Table of contents
The term "Anglo-Wars in India" refers to a series of conflicts fought between the British East India Company (EIC) and various Indian kingdoms and empires over a period of about two centuries, from the 17th to the 19th centuries. These wars played a pivotal role in establishing British colonial rule over the Indian subcontinent.
Battle of Plassey 1757
- Fought between the East India Company led by Robert Clive vs. the Nawab of Bengal (Siraj-Ud-Daulah).
- It was a historic turning point for the British in India as EIC won and established the political and military supremacy of the British in Bengal.


Battle of Buxar 1764
- The British East India Company led by Hector Munro vs the combined armies of Mir Qasim (Nawab of Bengal); Shuja-ud-Daulah (Nawab of Awadh); and Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II.
- The English won and Treaty of Allahabad 1765 was signed which established British supremacy in North India.



The Carnatic Wars



First Carnatic War (1740-48)
- The First Carnatic War was an extension of the Anglo-French War caused by the Austrian War of Succession.
- The Battle of St. Thome (in Madras) was fought among the French forces, the Nawab of Carnatic Anwar-ud-din and the British.
- It ended in 1748 when the Treaty of Aix-La Chapelle was signed.
Second Carnatic War (1749-54)
- Nizam-ul-Mulk, the Mughal governor of the Deccan died in 1748.
- Nasir Jang, the son of the Nizam acceded to the throne of Hyderabad which was opposed by Muzaffar Jang, grandson of the Nawab.
- Anwar-ud-Din had been appointed Nawab of the Carnatic in 1743 which was resented by Chanda Sahib.
- The French supported Muzaffar Jang and Chanda Sahib while the English sided with Nasir Jang and Anwar-ud-din.
- Muzaffar Jang, Chanda Sahib and the French defeated and killed Anwar- ud-din at the Battle of Ambur (near Vellore).
- Robert Clive suddenly raided Arcot and Chanda Sahib was executed by Muhammad Ali who was later installed as the Nawab of Carnatic.
Third Carnatic War (1758-63)
- The French under Count Thomas Arthur de Lally captured the English forts of St. David and Vizianagaram in 1758.
- The English General Eyre Coote routed the French army under Count de Lally at Wandiwash.
Anglo-Mysore Wars

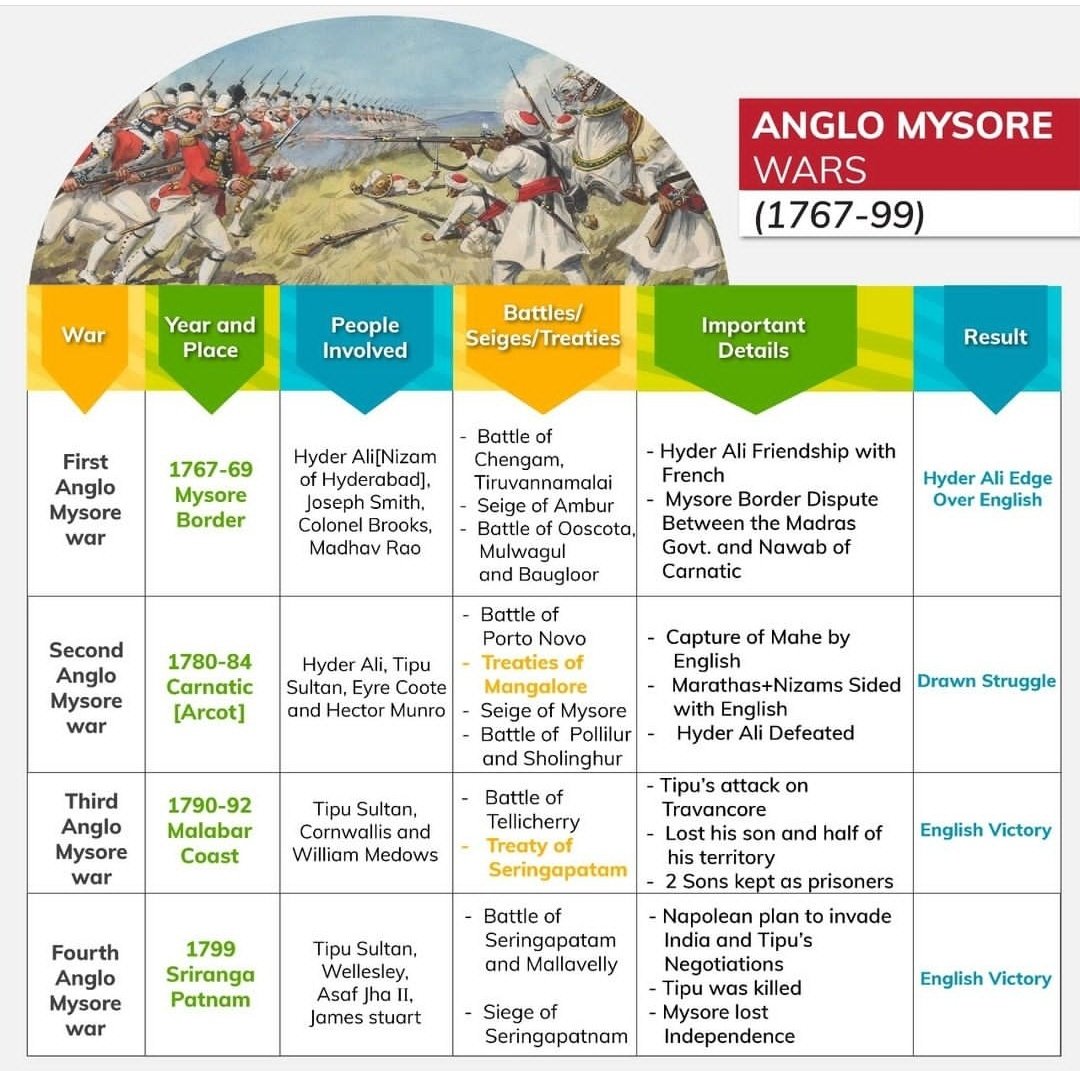
First Anglo-Mysore War (1767-69)
- It started when the East India Company joined the Nizam of Hyderabad against Hyder Ali in return for the cession of the Northern Sarkars.
- The British, Marathas and the Nizam declared war on Mysore.
- Hyder Ali took Marathas and the Nizam to his side which resulted in his victory and the Treaty of Madras was signed.
Second Anglo-Mysore War (1780-84)
- The Marathas attacked Mysore in 1771, and the British refused to honour the Treaty of Madras.
- But Hyder Ali made an alliance with the Nizam and the Marathas and defeated the British forces in Arcot.
- Treaty of Mangalore was signed.
Third Anglo-Mysore War (1786-92)
- Tipu Sultan succeeded Hyder Ali and took French help in modernizing the military.
- Tipu declared war on Travancore in 1789, a friendly state of the British.
- The English were led by Lord Cornwallis and war ended with the Treaty of Seringapatam.
Fourth Anglo-Mysore War (1799)
- Tipu refused to accept the Subsidiary Alliance of Lord Wellesley, due to which the English, along with Marathas and Nizams, attacked Tipu.
- The British won at Seringapatam and Tipu’s territories were divided between the British and the Nizam of Hyderabad.
Anglo-Maratha War

