Table of contents
New Discovery
A new species of marine tardigrade, Batillipes Chandrayaani, was discovered off the southeast coast of Tamil Nadu.
This species was named in honour of India's Chandrayaan-3 moon mission, reflecting a symbolic connection between India's advancements in space exploration and marine biology.
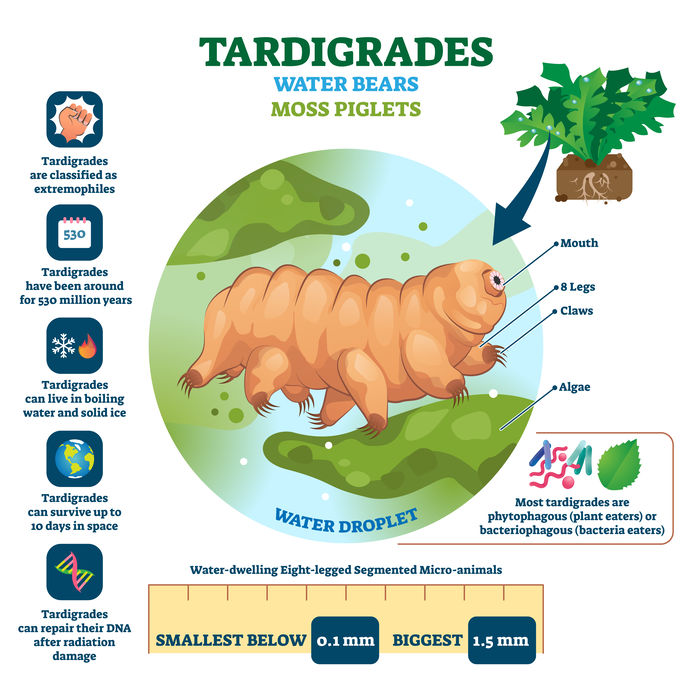
Tardigrades
- Also known as "water bears," tardigrades are microscopic, resilient creatures renowned for their ability to survive extreme conditions, including dehydration, radiation, and extreme temperatures.
- These micro-metazoans measure a fraction of a millimeter, often requiring advanced microscopes for study.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/10184101/1_s2.0_S0022191011000874_fx1.jpg)
Batillipes Chandrayaani
- This is the 39th species classified under the genus Batillipes and the third marine tardigrade species described from Indian waters.
- It is found in the intertidal beach sediments at Mandapam, Tamil Nadu.
- Similar in size to other tardigrades, it grows to a length of 0.15 millimetres and 0.04 millimetres in width.
- Its distinct characteristics include a trapezoid-shaped head and four pairs of legs equipped with sharp-tipped sensory spines.
- Both sexes are similar in terms of morphology and size.


Significance of the Discovery
- Biodiversity Documentation: The identification of Batillipes chandrayaani adds to the global and regional tardigrade species catalog, contributing to our understanding of marine biodiversity in Indian waters.
- This is particularly important as marine ecosystems are rich in biodiversity but are less studied compared to terrestrial ecosystems.
- Marine Ecosystem Understanding: Tardigrades play a role in the ecological dynamics of their habitats.
- Understanding their life cycles, habitat requirements, and ecological roles can provide insights into the functioning of marine ecosystems, particularly the intertidal zones.
- Scientific Research and Taxonomy: The discovery underscores the ongoing research and the need for detailed taxonomic studies in marine biology.
- Tardigrade taxonomy is challenging due to their minute size and limited distinct morphological features, making discoveries like this crucial for advancing scientific knowledge.
- Conservation Implications: Documenting new species helps in assessing the health of ecosystems and can guide conservation efforts, especially in coastal regions that are vulnerable to human impact and climate change.
- Educational and Inspirational Value: Naming the new tardigrade species after a space mission not only celebrates scientific achievement but also inspires multidisciplinary interest and awareness about the interconnectedness of different scientific fields.
Did you know?
