Table of contents
India has been actively pursuing bilateral partnerships to secure critical minerals, recognizing their importance for economic growth, technological advancement, and national security.
These partnerships aim to diversify supply sources, reduce dependency on a few dominant suppliers, and ensure a stable and sustainable supply chain.
Here are some key bilateral partnerships and initiatives through which India procures critical minerals:
India-U.S. Partnership

- Objective: Enhance cooperation on critical minerals, including graphite, gallium, and germanium.
- Initiatives:
- Bilateral Agreement: India and the U.S. are working towards a bilateral agreement to strengthen supply chains for critical minerals.
- Co-Investment: Promoting India's role in the mineral security partnership by co-investing in lithium resource projects in South America and rare earth deposits in Africa.
- iCET Dialogue: The India-U.S. Initiative for Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET) dialogue aims to drive collaboration in critical mineral supply chains.
India-Australia Partnership

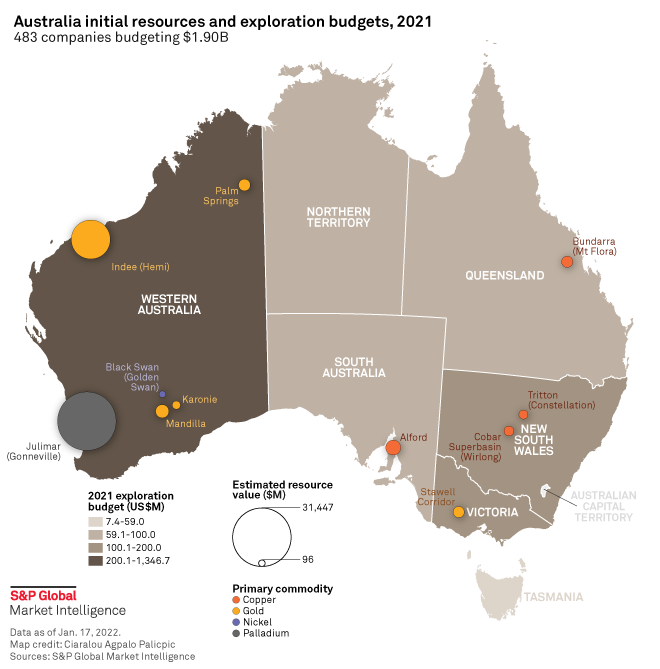
Understanding these bilateral initiatives, their geopolitical implications, and the policies driving them is essential for UPSC preparation
- Objective: Secure supplies of lithium and other critical minerals.
- Initiatives:
- KABIL Ventures: Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL) is exploring opportunities to acquire lithium and other critical mineral assets in Australia.
- Strategic Agreements: India and Australia have signed agreements to collaborate on the mining and processing of critical minerals.
India-Argentina Partnership


- Objective: Access lithium resources.
- Initiatives:
- KABIL Ventures: KABIL is actively exploring lithium mining opportunities in Argentina, part of the "Lithium Triangle" known for its rich lithium reserves.
- Bilateral Cooperation: Strengthening bilateral ties to facilitate investment and technology exchange in the mining sector.
