synthetic gas.
- Oxyfuel combustion involves burning fossil fuel with pure oxygen to produce CO2 and water vapour.
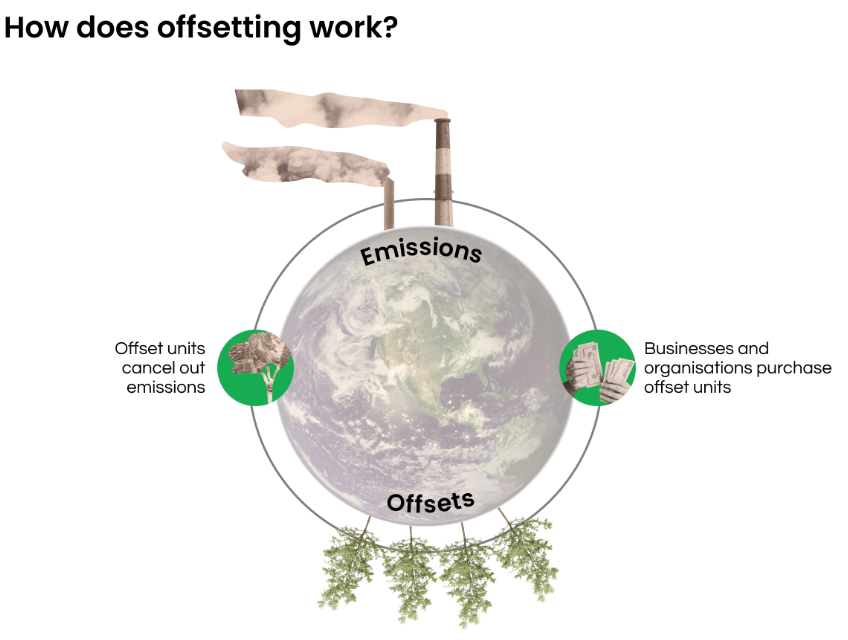
Carbon Offsetting
- Carbon offsets are tradable “rights” or certificates in exchange for activities that decrease carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- These certificates help a person, an industrial group or governments to fund projects that fight climate change by offsetting CO2 emissions with an equal amount of CO2 reductions.
- For offsetting, entities calculate their carbon footprint and then purchase carbon credits from projects that remove the equivalent amount of carbon dioxide, where one carbon credit is equal to one tonne of carbon dioxide removed from the atmosphere.
- Carbon offsets specifically fund projects which are aimed at lowering or sequestering CO2 emissions.

Carbon Farming
- Carbon farming is a combination of concepts of carbon and farming by use of regenerative agricultural practices to prevent soil degradation, climate variability challenges and water scarcity.
- Some forms of Carbon Farming include rotational grazing, agroforestry, agroecology, livestock management, conservation agriculture, integrated nutrient management and land restoration.
- Carbon Farming requires certain conditions, such as long growing seasons, substantial irrigation, and adequate rainfall, which aid fast vegetation growth.
- Initiatives by the Indian government include-
- Green Credit Scheme
- National Mission on Natural Farming
- Some global initiatives include:
- Chicago Climate Exchange and the Carbon Farming Initiative
- Kenya’s Agricultural Carbon Project
Carbon Credit
- Carbon credit is like a license that permits the business entity to emit a certain amount of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gasses.
- It is a component of the "cap-and-trade" programme in which polluters are given credits allowing them to pollute to a certain limit.
- If there are any unsold credits, a company can sell it to another company that requires them.
- The types of Carbon Credit include-
- Voluntary Emissions Reduction-
- It is a carbon offset traded for credits in the voluntary market.
- Certified Emissions Reduction-
- It is based on emission units through a regulatory framework to offset for a project.
- Voluntary Emissions Reduction-