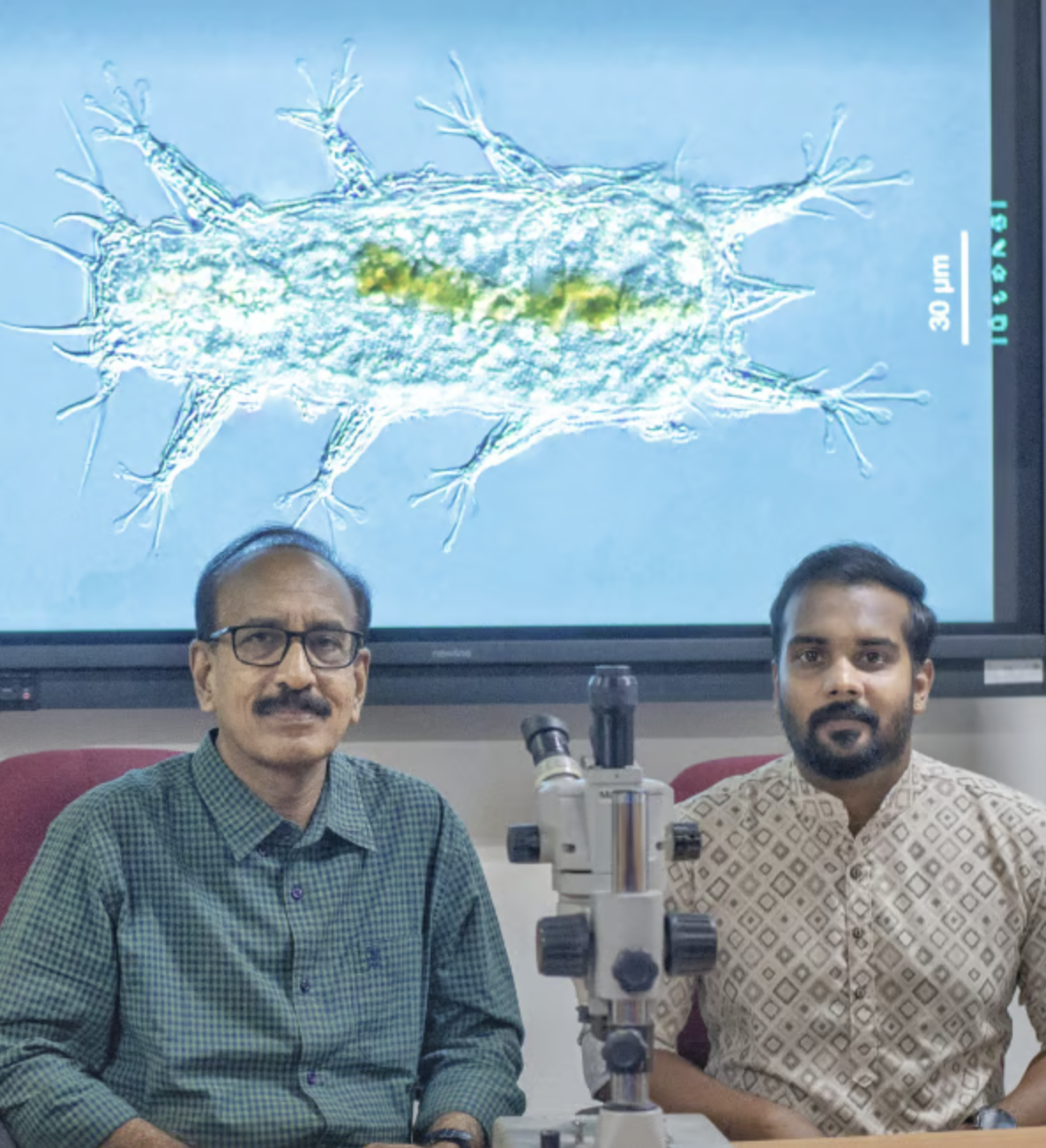
The duo had previously discovered Batillipes kalami.