India-Chile Partnership
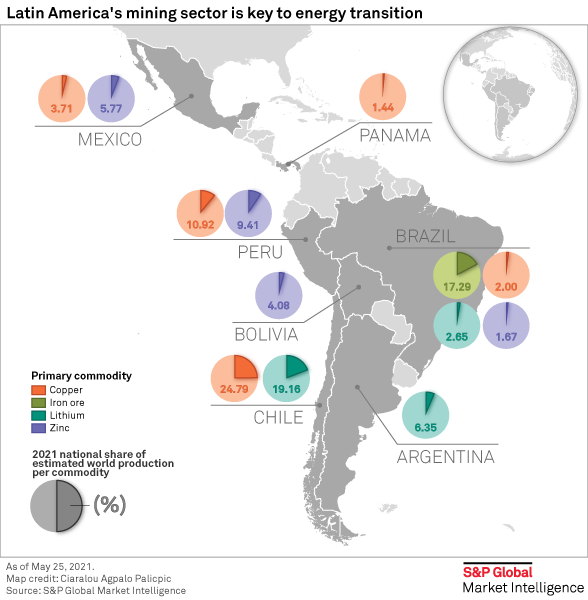
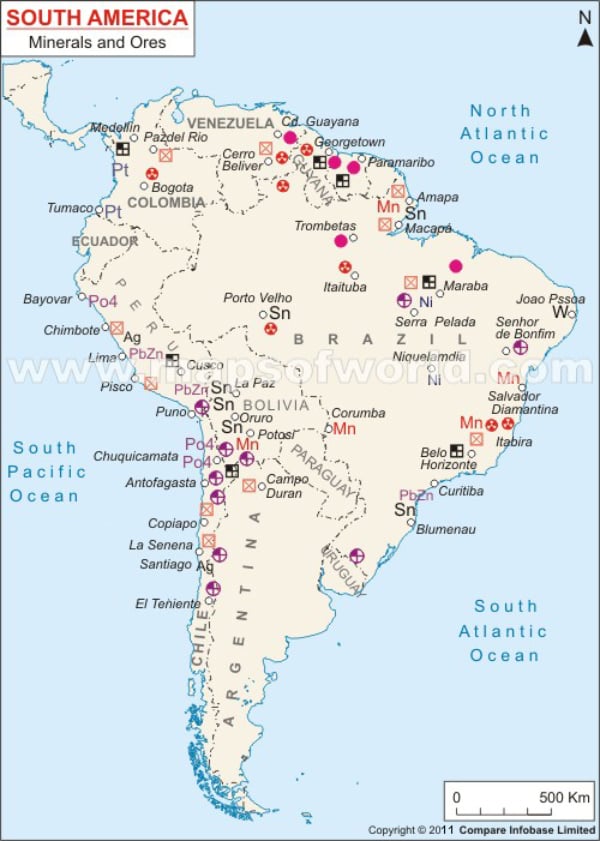
- Objective: Secure lithium and other critical minerals.
- Initiatives:
- KABIL Ventures: KABIL is also exploring lithium mining opportunities in Chile, another key player in the "Lithium Triangle."
- Bilateral Agreements: India and Chile have agreements to enhance cooperation in mining and mineral processing.
India-Africa Partnerships
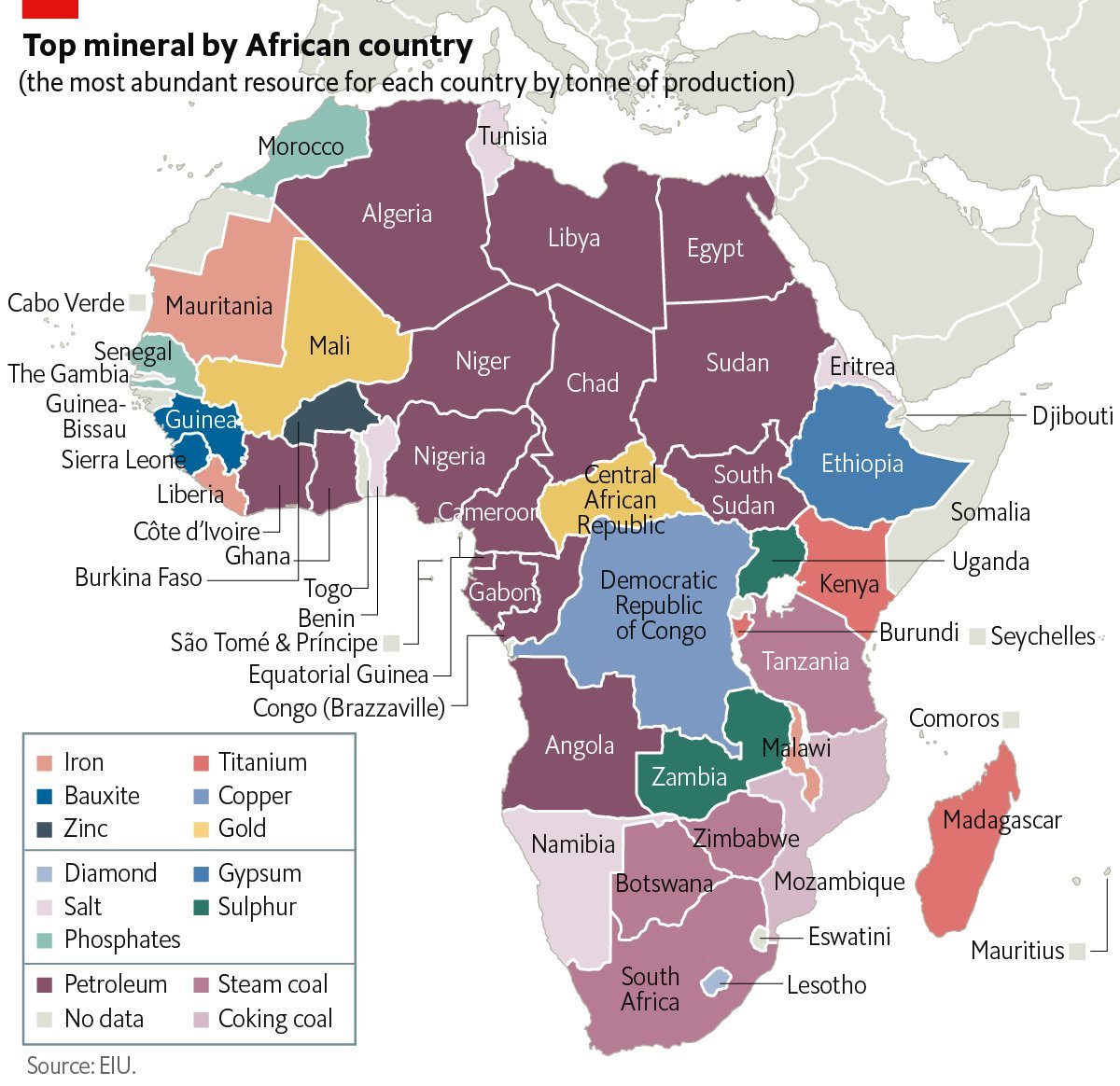

- Objective: Diversify sources of rare earth elements (REEs) and other critical minerals.
- Initiatives:
- Investment in Africa: India is exploring opportunities to invest in rare earth deposits in African countries.