Carbon Budget
- As per a report, developed countries have consumed more than 80 percent of the global carbon budget.
- Carbon budget is the amount of greenhouse gasses that can be emitted but ensures that global warming is contained within 1.5 degrees centigrade compared with pre-industrial levels.
- A limit is set on the total amount of CO2 that can be emitted over a certain period of time which is divided among different countries or sectors based on their population, historical emissions and economic activity.
- At 2.4 tCO2e (tonne carbon dioxide equivalent), India’s per capita greenhouse gas emission is less than the global average of 6.3 tCO2e as per UNEP.
Embodied Carbon
- Embodied carbon involves carbon dioxide emissions originating from materials and construction processes during the lifecycle of a building or infrastructure.
- Carbon dioxide is released during the manufacturing of building materials, its demolition and transportation.
- Simply said, embodied carbon is the carbon footprint of a building or any infrastructure before its operationalization.
- Data from the World Green Building Council suggests that embodied carbon is contributing more to a building's overall carbon footprint.
- Embodied carbon is different from operational carbon (carbon released from energy, heat, lighting, etc).

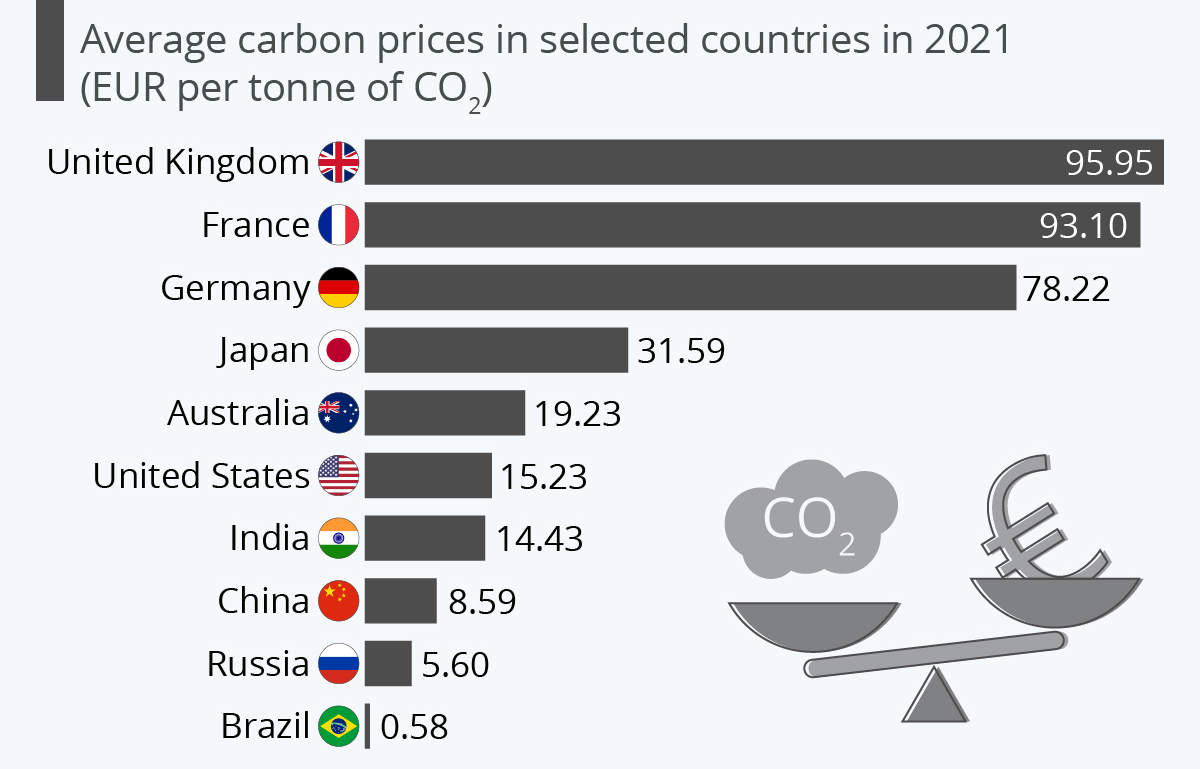
Carbon Tax
- David Gordon Wilson proposed a carbon tax for the first time in 1973.
- A carbon tax is levied as a fee for making fossil fuel users pay for damage to the climate and the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
- The goal of carbon tax is to reduce fossil fuels usage and incentivize usage of alternative energy sources.
- Human activity produces 27 billion tonnes of CO2 per year globally.
- India introduced carbon tax in 2010 which is currently Rs.400/tonne.