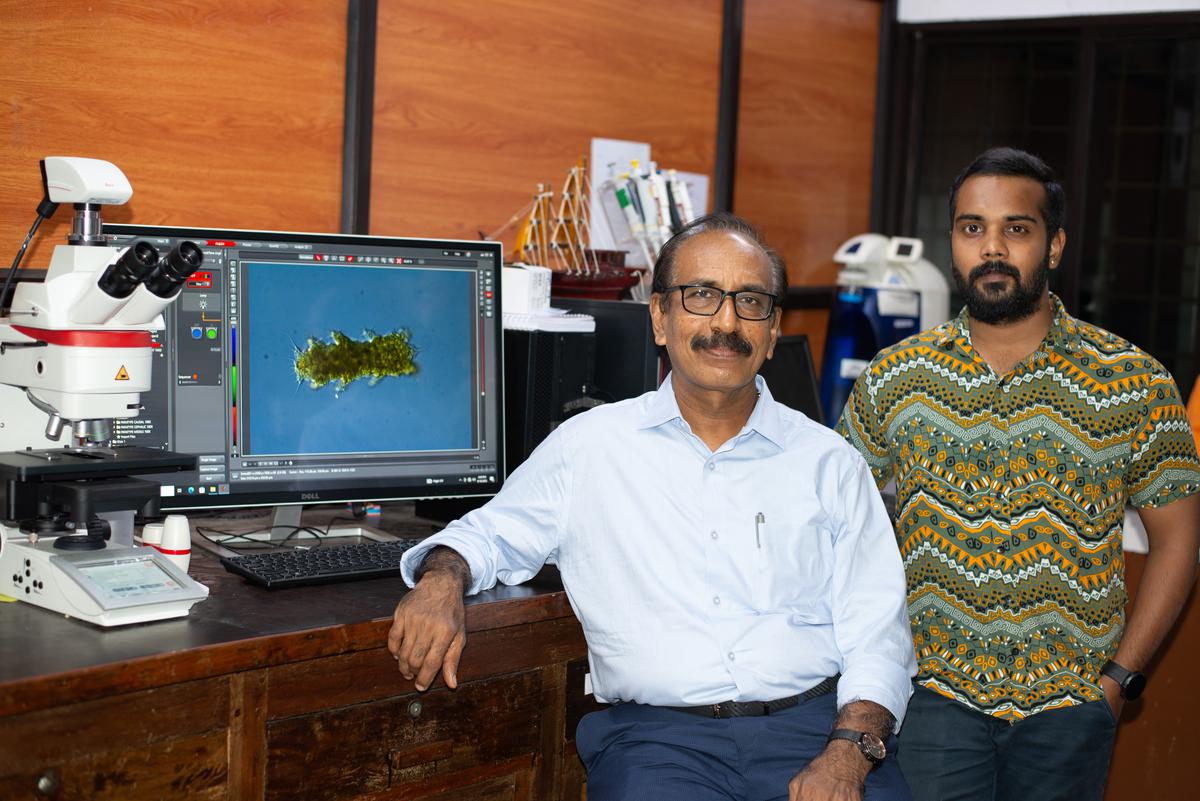
The same researchers at the Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT) had previously identified a new species of marine tardigrade and named it after the late former President and scientist A.P.J. Abdul Kalam.
A paper on the discovery by Vishnudattan N.K. (research scholar) and S. Bijoy Nandan (Professor) of the Department of Marine Biology, Microbiology and Biochemistry, CUSAT, and Marcus Rubal, Centre of Molecular and Environmental Biology, University of Minho, Portugal, had appeared in the latest issue of Zootaxa.

Relevance for UPSC
For UPSC aspirants, this discovery is relevant for the Environment and Ecology segment, which often covers topics related to biodiversity, conservation efforts, and scientific advancements.
Aspirants should be aware of:
- The role of marine organisms in ecological balance.
- The importance of taxonomy in biodiversity conservation.
- The impact of environmental changes on marine life.
- India’s contributions to global biodiversity research.
The discovery of Batillipes chandrayaani is a testament to the rich marine biodiversity of India and the critical ongoing efforts in marine biology research.
For UPSC aspirants, understanding such discoveries helps them appreciate the complexity of marine ecosystems and the importance of scientific research in forming conservation policies and practices.
Previous Post