- Bilateral Cooperation: Strengthening ties with African nations to facilitate the acquisition and sustainable mining of critical minerals.
India-Canada Partnership
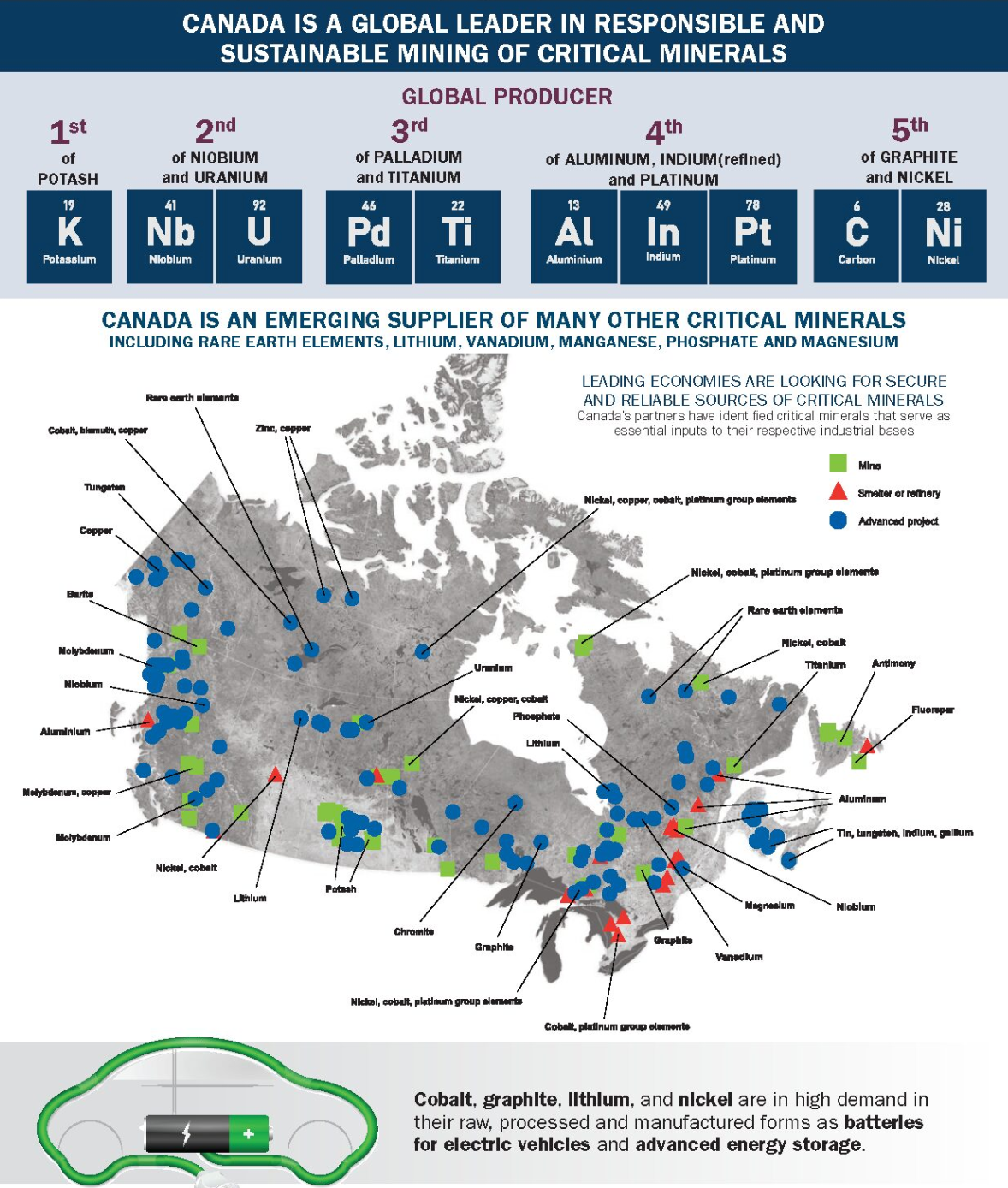

- Objective: Access to a variety of critical minerals, including cobalt and nickel.
- Initiatives:
- Strategic Agreements: India and Canada have signed agreements to collaborate on mining and processing of critical minerals.
- Investment Opportunities: Exploring joint ventures and investment opportunities in Canada's rich mineral resources.
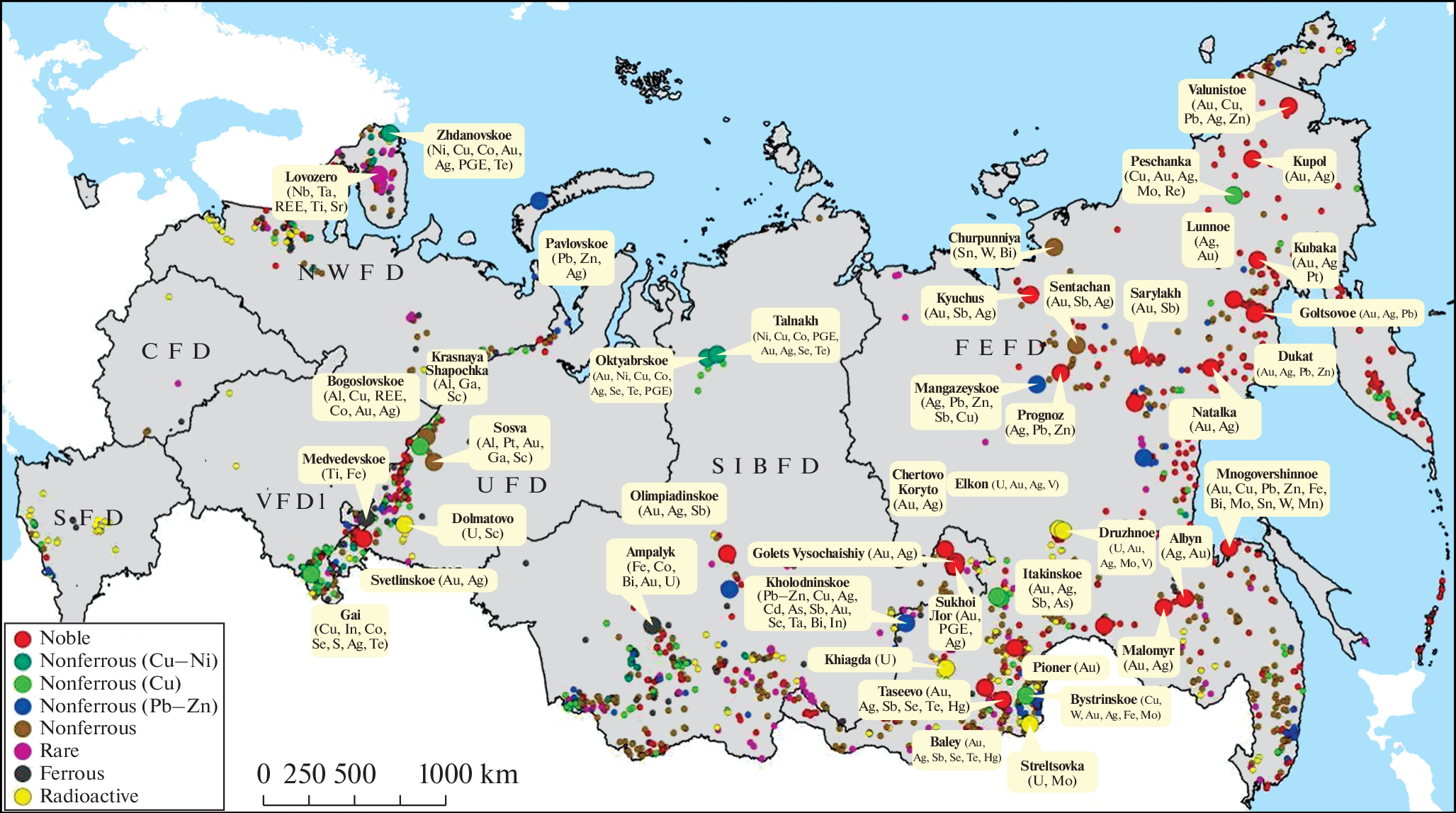
India-Russia Partnership
![Mineral deposits in the Russian Arctic [28]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352565375/figure/fig3/AS:1037124023377924@1624281044824/Mineral-deposits-in-the-Russian-Arctic-28.jpg)
- Objective: Secure supplies of critical minerals, including rare earth elements.
- Initiatives:
- Bilateral Agreements: India and Russia have agreements to enhance cooperation in the mining sector.
- Joint Ventures: Exploring joint ventures for the extraction and processing of critical minerals.
Strategic Initiatives and Policies
- Khanij Bidesh India Ltd. (KABIL): A joint venture company with equity contributions from National Aluminium Company Ltd, Hindustan Copper Ltd, and Mineral Exploration and Consultancy Ltd. KABIL's objective is to acquire critical mineral assets abroad to ensure a consistent supply to the Indian domestic market.
- MMDR Amendment Act, 2023: The amendment of the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, facilitates the acquisition of critical mineral assets abroad and enhances domestic exploration.
- Sustainable Mining Practices: Emphasis on sustainable and responsible mining practices to ensure environmental protection and social responsibility.
Conclusion
India's bilateral partnerships for procuring critical minerals are crucial for securing a stable and diversified supply chain. These partnerships involve strategic agreements, joint ventures, and co-investments in key mineral-rich regions worldwide.
Understanding these bilateral initiatives, their geopolitical implications, and the policies driving them is essential for UPSC preparation.
Previous Post