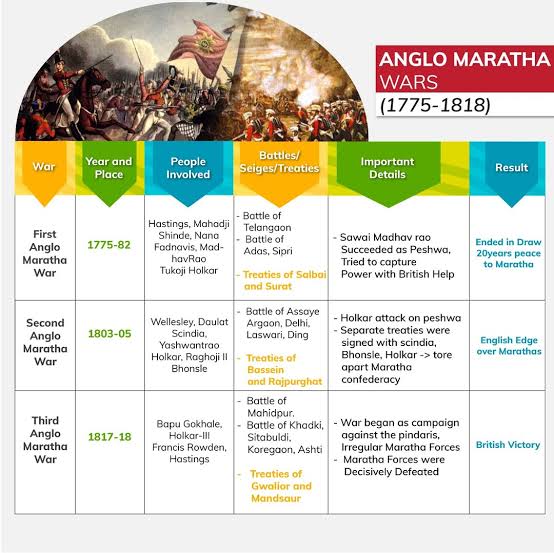
First Anglo-Maratha War (1775-1779)
- The death of Madhav Rao resulted in infighting, and Nana Phadnavis granted a port on the west coast to the French.
- The Marathas, under Mahadji Shinde, won against the English at the battle of Wadgaon.
Second Anglo-Maratha War (1803-05)
- In the Battle of Poona, Yashwant Rao Holkar defeated the Peshwas and the Scindias.
- Baji Rao II sought British protection and signed the Treaty of Bassein.
- Scindias and the Bhonsles rejected this treaty, and a second Anglo-Maratha war started.
- Large parts of central India came under British control.
Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817-18)
- It was started due to the British conflict with the Pindaris.
- The Maratha chiefs Peshwa Bajirao II, Malharrao Holkar and Mudhoji II Bhonsle forged a united front against the English but the British won decisively.
Anglo-Afghan War


First Anglo-Afghan War
- Governor General Lord Auckland ordered the invasion of Afghanistan in 1838 due to growing Persian and Russian influences.
- The fortress of Ghazni was breached and the British restored Shah Shuja to the throne.
- New governor-general of India, Lord Ellenborough, retreated from Afghanistan, Dost Moḥammad was restored to the throne in 1843 and the Treaty of Peshawar (non-interference) was signed.
- The death of Maharaja Ranjit Singh in 1839 and the end of the First Anglo-Afghan War gave way to a series of Anglo-Sikh Wars.
Second Anglo-Afghan War
- Under Viceroy Lytton, the British attacked Afghanistan, and Sher Ali fled his capital in 1878.
- Sher Ali’s son, Yakub Khan, signed the ‘Treaty of Gandamak’ for peace.
- In 1880, Ripon replaced Lytton as the Viceroy and the policy of non-interference was continued.
Anglo-Sikh War


First Anglo-Sikh War (1845-46)
- After the death of Ranjit Singh, the Sikh forces crossed the Sutlej and took the offensive against the English forces.
- Maharaja Duleep Singh was against the British but the latter won and the Lahore Treaty was signed.
Second Anglo-Sikh War (1848-49)
- The battle was fought near Chenab and was won by the British forces.
- The famous Koh-i-Noor diamond went into British hands.
